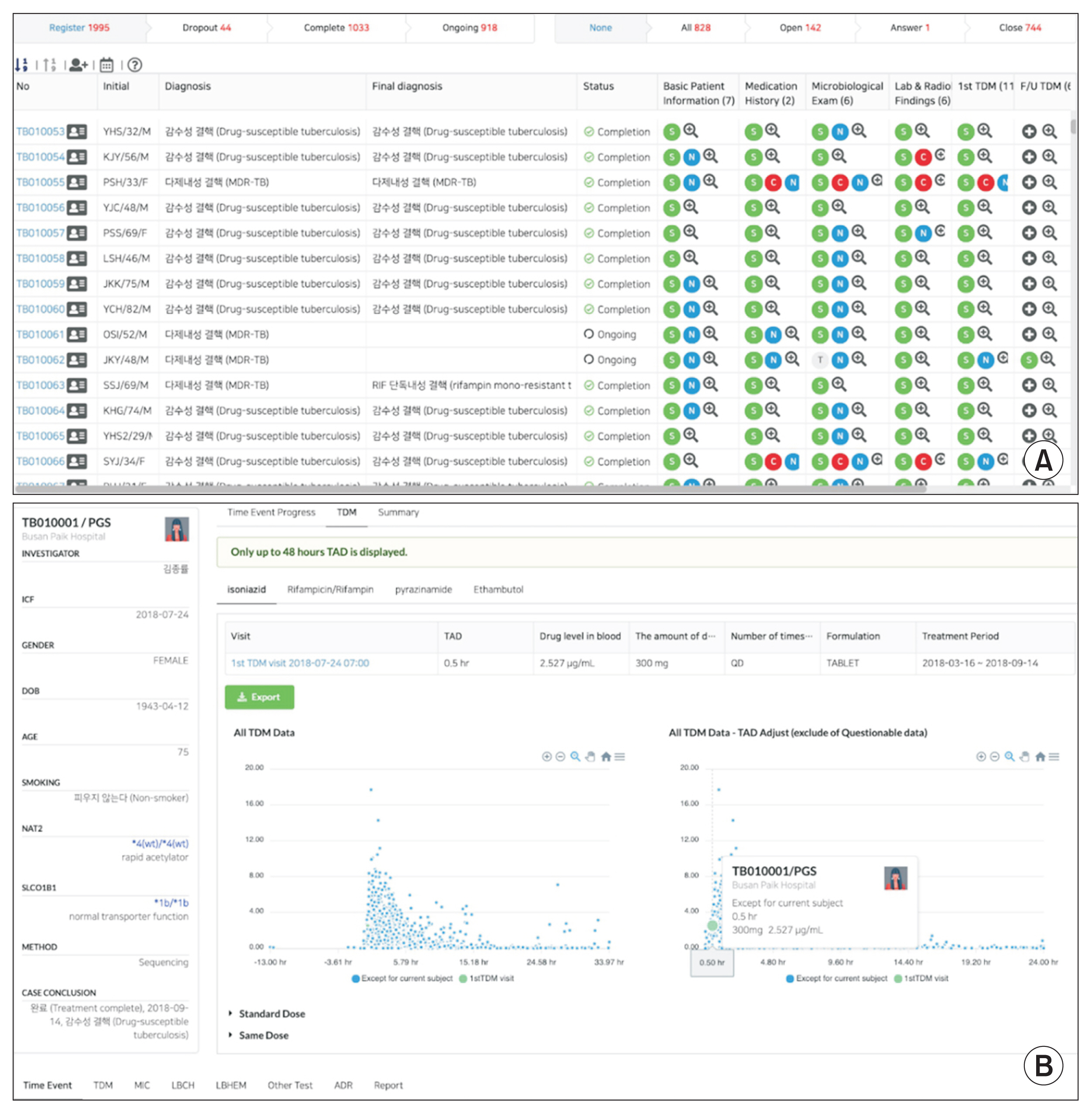
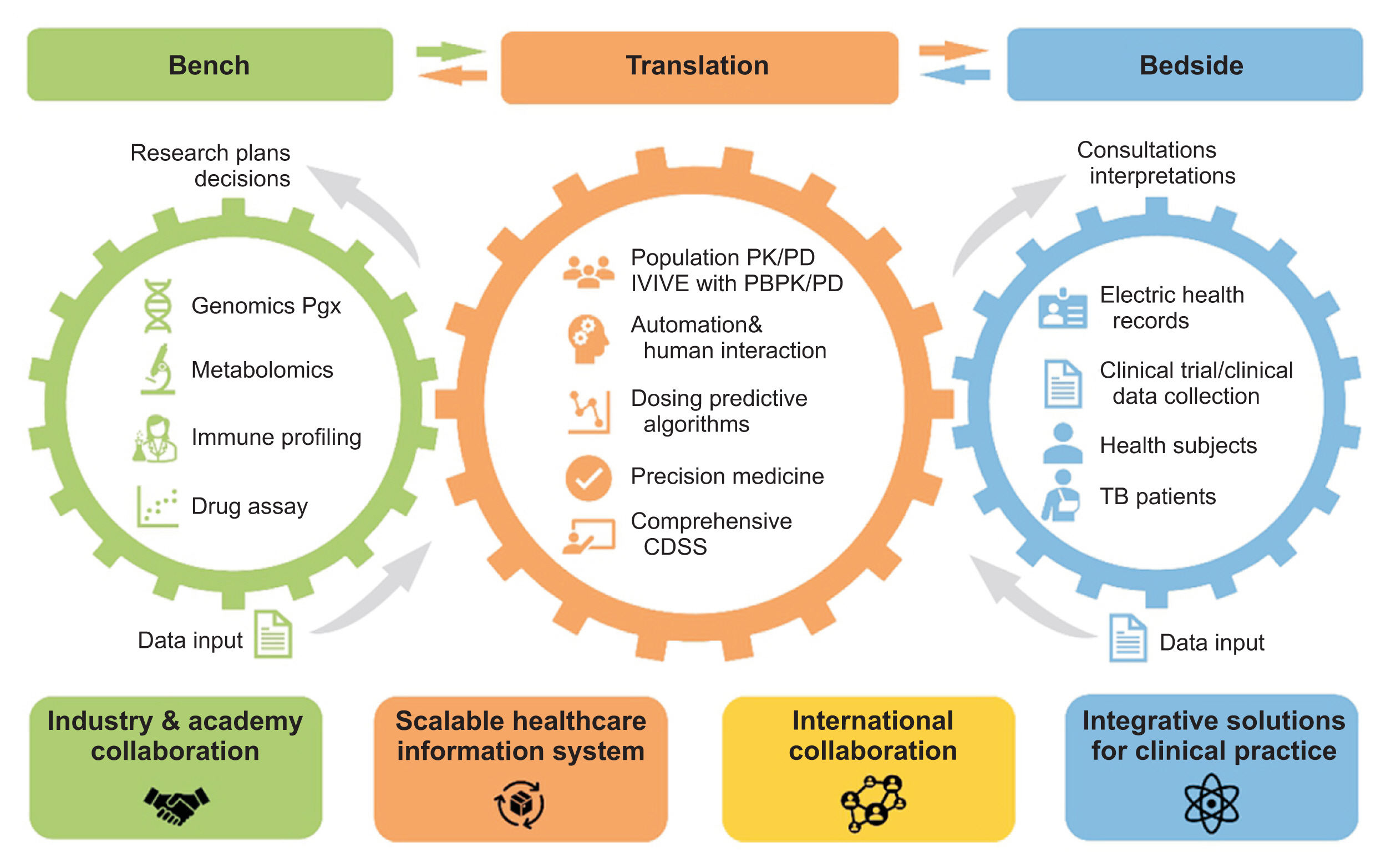
Healthc Inform Res.
2022 Apr;28(2):176-180. 10.4258/hir.2022.28.2.176.
Center for Personalized Precision Medicine for Tuberculosis: Smart Research and Development Workstation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Personalized Precision Medicine of Tuberculosis, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacogenomics Research Center, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2529800
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2022.28.2.176
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2020. [cited at 2022 Apr 10]. Available from: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/data .2. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Annual report on the notified tuberculosis in Korea, 2019. Cheongju, Korea: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency;2020.3. Lange C, Dheda K, Chesov D, Mandalakas AM, Udwadia Z, Horsburgh CR Jr. Management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Lancet. 2019; 394(10202):953–66.
Article4. Furin J, Cox H, Pai M. Tuberculosis. Lancet. 2019; 393 (10181):1642–56.
Article5. Lee Y, Raviglione MC, Flahault A. Use of digital technology to enhance tuberculosis control: scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2020; 22(2):e15727.
Article6. Kim HJ, Seo KA, Kim HM, Jeong ES, Ghim JL, Lee SH, et al. Simple and accurate quantitative analysis of 20 anti-tuberculosis drugs in human plasma using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015; 102:9–16.
