Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2022 Feb;26(1):98-103. 10.14701/ahbps.21-077.
Clinical application of a new hemostatic material using mussel-inspired catecholamine hemostat: A pilot study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Trauma Surgery and Surgical Critical Care, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Surgery, Gang-an Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 4Department of Chemistry, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea
- 5InnoTherapy Inc., Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526838
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.21-077
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
This study aimed to evaluate clinical application of InnoSEAL Plus (a mussel-inspired catecholamine hemostat) as a new hemostatic material for humans.
Methods
Patients treated with topical hemostatic patches after liver resection were enrolled. They were divided into an experimental group (InnoSEAL Plus group) and two control groups (TachoSil® group and Surgicel Fibrillar® group) for efficacy evaluation.
Results
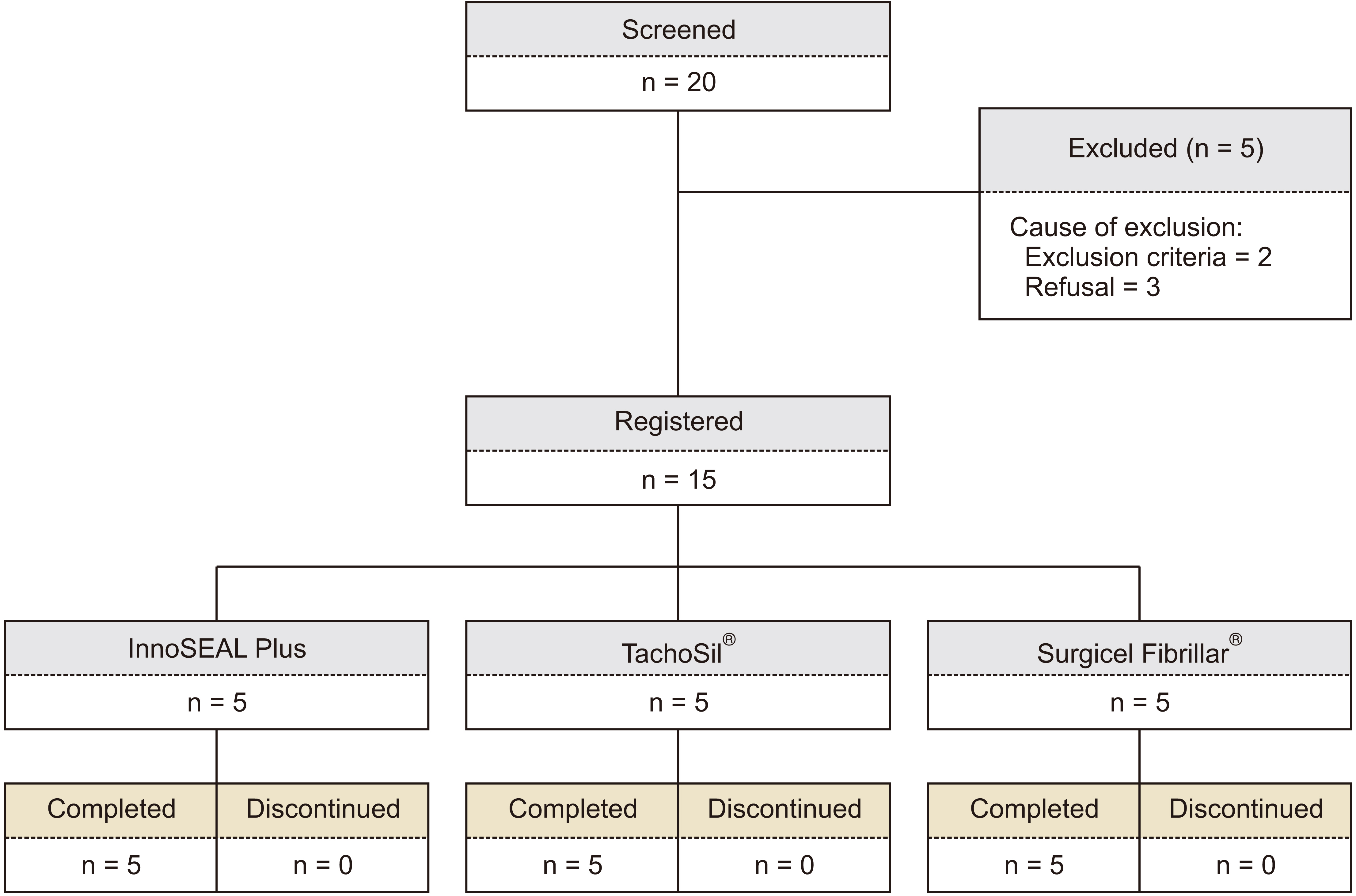
A total of 15 patients were enrolled. Each group had five patients. The 3-minute hemostasis success rate was 80.0% (4/5 patients) in the InnoSEAL Plus group, 80.0% (4/5 patients) in the TachoSil® group, and 40.0% (2/5 patients) in the Surgicel Fibrillar® group, showing no significant difference in the success rate among these groups (p > 0.05). All three groups exhibited 100% success rate for 10-minute hemostasis. Both InnoSEAL Plus and TachoSil® groups had one patient developing adverse events, which were treated easily with drug administrations.
