Korean J Sports Med.
2022 Jun;40(2):86-93. 10.5763/kjsm.2022.40.2.86.
Association between Physical Activity and Chronotropic Incompetence in Patients with Complex Congenital Heart Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Sport Science, University of Seoul, Seoul, 2 Department of Pediatrics, Sejong General Hospital, Bucheon, Korea
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Disease, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
- 3Preventive Cardiology and Cardiac Rehabilitation, William Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, MI, USA
- KMID: 2530311
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2022.40.2.86
Abstract
- Purpose
Although chronotropic incompetence (CI) is common in patients with complex congenital heart disease (CHD) and is associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes, few data are available regarding modifiable predictors of CI in this escalating patient population. We tested the hypothesis that higher levels of physical activity (PA) are associated with a lower prevalence of CI in patients with complex CHD and evaluated the receiver operating characteristic curve to identify the PA level that best predicted CI.
Methods
We evaluated 111 adolescents with complex CHD. CI was defined as the failure to achieve 80% of the chronotropic response index during peak cardiopulmonary exercise test. Self-reported habitual activity was obtained using a global PA questionnaire.
Results
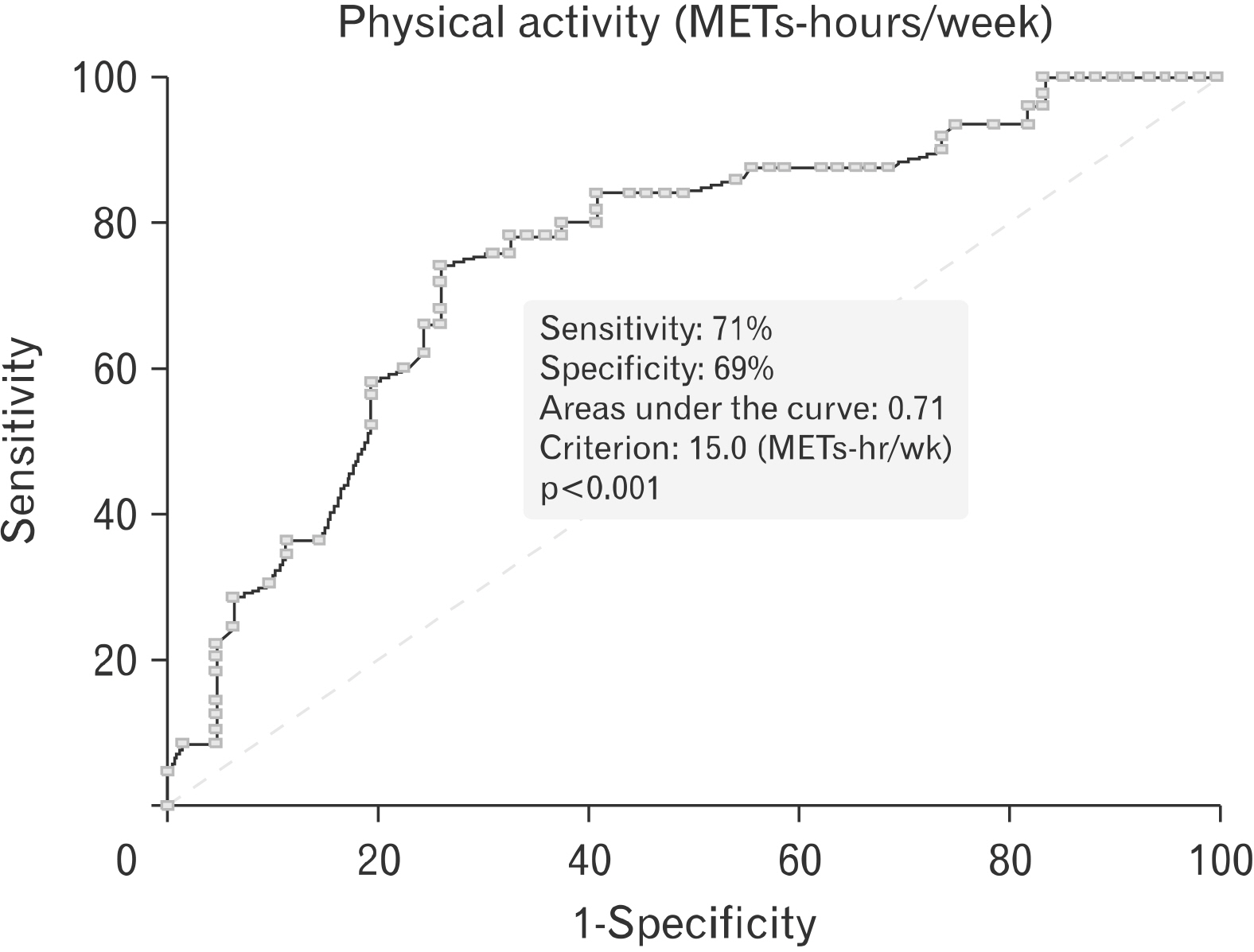
CI was identified in 45 of the 111 cases (40.5%). After adjusting for potential confounding variables, the high PA group demonstrated a lower odds ratio for having CI (odds ratios, 0.25; 95% confidence interval, 0.06‒0.99) compared with the low PA group. The most accurate cut-point for PA to predict the prevalence of CI was 15 metabolic equivalents (METs)-hours/week (areas under the curve, 0.71; 95% confidence interval, 0.61‒0.81; sensitivity, 71%; specificity, 69%).
