Arch Hand Microsurg.
2022 Jun;27(2):180-186. 10.12790/ahm.21.0144.
Reconstruction of soft tissue defects caused by spinal surgery using a dorsal intercostal artery perforator flap
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2531926
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.21.0144
Abstract
- Purpose
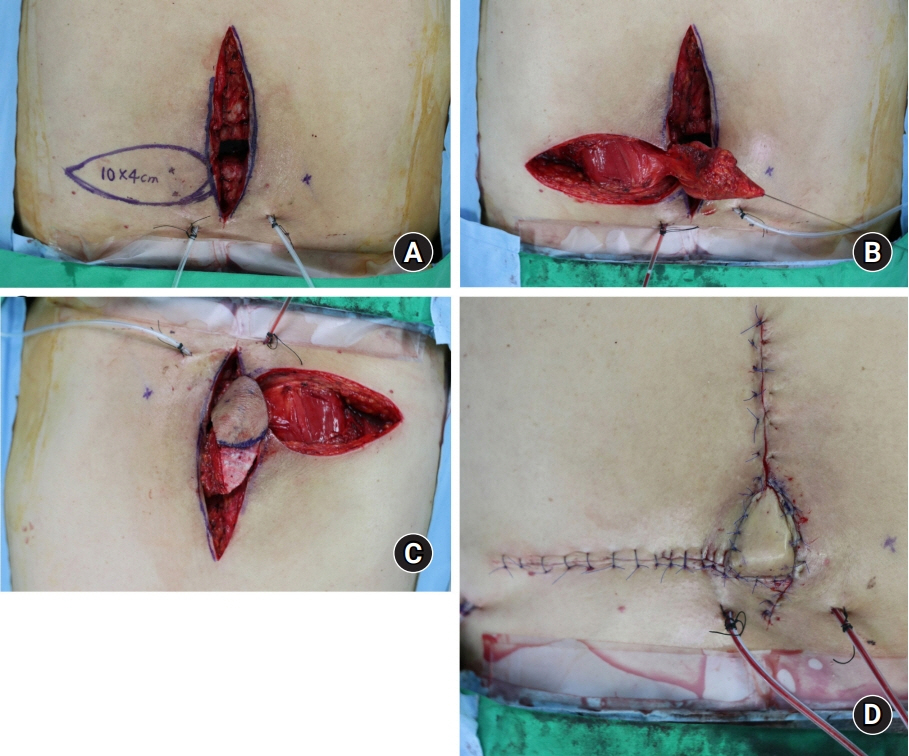
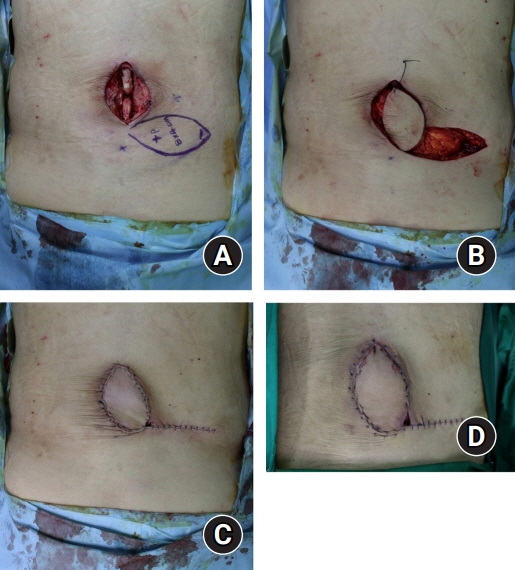
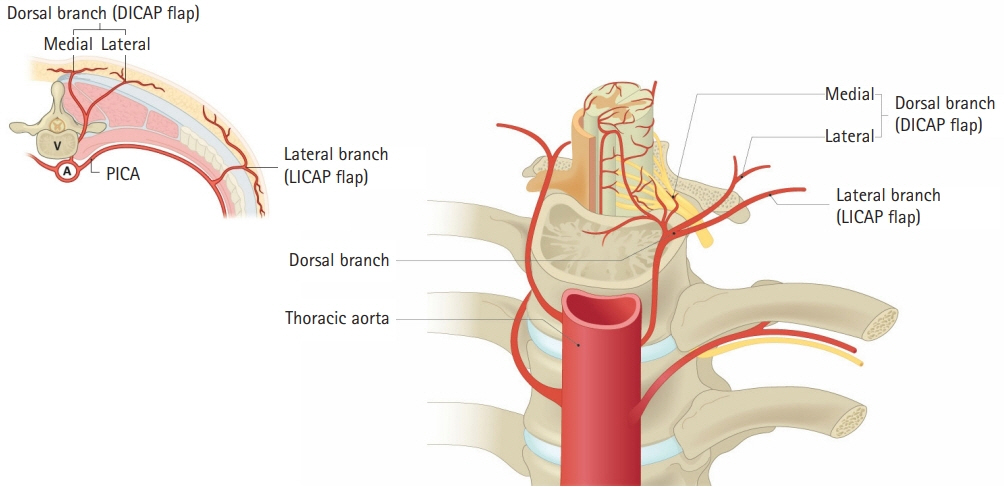
The reconstruction of defects resulting from spinal surgery poses a challenge to plastic surgeons due to the curved contour and strong skin tension of the back. Implant and metal exposure can also increase the difficulty of covering such defects. This study presents our experiences of covering defects after spinal surgery using dorsal intercostal artery perforator (DICAP) flaps.
