Kosin Med J.
2022 Jun;37(2):107-118. 10.7180/kmj.22.108.
Alcohol-related liver disease and liver transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Bach Christian Hospital, Abbottabad, Pakistan
- 2Department of Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2532040
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.22.108
Abstract
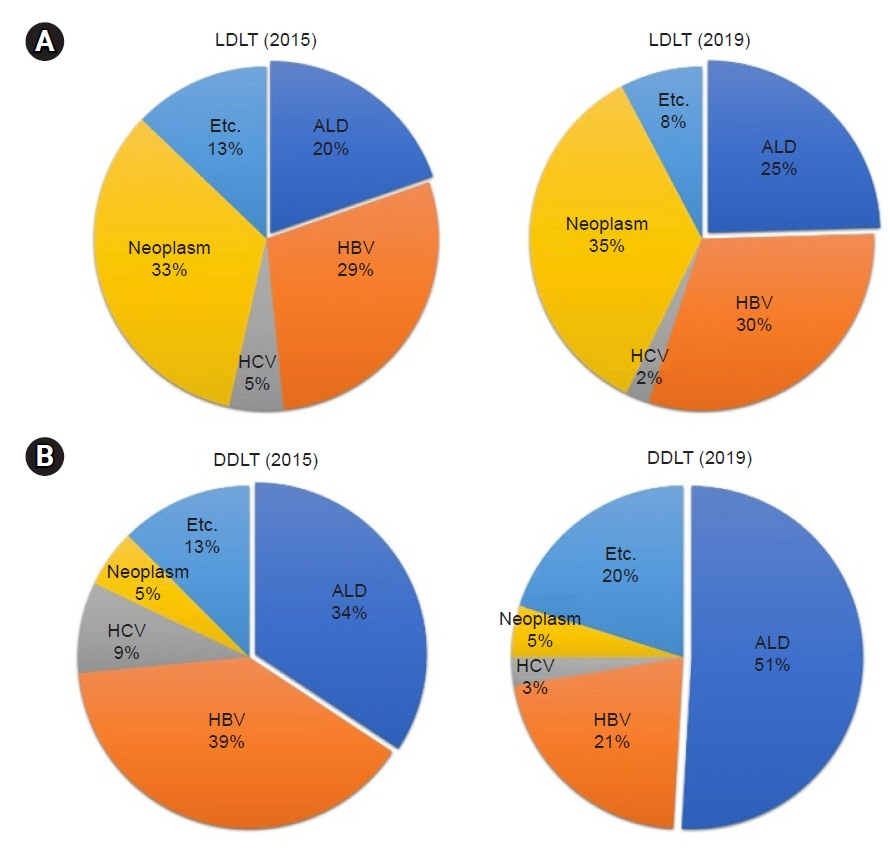
- Alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) has become the major cause of liver transplantation (LT) in Korea, and is currently the most common cause of LT in Europe and the United States. Although, ALD is one of the most common indications for LT, it is traditionally not considered as an option for patients with ALD due to organ shortages and concerns about relapse. To select patients with terminal liver disease due to ALD for transplants, most LT centers in the United States and European countries require a 6-month sober period before transplantation. However, Korea has a different social and cultural background than Western countries, and most organ transplants are made from living donors, who account for approximately twice as many procedures as deceased donors. Most LT centers in Korea do not require a specific period of sobriety before transplantation in patients with ALD. As per the literature, 8%–20% of patients resume alcohol consumption 1 year after LT, and this proportion increases to 30%–40% at 5 years post-LT, among which 10%–15% of patients resume heavy drinking. According to previous studies, the risk factors for alcohol relapse after LT are as follows: young age, poor familial and social support, family history of alcohol use disorder, previous history of alcohol-related treatment, shorter abstinence before LT, smoking, psychiatric disorders, irregular follow-up, and unemployment. Recognition of the risk factors, early detection of alcohol consumption after LT, and regular follow-up by a multidisciplinary team are important for improving the short- and long-term outcomes of LT patients with ALD.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Varied strategies for alcohol-related liver transplants in South Korea
Hyun Hwa Choi, Kwang-Woong Lee, Bong-Wan Kim, Dong-Sik Kim, Gyu-Seong Choi, Hae Won Lee, Ho Joong Choi, Jaryung Han, Je Ho Ryu, Kwan Woo Kim, Man Ki Ju, Min-Su Park, Myoung Soo Kim, Seok-Hwan Kim, Seoung Hoon Kim, Shin Hwang, Sung Won Jung, Tae-Seok Kim, Woo Young Shin
Ann Liver Transplant. 2024;4(2):95-101. doi: 10.52604/alt.24.0013.
