J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Aug;37(30):e235. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e235.
The Risk of Gastrointestinal Cancer on Daily Intake of Low-Dose BaP in C57BL/6 for 60 Days
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Public Health, Xinxiang Medical University, Henan, China
- 2Department of Environmental Technology, Food Technology, and Molecular Technology, Ghent University Global Campus, Incheon, Korea
- 3Raphagen Co., Ltd. Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 5College of Pharmacy, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 6The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical College, Henan, China
- 7HealingBio Co., Ltd. Cheongju, Korea
- 8Department of Biotechnology, College of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2532229
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e235
Abstract
- Background
Benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) is a carcinogenic compound in contaminated foodstuffs. The effect of oral intake of the environmental carcinogen BaP under low doses and frequent exposure on a digestive system has not been thoroughly verified.
Methods
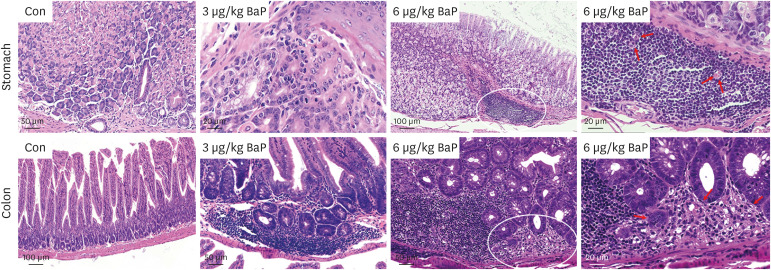
