Anat Cell Biol.
2022 Jun;55(2):113-117. 10.5115/acb.21.032.
The function of the tensor tympani muscle: a comprehensive review of the literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Structural & Cellular Biology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Tulane Center for Clinical Neurosciences, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 3Department of Neurology, Tulane Center for Clinical Neurosciences, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 4Division of Gross and Clinical Anatomy, Department of Anatomy, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Fukuoka, Japan
- 5Department of Anatomical Dissection and Donation, Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland
- 6Department of Neurosurgery and Ochsner Neuroscience Institute, Ochsner Health System, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 7Department of Anatomical Sciences, St. George’s University, St. George’s, Grenada
- 8Department of Surgery, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- KMID: 2531195
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.21.032
Abstract
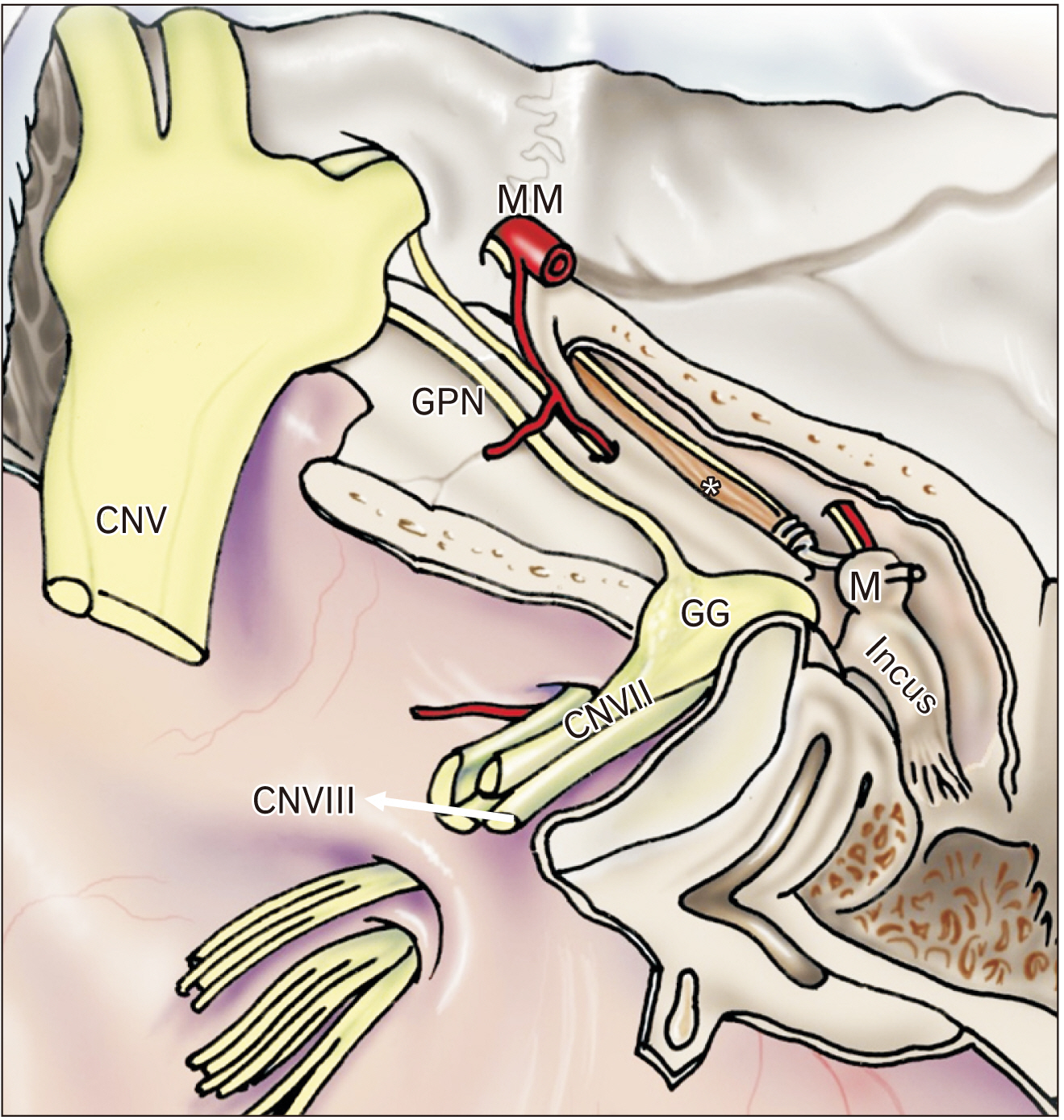
- The tensor tympani muscle is structurally important in the middle ear, specifically through its involvement in the impedance of sound in response to intense auditory and non-auditory stimuli. Despite numerous studies, its true function has been debated for many years; questions still remain about its role in auditory and non-auditory reflexes and in sound damping. Some studies suggest that the tensor tympani muscle contracts as a result of non-auditory stimulation such as facial or head movements; others suggest that it contracts due to input from the cochlear nucleus, therefore by way of auditory stimulation. Whatever the cause, contraction of the tensor tympani muscle results in low frequency mixed hearing loss, either to protect the inner ear from loud sounds or to desensitize the ear to self-generated sounds. A review of these studies indicated that the tensor tympani muscle has a wide range of functions, yet the mechanisms of some of them have not been clearly demonstrated. One major question is whether the tensor tympani muscle contributes to sound damping; and if it does, what specific role it serves. The primary purpose of this review article is to explore the functions of the tensor tympani muscle in light of recent research advances.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Møller AR. 2006. Hearing: anatomy, physiology, and disorders of the auditory system. 2nd ed. Elsevier;Amsterdam:2. Standring S. 2015. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 41st ed. Elsevier;London:3. Wickens B, Floyd D, Bance M. 2017; Audiometric findings with voluntary tensor tympani contraction. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 46:2. DOI: 10.1186/s40463-016-0182-y. PMID: 28057076. PMCID: PMC5217611.