Reference
-
References
1. Busuttil RW, DuBray BJ. Liver transplantation for alcoholic hepatitis. Ann Surg. 2017; 265:30–1.
Article2. Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, Patra J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet. 2009; 373:2223–33.
Article3. Center for Korean Network for Organ Sharing. Annual report of organ transplantation statistics [Internet]. Cheongju: Center for Korean Network for Organ Sharing; c2022 [cited Jun 17]. https://www.konos.go.kr/board/boardListPage.do?page=sub4_2_1&boardId=30.4. Cabezas J. Management of alcohol-related liver disease and its complications. Clin Drug Investig. 2022; 42(Suppl 1):47–53.
Article5. Chuncharunee L, Yamashiki N, Thakkinstian A, Sobhonslidsuk A. Alcohol relapse and its predictors after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019; 19:150.
Article6. Crabb DW, Im GY, Szabo G, Mellinger JL, Lucey MR. Diagnosis and treatment of alcohol-associated liver diseases: 2019 practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2020; 71:306–33.
Article7. Veldt BJ, Laine F, Guillygomarc’h A, Lauvin L, Boudjema K, Messner M, et al. Indication of liver transplantation in severe alcoholic liver cirrhosis: quantitative evaluation and optimal timing. J Hepatol. 2002; 36:93–8.
Article8. Watt KD, McCashland TM. Transplantation in the alcoholic patient. Semin Liver Dis. 2004; 24:249–55.
Article9. Cholankeril G, Ahmed A. Alcoholic liver disease replaces hepatitis C virus infection as the leading indication for liver transplantation in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 16:1356–8.10. Burra P, Senzolo M, Adam R, Delvart V, Karam V, Germani G, et al. Liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease in Europe: a study from the ELTR (European Liver Transplant Registry). Am J Transplant. 2010; 10:138–48.
Article11. Hong SK, Yi NJ, Kim HS, Ahn SW, Yoon KC, Kim H, et al. Korean patients undergoing deceased donor liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease have non-inferior survival outcomes than for hepatitis B virus: a real-world experience without minimum abstinence before transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:919–25.
Article12. Zakhari S, Li TK. Determinants of alcohol use and abuse: impact of quantity and frequency patterns on liver disease. Hepatology. 2007; 46:2032–9.
Article13. Bellentani S, Saccoccio G, Costa G, Tiribelli C, Manenti F, Sodde M, et al. Drinking habits as cofactors of risk for alcohol induced liver damage. The Dionysos Study Group. Gut. 1997; 41:845–50.
Article14. European Association for the Study of Liver. EASL clinical practical guidelines: management of alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:399–420.15. Baraona E, Lieber CS. Alcohol and lipids. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1998; 14:97–134.
Article16. You M, Considine RV, Leone TC, Kelly DP, Crabb DW. Role of adiponectin in the protective action of dietary saturated fat against alcoholic fatty liver in mice. Hepatology. 2005; 42:568–77.
Article17. Ji C, Chan C, Kaplowitz N. Predominant role of sterol response element binding proteins (SREBP) lipogenic pathways in hepatic steatosis in the murine intragastric ethanol feeding model. J Hepatol. 2006; 45:717–24.
Article18. Torok NJ. Update on alcoholic hepatitis. Biomolecules. 2015; 5:2978–86.