In this regard, this study was conducted to prove the toxicity effects of BaP on the stomach and colon tissue after exposure to C57BL/6 mouse (3 and 6 µg/kg) following daily oral administration for 60 days. This study investigated acute gastric mucosal injury, severe gastric edema, cell infiltration, and mononuclear cells, multifocal cells, and tumoral inflammatory cells.
Results
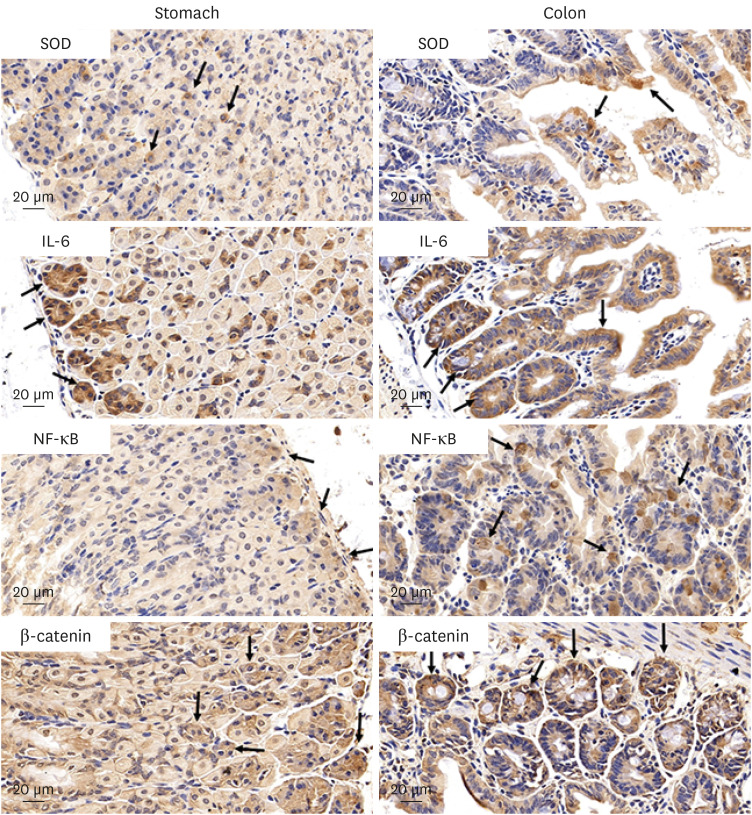
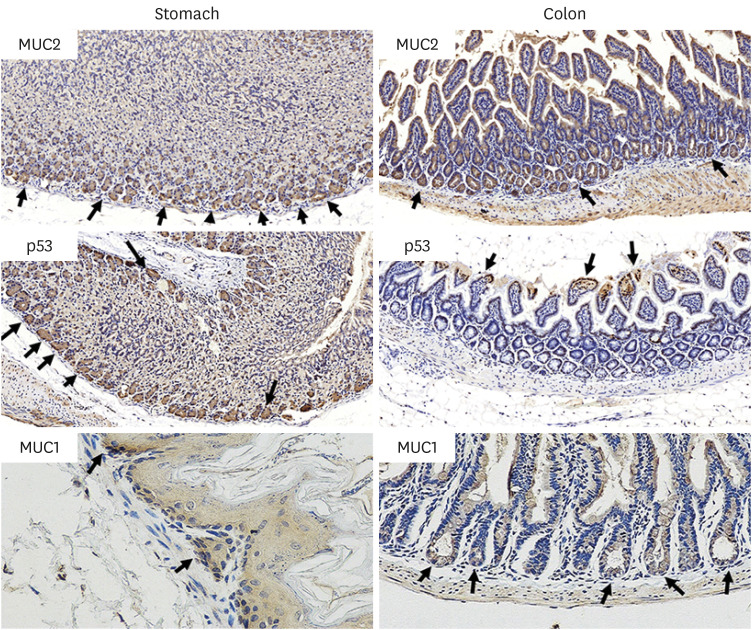
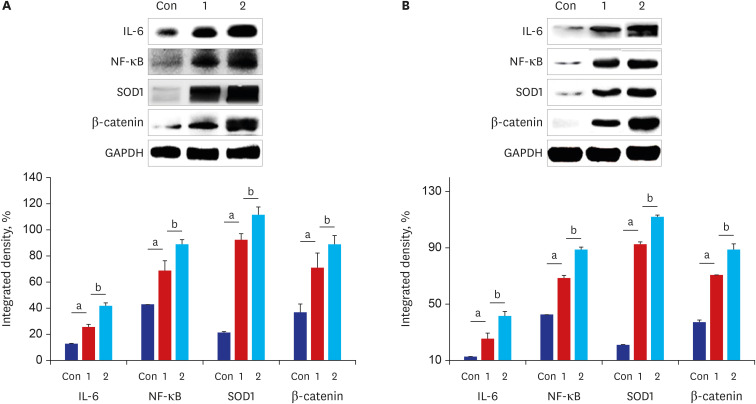
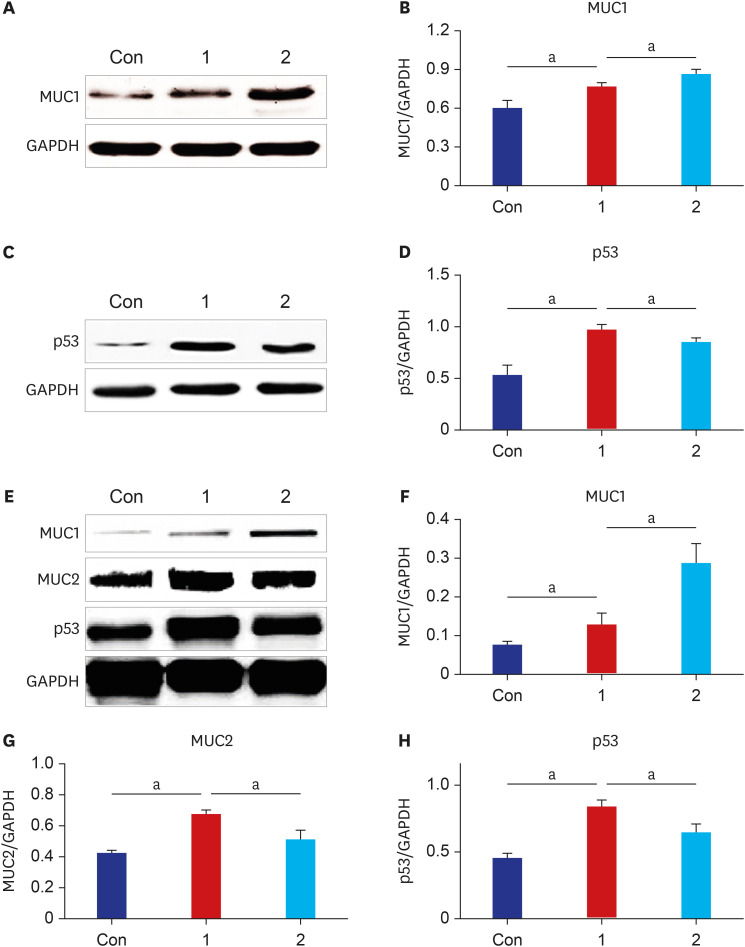
The results of ELISA showed that the expression of serum interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in the BaP exposure group were significantly increased, and a high level of DNA adduct distribution in their stomach and colon. Moreover, this study has confirmed the expression of early carcinogenesis markers: nuclear factor (NF)-κB, p53, IL-6, superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), mucin (MUC1 and MUC2), and β-catenin in the stomach and colon, and showed that there was a significant increase in IL-6, NF-κB, SOD1, β-catenin, and MUC1 (P< 0.05). At the same time, there was a significant decrease in MUC2 and p53 (P < 0.05). Thus, even in low doses, oral intake of BaP can induce DNA damage, increasing the potential risk of gastrointestinal cancer.