Article7. Cremers S, Guha N, Shine B. Therapeutic drug monitoring in the era of precision medicine: opportunities! Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016; 82(4):900–2.
Article8. Parvez MM, Jung JA, Shin HJ, Kim DH, Shin JG. Characterization of 22 antituberculosis drugs for inhibitory interaction potential on organic anionic transporter polypeptide (OATP)-mediated uptake. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016; 60(5):3096–105.
Article9. Sun Q, Liu HP, Zheng RJ, Wang P, Liu ZB, Sha W, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of SLCO1B1, CYP2E1 and UGT1A1 and susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: a Chinese population-based prospective case-control study. Clin Drug Investig. 2017; 37(12):1125–36.
Article10. Cho YS, Jang TW, Kim HJ, Oh JY, Lee HK, Park HK, et al. Isoniazid population pharmacokinetics and dose recommendation for Korean patients with tuberculosis based on target attainment analysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021; 61(12):1567–78.
Article11. Soedarsono S, Jayanti RP, Mertaniasih NM, Kusmiati T, Permatasari A, Indrawanto DW, et al. Development of population pharmacokinetics model of isoniazid in Indonesian patients with tuberculosis. Int J Infect Dis. 2022; 117:8–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultra-rare Disease and Genomics-Driven Precision Medicine
- Application of the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model to Personalized Precision Dosing of Isoniazid in a Clinical Setting
- A use case of ChatGPT in a flipped medical terminology course
- The impending impacts of large language models on medical education
- Precision Medicine in Head and Neck Cancer