Anat Cell Biol.
2022 Mar;55(1):72-78. 10.5115/acb.21.136.
Quantitative and qualitative evaluation on the accuracy of three intraoral scanners for human identification in forensic odontology
- Affiliations
-
- 13D Printer Technology Analysis Research Team, Cybermed Inc., Daejeon, Korea
- 2Department of History, College of Liberal Art, Sejong University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2527671
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.21.136
Abstract
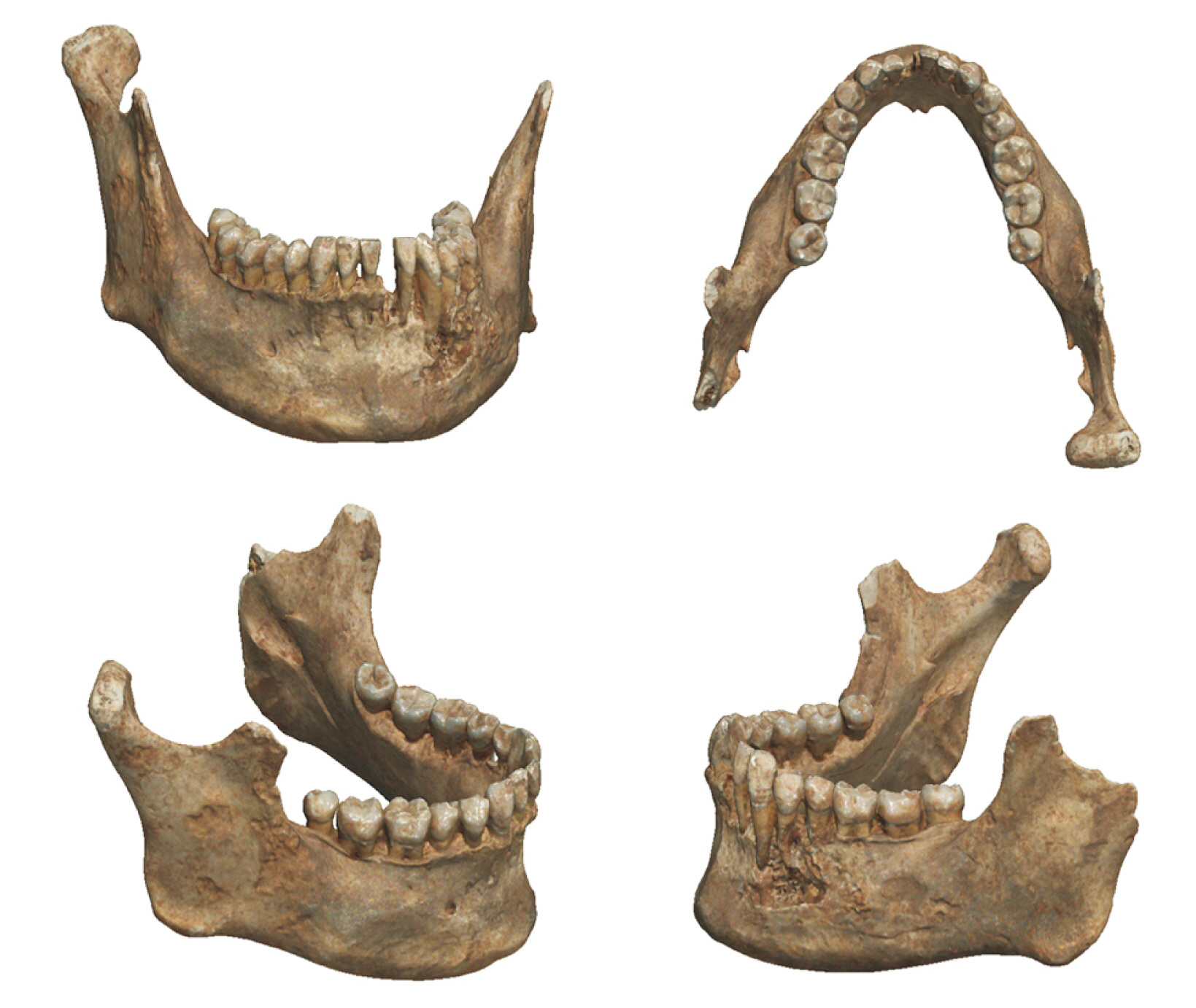
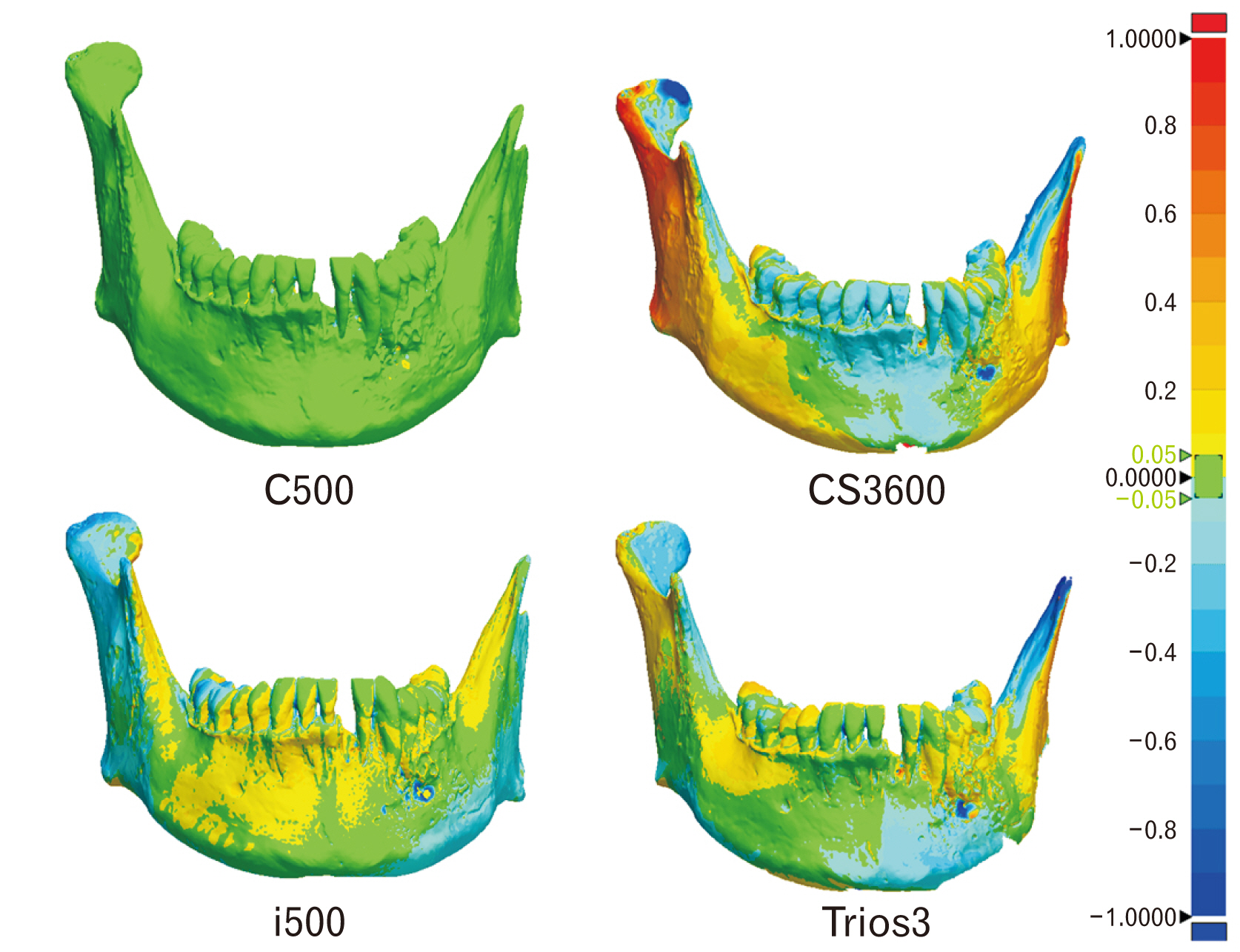
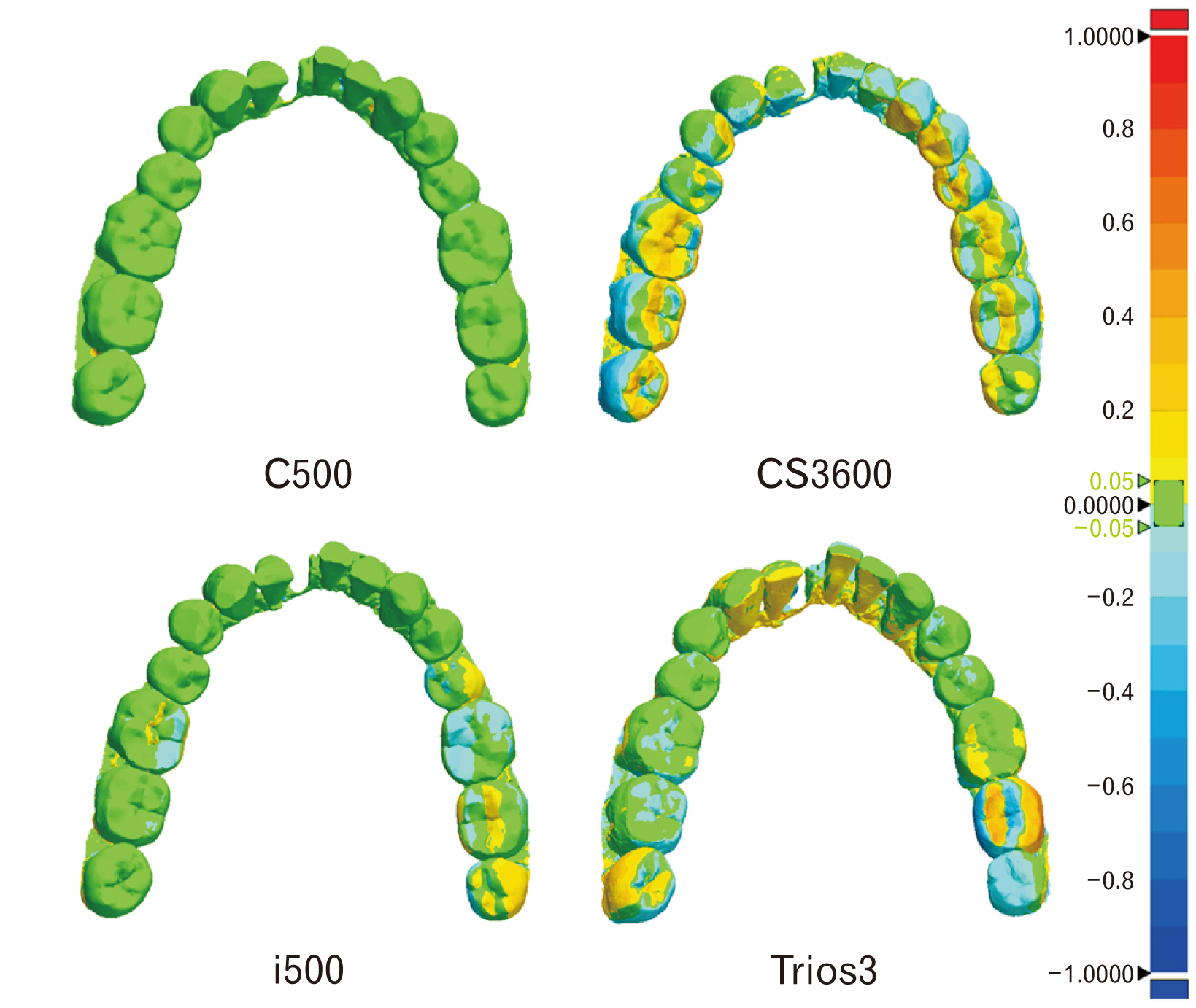
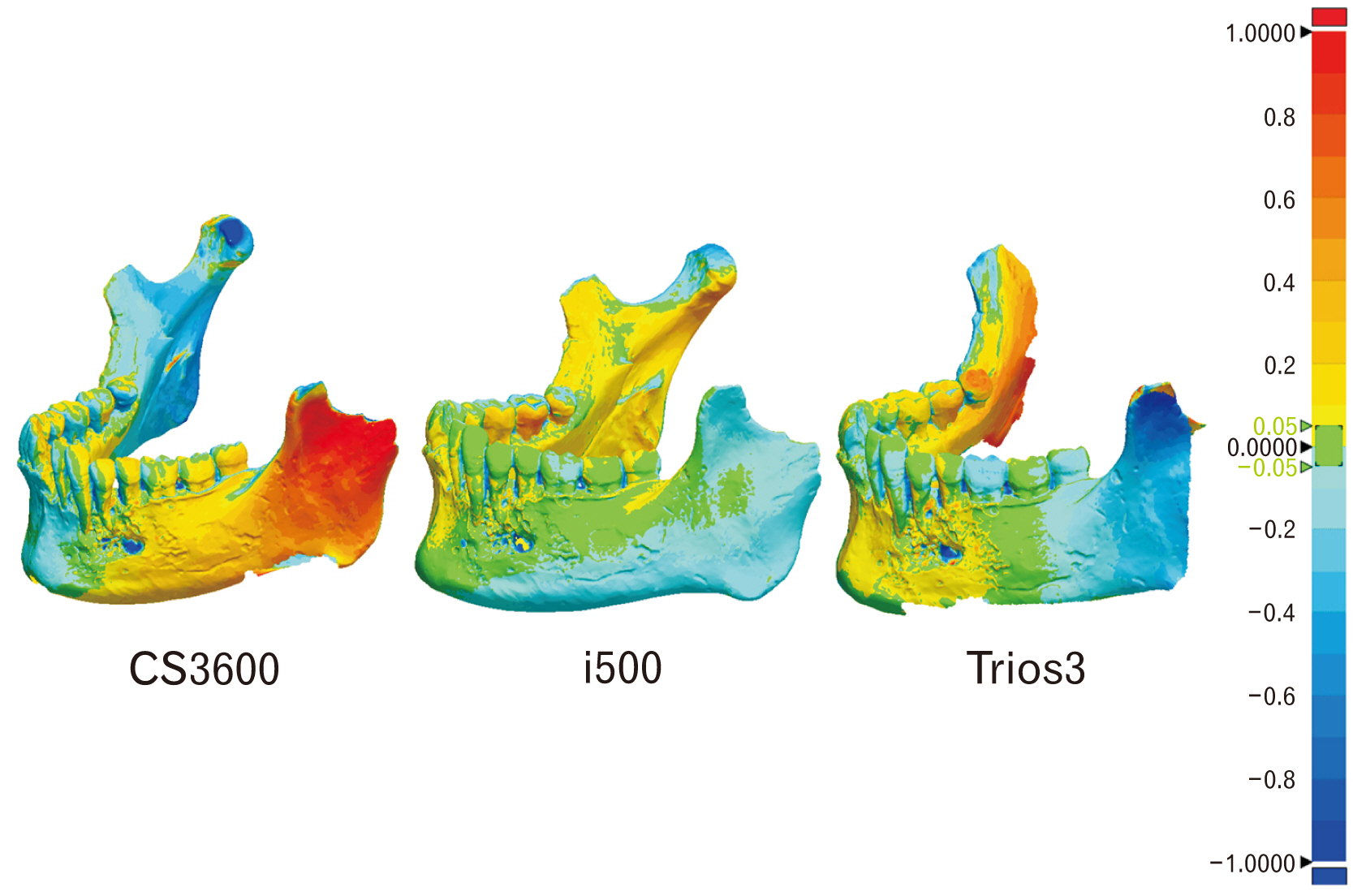
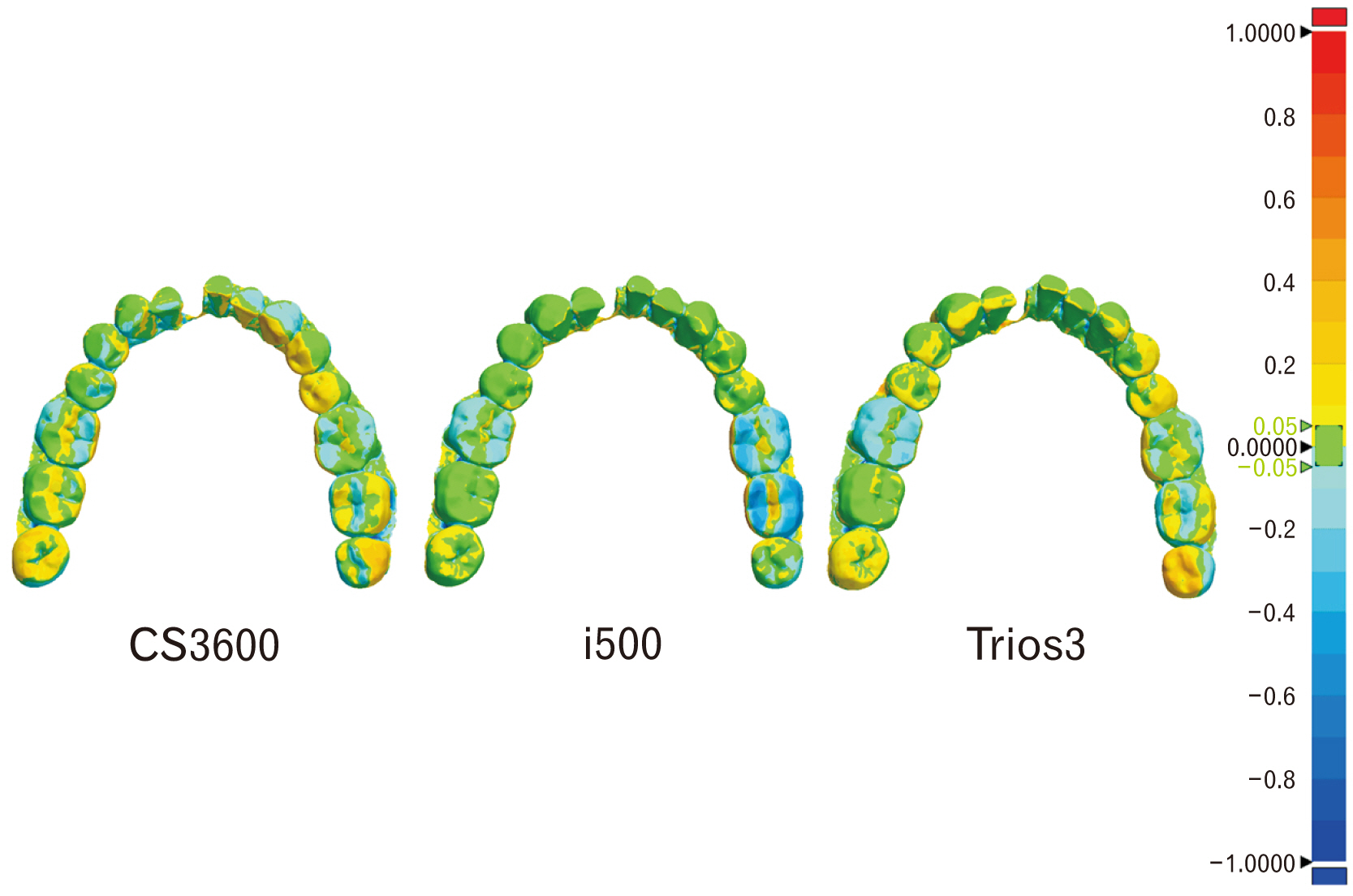