Methods
From November 2018 to August 2021, 14 patients with spinal soft tissue defects underwent DICAP flap reconstructive surgery at our department. The mean age of the patients was 54.3 years (range, 35–70 years). Age, sex, etiology, the dimensions of the defect and the flap, the site of the defect, surgical technique, and postoperative complications were recorded.
Results
All flaps survived, with no major complications such as total flap necrosis. Minor complications were observed in four cases. One patient developed an infection with erythematous changes and another developed partial flap necrosis. Two patients experienced wound dehiscence. These minor complications were all resolved with conservative treatment. No additional complications occurred during the follow-up period.
Conclusion
The use of DICAP flaps was successful in all cases. DICAP flaps can adequately cover defects following spinal surgery and have a low complication rate. Thus, DICAP flaps are a good choice for covering defects resulting from spinal surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. DI Summa PG, Largo RD, Ismail T, et al. Reconstruction of spinal soft tissue defects with perforator flaps from the paraspinal region. In Vivo. 2019; 33:827–32.
Article2. Labler L, Keel M, Trentz O, Heinzelmann M. Wound conditioning by vacuum assisted closure (V.A.C.) in postoperative infections after dorsal spine surgery. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:1388–96.
Article3. Mericli AF, Mirzabeigi MN, Moore JH Jr, Fox JW 4th, Copit SE, Tuma GA. Reconstruction of complex posterior cervical spine wounds using the paraspinous muscle flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011; 128:148–53.
Article4. May JW Jr, Rohrich RJ. Foot reconstruction using free microvascular muscle flaps with skin grafts. Clin Plast Surg. 1986; 13:681–9.
Article5. de Weerd L, Weum S. The sensate medial dorsal intercostal artery perforator flap for closure of cervicothoracic midline defects after spinal surgery: an anatomic study and case reports. Ann Plast Surg. 2009; 63:418–21.6. Weum S, de Weerd L. The sensate medial dorsal intercostal artery perforator flap as an option for treatment of dorsal cervicothoracic midline defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010; 126:1122–4.
Article7. Lazzeri D, Huemer GM, Nicoli F, et al. Indications, outcomes, and complications of pedicled propeller perforator flaps for upper body defects: a systematic review. Arch Plast Surg. 2013; 40:44–50.
Article8. Oh TS, Hallock G, Hong JP. Freestyle propeller flaps to reconstruct defects of the posterior trunk: a simple approach to a difficult problem. Ann Plast Surg. 2012; 68:79–82.
Article9. Garvey PB, Rhines LD, Dong W, Chang DW. Immediate soft-tissue reconstruction for complex defects of the spine following surgery for spinal neoplasms. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010; 125:1460–6.
Article10. Kovar A, Colakoglu S, Iorio ML. Choosing between muscle and fasciocutaneous free flap reconstruction in the treatment of lower extremity osteomyelitis: available evidence for a function-specific approach. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2020; 36:197–203.
Article11. de Weerd L, Solberg TK, Weum S. Closure of complex posterior midline defects after spinal surgery with sensate midline-based perforator flaps and the long-term results. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40:E1233–8.
Article12. Hamdi M, Van Landuyt K, de Frene B, Roche N, Blondeel P, Monstrey S. The versatility of the inter-costal artery perforator (ICAP) flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006; 59:644–52.
Article13. Kocak OF, Demir CY. An ideal flap alternative for closure of myelomeningocele defects: dorsal intercostal artery perforator flap. J Craniofac Surg. 2016; 27:1951–5.14. Prasad V, Morris SF. Propeller DICAP flap for a large defect on the back-case report and review of the literature. Microsurgery. 2012; 32:617–21.
Article15. Mathes DW, Thornton JF, Rohrich RJ. Management of posterior trunk defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 118:73e–83e.
Article16. Saint-Cyr M, Nikolis A, Moumdjian R, et al. Paraspinous muscle flaps for the treatment and prevention of cerebrospinal fluid fistulas in neurosurgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:E86–92.
Article17. Datli A, Suh H, Kim YC, Choi DH, Hong JP. Free-style deepithelialized propeller flaps: an ideal local flap to obliterate wounds with dead space. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017; 5:e1249.18. Savage JW, Anderson PA. An update on modifiable factors to reduce the risk of surgical site infections. Spine J. 2013; 13:1017–29.
Article19. Dipaola CP, Saravanja DD, Boriani L, et al. Postoperative infection treatment score for the spine (PITSS): construction and validation of a predictive model to define need for single versus multiple irrigation and debridement for spinal surgical site infection. Spine J. 2012; 12:218–30.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reconstruction of the Soft Tissue Defect Using Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator Skin Flap
- Soft Tissue Coverage Using a Combined Gastrocnemius-medial Sural Artery Perforator Flap
- Dual Perforator Flap for Reconstruction of Large Sacral Defects: Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator Super-Flap with Parasacral Perforator
- Face Reconstruction Using Lateral Intercostal Artery Perforator-Based Adipofascial Free Flap
- Lower Extremity Reconstruction of Soft Tissue Defects with Perforator Island Flap