Conclusion
Our findings demonstrate that higher levels of PA are associated with a lower prevalence of CI, independent of potential confounders, and that 15 METs-hours/week of PA provides a cut-point for accurately predicting the presence of CI in adolescents with complex CHD.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hammond HK, Froelicher VF. 1985; Normal and abnormal heart rate responses to exercise. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 27:271–96. DOI: 10.1016/0033-0620(85)90010-6. PMID: 2857054.
Article2. Arai Y, Saul JP, Albrecht P, et al. 1989; Modulation of cardiac autonomic activity during and immediately after exercise. Am J Physiol. 256(1 Pt 2):H132–41. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.1.H132. PMID: 2643348.
Article3. Ellestad MH. 1996; Chronotropic incompetence: the implications of heart rate response to exercise (compensatory parasympathetic hyperactivity?). Circulation. 93:1485–7. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.93.8.1485. PMID: 8608613.4. Lauer MS, Okin PM, Larson MG, Evans JC, Levy D. 1996; Impaired heart rate response to graded exercise: prognostic implications of chronotropic incompetence in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 93:1520–6. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.93.8.1520. PMID: 8608620.5. Martins S, Soares RM, Cotrim C, et al. 1999; The metabolic-chronotropic relation in patients with heart failure: a correlation with functional capacity. Rev Port Cardiol. 18:887–94. PMID: 10590653.6. Clark AL, Coats AJ. 1995; Chronotropic incompetence in chronic heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 49:225–31. DOI: 10.1016/0167-5273(95)02316-O. PMID: 7649668.
Article7. Diller GP, Dimopoulos K, Okonko D, et al. 2006; Heart rate response during exercise predicts survival in adults with congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48:1250–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.05.051. PMID: 16979014.
Article8. Lui GK, Silversides CK, Khairy P, et al. 2011; Heart rate response during exercise and pregnancy outcome in women with congenital heart disease. Circulation. 123:242–8. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.953380. PMID: 21220738.
Article9. Norozi K, Wessel A, Alpers V, et al. 2007; Chronotropic incompetence in adolescents and adults with congenital heart disease after cardiac surgery. J Card Fail. 13:263–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2006.12.002. PMID: 17517345.
Article10. Ohuchi H, Arakaki Y, Yagihara T, Kamiya T. 1997; Cardiores-piratory responses to exercise after repair of the univentricular heart. Int J Cardiol. 58:17–30. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-5273(96)02848-3. PMID: 9021424.
Article11. Hannon JD, Danielson GK, Puga FJ, Heise CT, Driscoll DJ. 1985; Cardiorespiratory response to exercise after repair of tetralogy of Fallot. Tex Heart Inst J. 12:393–400. PMID: 15227002. PMCID: PMC341897.12. Massin MM, Dessy H, Malekzadeh-Milani SG, Khaldi K, Topac B, Edelman R. 2009; Chronotropic impairment after surgical or percutaneous closure of atrial septal defect. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 73:564–7. DOI: 10.1002/ccd.21857. PMID: 19133677.
Article13. Thompson PD, Buchner D, Pina IL, et al. 2003; Exercise and physical activity in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology (Subcommittee on Exercise, Rehabilitation, and Prevention) and the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism (Subcommittee on Physical Activity). Circulation. 107:3109–16. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000075572.40158.77. PMID: 12821592.
Article14. Müller J, Christov F, Schreiber C, Hess J, Hager A. 2009; Exercise capacity, quality of life, and daily activity in the long-term follow-up of patients with univentricular heart and total cavopulmonary connection. Eur Heart J. 30:2915–20. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp305. PMID: 19692392.
Article15. Buys R, Van De Bruaene A, Budts W, Delecluse C, Vanhees L. 2012; In adults with atrial switch operation for transposition of the great arteries low physical activity relates to reduced exercise capacity and decreased perceived physical functioning. Acta Cardiol. 67:49–57. DOI: 10.1080/AC.67.1.2146565. PMID: 22455089.
Article16. Rosenthal TM, Leung ST, Ahmad R, et al. 2016; Lifestyle modification for the prevention of morbidity and mortality in adult congenital heart disease. Congenit Heart Dis. 11:189–98. DOI: 10.1111/chd.12341. PMID: 26931766.