- The purpose of this study was to analyze the accuracy of intra oral scanner (IOS) to confirm the applicability of IOS for the recording and analysis of tooth morphology in forensics. The less damaged mandible specimen with many teeth remaining was scanned three times using three types of intraoral scanners (CS3600, i500, and Trios3). For quantitative comparisons of the scanned images produced by these intraoral scanners, root mean square (RMS) values were computed using a three-dimensional analysis program and a one-way ANOVA was conducted with Tukey HSD (honestly significant difference) as a post-hoc analysis (α=0.05). The repeatability of the full scan data was highest with the i500 (0.14±0.03 mm), and the post-hoc analysis confirmed significant differences between the CS3600 and the i500 outcomes (P-value=0.003). The repeatability of the partial scan data for the teeth in the mandible was highest with the i500 (0.08±0.02 mm), and the post-hoc analysis confirmed significant differences between the CS3600 and the i500 (P-value=0.016). The precision of the full scan data was highest with the i500 (0.16±0.01 mm) but the differences were not statistically significant (P-value=0.091). Meanwhile, the precision of the partial scan data for the teeth in the mandible was highest with the Trios3 (0.22±0.02 mm), but the differences were not statistically significant (P-value=0.762). Considering that the scanning of other areas of the oral cavity in addition to the teeth is important in forensic odontology, the i500 scanner appears to be the most appropriate intraoral scanner for human identification. However, as the scope of oral scanning is generally limited to