Article4. Azuma T, Nogaki T, Schachern P, Paparella MM, Cureoglu S. 2018; Structural analysis of tensor tympani muscle, tympanic diaphragm, epitympanum, and protympanum in Menière's disease: a human temporal bone study. Otol Neurotol. 39:499–505. DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001748. PMID: 29498964.
Article5. Mascarello F, Veggetti A, Cerpenè E, Rowlerson A. 1983; An immunohistochemical study of the middle ear muscles of some carnivores and primates, with special reference to the IIM and slow-tonic fibre types. J Anat. 137(Pt 1):95–108. PMID: 6415024. PMCID: PMC1171795.6. Mukerji S, Windsor AM, Lee DJ. 2010; Auditory brainstem circuits that mediate the middle ear muscle reflex. Trends Amplif. 14:170–91. DOI: 10.1177/1084713810381771. PMID: 20870664. PMCID: PMC3624626.
Article7. Borg E, Counter SA, Rösler G. Silman S, editor. 1984. Theories of middle-ear muscle functions. The Acoustic Reflex. Academic Press;London: p. 63–99. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-643450-7.50008-1.8. Møller AR. Silman S, editor. 1984. Neurophysiological basis of the acoustic middle-ear reflex. The Acoustic Reflex. Academic Press;London: p. 1–34. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-643450-7.50006-8. PMID: 6232702.
Article9. Stach BA, Jerger JF, Jenkins HA. 1984; The human acoustic tensor tympani reflex. A case report. Scand Audiol. 13:93–9. DOI: 10.3109/01050398409043046. PMID: 6463558.10. Benson TE, Lee DJ, Brown MC. 2013; Tensor tympani motoneurons receive mostly excitatory synaptic inputs. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 296:133–45. DOI: 10.1002/ar.22620. PMID: 23165747. PMCID: PMC3896885.
Article11. Salomon G, Starr A. 1963; Electromyography of middle ear muscles in man during motor activities. Acta Neurol Scand. 39:161–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1963.tb05317.x. PMID: 13991171.
Article12. van den Berge H, Kingma H, Kluge C, Marres EH. 1990; Electrophysiological aspects of the middle ear muscle reflex in the rat: latency, rise time and effect on sound transmission. Hear Res. 48:209–19. DOI: 10.1016/0378-5955(90)90061-S. PMID: 2272930.
Article13. Gelfand SA. Silman S, editor. 1984. The contralateral acoustic-reflex threshold. The Acoustic Reflex. Academic Press;London: p. 137–86. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-643450-7.50010-X.
Article14. Horner KC. 1986; The tensor tympani muscle reflex in the mouse. Hear Res. 24:117–23. DOI: 10.1016/0378-5955(86)90055-9. PMID: 3771374.
Article15. Relkin EM, Sterns A, Azeredo W, Prieve BA, Woods CI. 2005; Physiological mechanisms of onset adaptation and contralateral suppression of DPOAEs in the rat. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 6:119–35. DOI: 10.1007/s10162-004-5047-9. PMID: 15952049. PMCID: PMC2538334.
Article16. Rodríguez-Vázquez JF, Sakiyama K, Abe H, Amano O, Murakami G. 2016; Fetal tendinous connection between the tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini muscles: a single digastric muscle acting for morphogenesis of the cranial base. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 299:474–83. DOI: 10.1002/ar.23310. PMID: 26744237.
Article17. Maynard TM, Zohn IE, Moody SA, LaMantia AS. 2020; Suckling, feeding, and swallowing: behaviors, circuits, and targets for neurodevelopmental pathology. Annu Rev Neurosci. 43:315–36. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-100419-100636. PMID: 32101484. PMCID: PMC7359496.
Article18. Djupesland G. 1964; Middle ear muscle reflexes elicited by acoustic and nonacoustic stimulation. Acta Otolaryngol. 57(Suppl 188):287–92. DOI: 10.3109/00016486409134578. PMID: 14146687.
Article19. Bance M, Makki FM, Garland P, Alian WA, van Wijhe RG, Savage J. 2013; Effects of tensor tympani muscle contraction on the middle ear and markers of a contracted muscle. Laryngoscope. 123:1021–7. DOI: 10.1002/lary.23711. PMID: 23169583.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phylogenic Oto-stomatognathic Connection of the Mammalian Jaw: A Novel Hypothesis for Tensor Tympani Muscle and TMD-related Otologic Symptoms
- A Case of Schwannoma of the Chorda Tympani Nerve
- A Case of Objective Tinnitus due to Middle Ear Myoclonus Treated by Surgical Therapy
- Initial stage of fetal development of the pharyngotympanic tube cartilage with special reference to muscle attachments to the tube
- One Case of Objective Tinnitus due to Palatal and Middle Ear Myoclonus