Article17. van Tol BA, Huijsmans RJ, Kroon DW, Schothorst M, Kwakkel G. 2006; Effects of exercise training on cardiac performance, exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with heart failure: a meta-analysis. Eur J Heart Fail. 8:841–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2006.02.013. PMID: 16713337.
Article18. Brubaker PH, Kitzman DW. 2011; Chronotropic incompetence: causes, consequences, and management. Circulation. 123:1010–20. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.940577. PMID: 21382903. PMCID: PMC3065291.19. Miossi R, Benatti FB, Lúciade de Sá Pinto A, et al. 2012; Using exercise training to counterbalance chronotropic incompetence and delayed heart rate recovery in systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized trial. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 64:1159–66. DOI: 10.1002/acr.21678. PMID: 22438298.20. Keteyian SJ, Brawner CA, Schairer JR, et al. 1999; Effects of exercise training on chronotropic incompetence in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J. 138(2 Pt 1):233–40. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-8703(99)70106-7. PMID: 10426833.
Article21. Brubaker PH, Kitzman DW. 2007; Prevalence and management of chronotropic incompetence in heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rep. 9:229–35. DOI: 10.1007/BF02938355. PMID: 17470336.
Article22. Keytsman C, Dendale P, Hansen D. 2015; Chronotropic incompetence during exercise in type 2 diabetes: aetiology, assessment methodology, prognostic impact and therapy. Sports Med. 45:985–95. DOI: 10.1007/s40279-015-0328-5. PMID: 25834997.
Article23. Wilkoff BL, Miller RE. 1992; Exercise testing for chronotropic assessment. Cardiol Clin. 10:705–17. DOI: 10.1016/S0733-8651(18)30211-X. PMID: 1423382.
Article24. Armstrong T, Bull F. 2006; Development of the World Health Organization Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). J Public Health. 14:66–70. DOI: 10.1007/s10389-006-0024-x.
Article25. Kovacs AH, Kaufman TM, Broberg CS. 2018; Cardiac rehabilitation for adults with congenital heart disease: physical and psychosocial considerations. Can J Cardiol. 34(10 Suppl 2):S270–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjca.2018.07.016. PMID: 30274637.
Article26. Jae SY, Fernhall B, Heffernan KS, et al. 2006; Chronotropic response to exercise testing is associated with carotid atherosclerosis in healthy middle-aged men. Eur Heart J. 27:954–9. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi832. PMID: 16537555.
Article27. Bristow MR, Hershberger RE, Port JD, et al. 1990; Beta-adrenergic pathways in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium. Circulation. 82(2 Suppl):I12–25. PMID: 2164894.28. Colucci WS, Ribeiro JP, Rocco MB, et al. 1989; Impaired chronotropic response to exercise in patients with congestive heart failure: role of postsynaptic beta-adrenergic desensitization. Circulation. 80:314–23. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.80.2.314. PMID: 2546698.
Article29. Davos CH, Davlouros PA, Wensel R, et al. 2002; Global impairment of cardiac autonomic nervous activity late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot. Circulation. 106(12 Suppl 1):I69–75. DOI: 10.1161/01.cir.0000032886.55215.15. PMID: 12354712.
Article30. Gademan MG, Swenne CA, Verwey HF, et al. 2007; Effect of exercise training on autonomic derangement and neurohumoral activation in chronic heart failure. J Card Fail. 13:294–303. DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2006.12.006. PMID: 17517350.
Article31. Takken T, Giardini A, Reybrouck T, et al. 2012; Recommendations for physical activity, recreation sport, and exercise training in paediatric patients with congenital heart disease: a report from the Exercise, Basic & Translational Research Section of the European Association of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation, the European Congenital Heart and Lung Exercise Group, and the Association for European Paediatric Cardiology. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 19:1034–65. DOI: 10.1177/1741826711420000. PMID: 23126001.
Article32. Pimenta T, Rocha JA. 2021; Cardiac rehabilitation and improvement of chronotropic incompetence: is it the exercise or just the beta blockers? Rev Port Cardiol (Engl Ed). 40:947–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.repc.2021.01.014. PMID: 34922702.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Influencing Physical Activity in Adolescents with Complex Congenital Heart Disease
- Comparison of Physical Activity and Health-related Quality of Life in Adolescents with and without Congenital Heart Disease: A Propensity Matched Comparison
- Heart Rate Responses at Rest, during Exercise and after Exercise Periods in Relation to Adiposity Levels among Young Nigerian Adults
- Physical Activity and Activities of Daily Living in Older Adult Patients With Heart Failure Admitted for Subacute Musculoskeletal Disease
- Echocardiographic Evaluation of Complex Congenital Heart Disease