teeth in the practice of dentistry, additional discussions of how to apply the IOS in forensic odontology are needed. Ultimately, the results here can contribute to the overall discussion of the forensic applicability dental data produced by intraoral scanners.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Clark DH. 1994; An analysis of the value of forensic odontology in ten mass disasters. Int Dent J. 44:241–50.2. Eboh DEO. 2019; Odontometric sex discrimination in young Urhobo adults of South-South Nigeria. Anat Cell Biol. 52:269–77. DOI: 10.5115/acb.18.221. PMID: 31598356. PMCID: PMC6773907.
Article3. Santo E, Pinho T, Teixeira A, Perez-Mongiovi D. 2021; Use of intraoral three-dimensional images for the identification of dental morphological traits related to ancestry estimation. J Forensic Sci Med. 7:70–3. DOI: 10.4103/jfsm.jfsm_21_21.
Article4. Kim WH, Nam SE, Park YS, Lee SP. 2018; Maxillary first molar wear: a longitudinal study of children. Anat Cell Biol. 51:251–9. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2018.51.4.251. PMID: 30637159. PMCID: PMC6318455.
Article5. Clement JG. Siegel JA, Saukko PJ, Houck MM, editors. 2013. Odontology. Encyclopedia of Forensic Sciences. 2nd ed. Elsevier/Academic Press;Waltham: p. 106–14. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-382165-2.00018-0.
Article6. Dedouit F, Savall F, Mokrane FZ, Rousseau H, Crubézy E, Rougé D, Telmon N. 2014; Virtual anthropology and forensic identification using multidetector CT. Br J Radiol. 87:20130468. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20130468. PMID: 24234584. PMCID: PMC4067023.
Article7. Mangano F, Gandolfi A, Luongo G, Logozzo S. 2017; Intraoral scanners in dentistry: a review of the current literature. BMC Oral Health. 17:149. DOI: 10.1186/s12903-017-0442-x. PMID: 29233132. PMCID: PMC5727697.
Article8. Kravitz ND, Groth C, Jones PE, Graham JW, Redmond WR. 2014; Intraoral digital scanners. J Clin Orthod. 48:337–47.9. Suese K. 2020; Progress in digital dentistry: the practical use of intraoral scanners. Dent Mater J. 39:52–6. DOI: 10.4012/dmj.2019-224. PMID: 31723066.
Article10. Lee SH, Nam SE, Lee SP. 2015; Evaluation of the effectiveness of the new tooth wear measurement parameters. Anat Cell Biol. 48:284–91. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2015.48.4.284. PMID: 26770880. PMCID: PMC4701703.