Article19. Chedid A, Mendenhall CL, Gartside P, French SW, Chen T, Rabin L. Prognostic factors in alcoholic liver disease. VA Cooperative Study Group. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991; 86:210–6.20. Niemela O, Juvonen T, Parkkila S. Immunohistochemical demonstration of acetaldehyde-modified epitopes in human liver after alcohol consumption. J Clin Invest. 1991; 87:1367–74.
Article21. Thurman RG. II. Alcoholic liver injury involves activation of Kupffer cells by endotoxin. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275:G605–11.22. Saunders JB, Walters JR, Davies AP, Paton A. A 20-year prospective study of cirrhosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1981; 282:263–6.
Article23. Jepsen P, Ott P, Andersen PK, Sorensen HT, Vilstrup H. Clinical course of alcoholic liver cirrhosis: a Danish population-based cohort study. Hepatology. 2010; 51:1675–82.
Article24. Tarli C, Mirijello A, Addolorato G. Treating alcohol use disorder in patients with alcohol associated liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2022; 42:138–50.
Article25. Shipley LC, Kodali S, Singal AK. Recent updates on alcoholic hepatitis. Dig Liver Dis. 2019; 51:761–8.
Article26. Grant BF, Goldstein RB, Saha TD, Chou SP, Jung J, Zhang H, et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 alcohol use disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015; 72:757–66.27. Goldstein RB, Chou SP, Smith SM, Jung J, Zhang H, Saha TD, et al. Nosologic comparisons of DSM-IV and DSM-5 alcohol and drug use disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions-III. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2015; 76:378–88.
Article28. Moehring A, Rumpf HJ, Hapke U, Bischof G, John U, Meyer C. Diagnostic performance of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) in detecting DSM-5 alcohol use disorders in the General population. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019; 204:107530.
Article29. Tome S, Lucey MR. Timing of liver transplantation in alcoholic cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2003; 39:302–7.
Article30. O’Brien CP, McLellan AT. Myths about the treatment of addiction. Lancet. 1996; 347:237–40.
Article31. Vaillant GE. The natural history of alcoholism and its relationship to liver transplantation. Liver Transpl Surg. 1997; 3:304–10.
Article32. Addolorato G, Bataller R, Burra P, DiMartini A, Graziadei I, Lucey MR, et al. Liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Transplantation. 2016; 100:981–7.
Article33. Singal AK, Guturu P, Hmoud B, Kuo YF, Salameh H, Wiesner RH. Evolving frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation based on etiology of liver disease. Transplantation. 2013; 95:755–60.
Article34. Jain A, DiMartini A, Kashyap R, Youk A, Rohal S, Fung J. Long-term follow-up after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease under tacrolimus. Transplantation. 2000; 70:1335–42.
Article35. Faure S, Herrero A, Jung B, Duny Y, Daures JP, Mura T, et al. Excessive alcohol consumption after liver transplantation impacts on long-term survival, whatever the primary indication. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:306–12.
Article36. Cuadrado A, Fabrega E, Casafont F, Pons-Romero F. Alcohol recidivism impairs long-term patient survival after orthotopic liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:420–6.
Article37. Grat M, Lewandowski Z, Grat K, Wronka KM, Krasnodebski M, Barski K, et al. Negative outcomes after liver transplantation in patients with alcoholic liver disease beyond the fifth post-transplant year. Clin Transplant. 2014; 28:1112–20.
Article38. Poynard T, Barthelemy P, Fratte S, Boudjema K, Doffoel M, Vanlemmens C, et al. Evaluation of efficacy of liver transplantation in alcoholic cirrhosis by a case-control study and simulated controls. Lancet. 1994; 344:502–7.
Article39. Vanlemmens C, Di Martino V, Milan C, Messner M, Minello A, Duvoux C, et al. Immediate listing for liver transplantation versus standard care for Child-Pugh stage B alcoholic cirrhosis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:153–61.
Article40. Leong J, Im GY. Evaluation and selection of the patient with alcoholic liver disease for liver transplant. Clin Liver Dis. 2012; 16:851–63.