Conclusion
This study will provide a scientific basis for researching environmental contaminated food and intestinal health following daily oral administration of BaP.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. John EM, Stern MC, Sinha R, Koo J. Meat consumption, cooking practices, meat mutagens, and risk of prostate cancer. Nutr Cancer. 2011; 63(4):525–537. PMID: 21526454.
Article2. Rose M, Holland J, Dowding A, Petch SR, White S, Fernandes A, et al. Investigation into the formation of PAHs in foods prepared in the home to determine the effects of frying, grilling, barbecuing, toasting and roasting. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015; 78:1–9. PMID: 25633345.
Article3. Lee JG, Lim T, Kim SH, Kang DH, Yoon HJ. Determination and risk characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of tea by using the Margin of Exposure (MOE) approach. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2018; 27(6):1843–1856. PMID: 30483449.
Article4. Bak Y, Jang HJ, Seo JH, No SH, Chae JI, Hong J, et al. Benzo[a]pyrene alters the expression of genes in A549 lung cancer cells and cancer stem cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018; 28(3):425–431. PMID: 29316740.
Article5. Lee BM, Shim GA. Dietary exposure estimation of benzo[a]pyrene and cancer risk assessment. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2007; 70(15-16):1391–1394. PMID: 17654259.
Article6. Benford D, Dinovi M, Setzer RW. Application of the margin-of-exposure (MoE) approach to substances in food that are genotoxic and carcinogenic e.g.: benzo[a]pyrene and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010; 48(Suppl 1):S42–S48. PMID: 19818825.
Article7. Orisakwe OE, Mbagwu HO, Ukpai P, Udowelle NA. Survey of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and lead in Chinese teas sold in Nigeria: levels and health implications. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2015; 66(3):225–232. PMID: 26400118.8. Chou YC, Lin YH, Lin PH, Tung YC, Ho CT, Pan MH. Dietary 5-demethylnobiletin modulates xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes and ameliorates colon carcinogenesis in benzo[a]pyrene-induced mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021; 155:112380. PMID: 34216713.
Article9. Hakura A, Sonoda J, Tsutsui Y, Mikami T, Imade T, Shimada M, et al. Toxicity profile of benzo[a]pyrene in the male LacZ transgenic mouse (MutaMouse) following oral administration for 5 consecutive days. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1998; 27(3):273–279. PMID: 9693078.
Article10. Piberger AL, Krüger CT, Strauch BM, Schneider B, Hartwig A. BPDE-induced genotoxicity: relationship between DNA adducts, mutagenicity in the in vitro PIG-A assay, and the transcriptional response to DNA damage in TK6 cells. Arch Toxicol. 2018; 92(1):541–551. PMID: 28593498.
Article11. Allmann S, Mayer L, Olma J, Kaina B, Hofmann TG, Tomicic MT, et al. Benzo[a]pyrene represses DNA repair through altered E2F1/E2F4 function marking an early event in DNA damage-induced cellular senescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020; 48(21):12085–12101. PMID: 33166399.
Article12. Zheng X, Ren J, Peng B, Ye J, Wu X, Zhao W, et al. MALAT1 overexpression promotes the growth of colon cancer by repressing β-catenin degradation. Cell Signal. 2020; 73:109676. PMID: 32485228.
Article13. Kim S, Jeong S. Mutation hotspots in the β-catenin gene: Lessons from the human cancer genome databases. Mol Cells. 2019; 42(1):8–16. PMID: 30699286.14. Zheng Z, Park SY, Lee M, Phark S, Won NH, Kang HS, et al. Effects of benzo(a)pyrene on the expression of heat shock proteins, pro-inflammatory cytokines and antioxidant enzymes in hepatic tumors induced by rat hepatoma N1-S1 cells. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26(2):222–230. PMID: 21286013.