Article11. Chomdej T, Pankaow W, Choychumroon S. 2006; Intelligent dental identification system (IDIS) in forensic medicine. Forensic Sci Int. 158:27–38. DOI: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2005.05.001. PMID: 15936908.
Article12. Oh KC, Park JM, Moon HS. 2020; Effects of scanning strategy and scanner type on the accuracy of intraoral scans: a new approach for assessing the accuracy of scanned data. J Prosthodont. 29:518–23. DOI: 10.1111/jopr.13158. PMID: 32133690.
Article13. Nedelcu R, Olsson P, Nyström I, Rydén J, Thor A. 2018; Accuracy and precision of 3 intraoral scanners and accuracy of conventional impressions: a novel in vivo analysis method. J Dent. 69:110–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2017.12.006. PMID: 29246490.14. Chai T, Draxler RR. 2014; Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)? - Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci Model Dev. 7:1247–50. DOI: 10.5194/gmd-7-1247-2014.
Article15. Kim RJ, Park JM, Shim JS. 2018; Accuracy of 9 intraoral scanners for complete-arch image acquisition: a qualitative and quantitative evaluation. J Prosthet Dent. 120:895–903.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.01.035. PMID: 30006228.
Article16. Imburgia M, Logozzo S, Hauschild U, Veronesi G, Mangano C, Mangano FG. 2017; Accuracy of four intraoral scanners in oral implantology: a comparative in vitro study. BMC Oral Health. 17:92. DOI: 10.1186/s12903-017-0383-4. PMID: 28577366. PMCID: PMC5455075.17. Lee JH, Yun JH, Han JS, Yeo IL, Yoon HI. 2019; Repeatability of intraoral scanners for complete arch scan of partially edentulous dentitions: an in vitro study. J Clin Med. 8:1187. DOI: 10.3390/jcm8081187. PMID: 31398851. PMCID: PMC6722554.
Article18. McLean JW, von Fraunhofer JA. 1971; The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br Dent J. 131:107–11. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4802708. PMID: 5283545.
Article19. Medina-Sotomayor P, Pascual-Moscardo A, Camps A. 2019; Accuracy of 4 digital scanning systems on prepared teeth digitally isolated from a complete dental arch. J Prosthet Dent. 121:811–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.08.020. PMID: 30598308.
Article20. Chen Y, Zhai Z, Li H, Yamada S, Matsuoka T, Ono S, Nakano T. 2021; Apr. 7. Influence of liquid on the tooth surface on the accuracy of intraoral scanners: an in vitro study. J Prosthodont. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.13358. DOI: 10.1111/jopr.13358. PMID: 33829613.
Article21. Mizumoto RM, Yilmaz B. 2018; Intraoral scan bodies in implant dentistry: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 120:343–52. DOI: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2017.10.029. PMID: 29627211.
Article22. Cuperus AM, Harms MC, Rangel FA, Bronkhorst EM, Schols JG, Breuning KH. 2012; Dental models made with an intraoral scanner: a validation study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 142:308–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2012.03.031. PMID: 22920696.23. Soomer H, Lincoln MJ, Ranta H, Penttilä A, Leibur E. 2003; Dentists' qualifications affect the accuracy of radiographic identification. J Forensic Sci. 48:1121–6. DOI: 10.1520/JFS2003142. PMID: 14535679.
Article24. Pinchi V, Norelli GA, Caputi F, Fassina G, Pradella F, Vincenti C. 2012; Dental identification by comparison of antemortem and postmortem dental radiographs: influence of operator qualifications and cognitive bias. Forensic Sci Int. 222:252–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2012.06.015. PMID: 22770720.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A comparison of the accuracy of intraoral scanners using an intraoral environment simulator
- Review of the Estimation of Individual Identification in Mass Disaster
- iDENTIfyme Informative Campaign: Raising Forensic Dental Identification Awareness in the Community
- Full-arch accuracy of five intraoral scanners:In vivo analysis of trueness and precision
- Effect of the volumetric dimensions of a complete arch on the accuracy of scanners