Article41. Gaglio PJ Jr, Gaglio PJ Sr. Complications in patients with alcohol-associated liver disease who undergo liver transplantation. Clin Liver Dis. 2012; 16:865–75.
Article42. Perut V, Conti F, Scatton O, Soubrane O, Calmus Y, Vidal-Trecan G. Might physicians be restricting access to liver transplantation for patients with alcoholic liver disease? J Hepatol. 2009; 51:707–14.
Article43. Chung HG, Sinn DH, Kang W, Choi GS, Kim JM, Joh JW. Incidence of and risk factors for alcohol relapse after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease: comparison between deceased donor and living donor liver transplantation. J Gastrointest Surg. 2021; 25:672–80.
Article44. Rustad JK, Stern TA, Prabhakar M, Musselman D. Risk factors for alcohol relapse following orthotopic liver transplantation: a systematic review. Psychosomatics. 2015; 56:21–35.
Article45. Choudhary NS, Saraf N, Dhampalwar S, Saigal S, Gautam D, Rastogi A, et al. Poor outcomes after recidivism in living donor liver transplantation for alcohol-related liver disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022; 12:37–42.
Article46. DiMartini A, Day N, Dew MA, Lane T, Fitzgerald MG, Magill J, et al. Alcohol use following liver transplantation: a comparison of follow-up methods. Psychosomatics. 2001; 42:55–62.47. Iruzubieta P, Crespo J, Fabrega E. Long-term survival after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:9198–208.
Article48. Dew MA, DiMartini AF, Steel J, De Vito Dabbs A, Myaskovsky L, Unruh M, et al. Meta-analysis of risk for relapse to substance use after transplantation of the liver or other solid organs. Liver Transpl. 2008; 14:159–72.
Article49. Arab JP, Izzy M, Leggio L, Bataller R, Shah VH. Management of alcohol use disorder in patients with cirrhosis in the setting of liver transplantation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022; 19:45–59.
Article50. DiMartini A, Dew MA, Day N, Fitzgerald MG, Jones BL, deVera ME, et al. Trajectories of alcohol consumption following liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2010; 10:2305–12.
Article51. Kline-Simon AH, Litten RZ, Weisner CM, Falk DE. Posttreatment low-risk drinking as a predictor of future drinking and problem outcomes among individuals with alcohol use disorders: a 9-year follow-up. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017; 41:653–8.
Article52. Laramee P, Leonard S, Buchanan-Hughes A, Warnakula S, Daeppen JB, Rehm J. Risk of all-cause mortality in alcohol-dependent individuals: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. EBioMedicine. 2015; 2:1394–404.
Article53. Witkiewitz K, Pearson MR, Hallgren KA, Maisto SA, Roos CR, Kirouac M, et al. Who achieves low risk drinking during alcohol treatment? An analysis of patients in three alcohol clinical trials. Addiction. 2017; 112:2112–21.
Article54. Mathurin P, Lucey MR. Liver transplantation in patients with alcohol-related liver disease: current status and future directions. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 5:507–14.
Article55. Testino G, Burra P, Bonino F, Piani F, Sumberaz A, Peressutti R, et al. Acute alcoholic hepatitis, end stage alcoholic liver disease and liver transplantation: an Italian position statement. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:14642–51.
Article56. Hartl J, Scherer MN, Loss M, Schnitzbauer A, Farkas S, Baier L, et al. Strong predictors for alcohol recidivism after liver transplantation: non-acceptance of the alcohol problem and abstinence of <3 months. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:1257–66.
Article57. Kitajima T, Nagai S, Segal A, Magee M, Blackburn S, Ellithorpe D, et al. Posttransplant complications predict alcohol relapse in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2020; 26:379–89.
Article58. Jauhar S, Talwalkar JA, Schneekloth T, Jowsey S, Wiesner RH, Menon KV. Analysis of factors that predict alcohol relapse following liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:408–11.