Article15. Shukla S, Srivastava JK, Shankar E, Kanwal R, Nawab A, Sharma H, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant status in high-risk prostate cancer subjects. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020; 10(3):E126. PMID: 32120827.
Article16. Zhou Q, Tian W, Jiang Z, Huang T, Ge C, Liu T, et al. A Positive feedback loop of AKR1C3-mediated activation of NF-kappaB and STAT3 facilitates proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2021; 81(5):1361–1374. PMID: 33361392.
Article17. Butt J, Blot WJ, Visvanathan K, Le Marchand L, Wilkens LR, Chen Y, et al. Auto-antibodies to p53 and the subsequent development of colorectal cancer in a U.S. prospective cohort consortium. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2020; 29(12):2729–2734. PMID: 32972968.
Article18. Choi EK, Park EJ, Phan TT, Kim HD, Hoe KL, Kim DU. Econazole induces p53-dependent apoptosis and decreases metastasis ability in gastric cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020; 28(4):370–379. PMID: 32209732.
Article19. Tang D, Yue L, Yao R, Zhou L, Yang Y, Lu L, et al. P53 prevent tumor invasion and metastasis by down-regulating IDO in lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(33):54548–54557. PMID: 28903363.
Article20. Nakayama M, Oshima M. Mutant p53 in colon cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019; 11(4):267–276. PMID: 30496442.
Article21. Farombi EO, Ajayi BO, Adedara IA. 6-Gingerol delays tumorigenesis in benzo[a]pyrene and dextran sulphate sodium-induced colorectal cancer in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020; 142:111483. PMID: 32512025.
Article22. Kim DH, Yong HJ, Mander S, Nguyen HT, Nguyen LP, Park HK, et al. SP-8356, a (1S)-(-)-verbenone derivative, inhibits the growth and motility of liver cancer cells by regulating NF-κB and ERK signaling. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2021; 29(3):331–341. PMID: 33455945.
Article23. Jang J, Song J, Sim I, Yoon Y. Wnt-C59 inhibits proinflammatory cytokine expression by reducing the interaction between β-catenin and NF-κB in LPS-stimulated epithelial and macrophage cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021; 25(4):307–319. PMID: 34193644.
Article24. Astashchanka A, Shroka TM, Jacobsen BM. Mucin 2 (MUC2) modulates the aggressiveness of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 173(2):289–299. PMID: 30317423.
Article25. Lee HK, Kwon MJ, Seo J, Kim JW, Hong M, Park HR, et al. Expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) in ALK-positive lung cancer: Comparison with EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2019; 215(3):459–465. PMID: 30580903.
Article26. Pope JL, Bhat AA, Sharma A, Ahmad R, Krishnan M, Washington MK, et al. Claudin-1 regulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis through the modulation of Notch-signalling. Gut. 2014; 63(4):622–634. PMID: 23766441.
Article27. Pourjafar M, Samadi P, Saidijam M. MUC1 antibody-based therapeutics: the promise of cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy. 2020; 12(17):1269–1286. PMID: 33019839.
Article28. Jeong SJ, Kim JH, Lim BJ, Yoon I, Song JA, Moon HS, et al. Inhibition of MUC1 biosynthesis via threonyl-tRNA synthetase suppresses pancreatic cancer cell migration. Exp Mol Med. 2018; 50(1):e424. PMID: 29328069.
Article29. Yang J. Identification of novel biomarkers, MUC5AC, MUC1, KRT7, GAPDH, CD44 for gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2020; 37(5):34. PMID: 32219571.
Article30. Ge Y, Ma G, Liu H, Lin Y, Zhang G, Du M, et al. MUC1 is associated with TFF2 methylation in gastric cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 2020; 12(1):37. PMID: 32122390.
Article31. Szlendak M, Sitarz R, Berbecka M, Mielko J, Morsink F, Maciejewski R, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and mucin 1 in colorectal cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 2020; 13(5):52. PMID: 32874582.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Amount of Daily Protein Intake Is Not Associated with Skeletal Muscle Strength in Older Adults
- Effects of Low- or Moderate-dose Whole Body-X-ray Radiation on the Immune System of C57BL/6 Mice
- Low Dose versus High Dose Radioiodine Therapy
- Effect of Nutritional Risk at Admission on the Length of Hospital Stay and Mortality in Gastrointestinal Cancer Patients
- Effect of Vortioxetine on Alcohol Intake in C57BL/6 Mice