Article59. Kelly M, Chick J, Gribble R, Gleeson M, Holton M, Winstanley J, et al. Predictors of relapse to harmful alcohol after orthotopic liver transplantation. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006; 41:278–83.
Article60. Perney P, Bismuth M, Sigaud H, Picot MC, Jacquet E, Puche P, et al. Are preoperative patterns of alcohol consumption predictive of relapse after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease? Transpl Int. 2005; 18:1292–7.
Article61. DiMartini A, Day N, Dew MA, Javed L, Fitzgerald MG, Jain A, et al. Alcohol consumption patterns and predictors of use following liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2006; 12:813–20.
Article62. De Gottardi A, Spahr L, Gelez P, Morard I, Mentha G, Guillaud O, et al. A simple score for predicting alcohol relapse after liver transplantation: results from 387 patients over 15 years. Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167:1183–8.
Article63. Pfitzmann R, Schwenzer J, Rayes N, Seehofer D, Neuhaus R, Nussler NC. Long-term survival and predictors of relapse after orthotopic liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2007; 13:197–205.
Article64. Gedaly R, McHugh PP, Johnston TD, Jeon H, Koch A, Clifford TM, et al. Predictors of relapse to alcohol and illicit drugs after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Transplantation. 2008; 86:1090–5.
Article65. Karim Z, Intaraprasong P, Scudamore CH, Erb SR, Soos JG, Cheung E, et al. Predictors of relapse to significant alcohol drinking after liver transplantation. Can J Gastroenterol. 2010; 24:245–50.
Article66. Egawa H, Nishimura K, Teramukai S, Yamamoto M, Umeshita K, Furukawa H, et al. Risk factors for alcohol relapse after liver transplantation for alcoholic cirrhosis in Japan. Liver Transpl. 2014; 20:298–310.
Article67. Rice JP, Eickhoff J, Agni R, Ghufran A, Brahmbhatt R, Lucey MR. Abusive drinking after liver transplantation is associated with allograft loss and advanced allograft fibrosis. Liver Transpl. 2013; 19:1377–86.
Article68. Deruytter E, Van Steenkiste CV, Trepo E. Liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease: a retrospective analysis of recidivism, survival and risk factors predisposing to alcohol relapse. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2013; 76:282–90.69. Rodrigue JR, Hanto DW, Curry MP. The Alcohol Relapse Risk Assessment: a scoring system to predict the risk of relapse to any alcohol use after liver transplant. Prog Transplant. 2013; 23:310–8.
Article70. Satapathy SK, Eason JD, Nair S, et al. Recidivism in liver transplant recipients with alcoholic liver disease: analysis of demographic, psychosocial, and histology features. Exp Clin Transplant. 2015; 13:430–40.71. Saigal S, Choudhary NS, Yadav SK, Saraf N, Kumar N, Rai R, et al. Lower relapse rates with good post-transplant outcome in alcoholic liver disease: experience from a living donor liver transplant center. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2016; 35:123–8.
Article72. Skladany L, Adamcova Selcanova S, Koller T. Alcohol use relapse following liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Ann Transplant. 2019; 24:359–66.
Article73. Choudhary NS, Saraf N, Mehrotra S, Saigal S, Soin AS. Recidivism in liver transplant recipients for alcohol-related liver disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021; 11:387–96.
Article74. Lim J, Curry MP, Sundaram V. Risk factors and outcomes associated with alcohol relapse after liver transplantation. World J Hepatol. 2017; 9:771–80.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Burden of alcohol use disorder, alcohol-related liver disease, and alcohol-related liver cancer: Editorial on “Global epidemiology of alcohol-related liver disease, liver cancer, and alcohol use disorder, 2000–2021
- Liver transplantation for alcohol-related liver disease in Korea: The need for patient management guidelines
- Liver-lung axes in alcohol-related liver disease
- Pediatric liver transplantation in Korea: long-term outcomes and allocations
- Correspondence to editorial on “Global epidemiology of alcohol-related liver disease, liver cancer, and alcohol use disorder, 2000-2021”