Conclusions
InnoSEAL Plus is expected to be functionally not inferior to other conventional hemostatic agents. However, it is necessary to confirm this through multicenter prospective studies in the future.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aragon RJ, Solomon NL. 2012; Techniques of hepatic resection. J Gastrointest Oncol. 3:28–40. DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2012.006. PMID: 22811867. PMCID: PMC3397635.2. Nagano Y, Togo S, Tanaka K, Masui H, Endo I, Sekido H, et al. 2003; Risk factors and management of bile leakage after hepatic resection. World J Surg. 27:695–698. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-003-6907-x. PMID: 12732991.
Article3. Morgenstern L, Michel SL, Austin E. 1977; Control of hepatic bleeding with microfibrillar collagen. Arch Surg. 112:941–943. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1977.01370080039005. PMID: 880041.
Article4. Chapman WC, Clavien PA, Fung J, Khanna A, Bonham A. 2000; Effective control of hepatic bleeding with a novel collagen-based composite combined with autologous plasma: results of a randomized controlled trial. Arch Surg. 135:1200–1204. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.135.10.1200. PMID: 11030881.
Article5. Jackson MR, MacPhee MJ, Drohan WN, Alving BM. 1996; Fibrin sealant: current and potential clinical applications. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 7:737–746. DOI: 10.1097/00001721-199611000-00001. PMID: 9034553.6. Hong S, Yang K, Kang B, Lee C, Song IT, Byun E, et al. 2013; Hyaluronic acid catechol: a biopolymer exhibiting a pH-dependent adhesive or cohesive property for human neural stem cell engineering. Adv Funct Mater. 23:1774–1780. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201202365.
Article7. Lee BP, Dalsin JL, Messersmith PB. 2002; Synthesis and gelation of DOPA-modified poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 3:1038–1047. DOI: 10.1021/bm025546n. PMID: 12217051.
Article8. Park JY, Kim JS, Nam YS. 2013; Mussel-inspired modification of dextran for protein-resistant coatings of titanium oxide. Carbohydr Polym. 97:753–757. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.064. PMID: 23911511.
Article9. Lee C, Shin J, Lee JS, Byun E, Ryu JH, Um SH, et al. 2013; Bioinspired, calcium-free alginate hydrogels with tunable physical and mechanical properties and improved biocompatibility. Biomacromolecules. 14:2004–2013. DOI: 10.1021/bm400352d. PMID: 23639096.
Article10. Hong SH, Shin M, Lee J, Ryu JH, Lee S, Yang JW, et al. 2016; STAPLE: stable alginate gel prepared by linkage exchange from ionic to covalent bonds. Adv Healthc Mater. 5:75–79. DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201400833. PMID: 25761562.
Article11. You I, Kang SM, Byun Y, Lee H. 2011; Enhancement of blood compatibility of poly(urethane) substrates by mussel-inspired adhesive heparin coating. Bioconjug Chem. 22:1264–1269. DOI: 10.1021/bc2000534. PMID: 21675788.
Article12. Lee Y, Lee SH, Kim JS, Maruyama A, Chen X, Park TG. 2011; Controlled synthesis of PEI-coated gold nanoparticles using reductive catechol chemistry for siRNA delivery. J Control Release. 155:3–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.09.009. PMID: 20869409.
Article13. Ryu JH, Lee Y, Kong WH, Kim TG, Park TG, Lee H. 2011; Catechol-functionalized chitosan/pluronic hydrogels for tissue adhesives and hemostatic materials. Biomacromolecules. 12:2653–2659. DOI: 10.1021/bm200464x. PMID: 21599012.
Article14. Kim YM, Kim CH, Park MR, Song SC. 2016; Development of an injectable dopamine-conjugated poly(organophophazene) hydrogel for hemostasis. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 37:372–377. DOI: 10.1002/bkcs.10686.
Article15. Mehdizadeh M, Weng H, Gyawali D, Tang L, Yang J. 2012; Injectable citrate-based mussel-inspired tissue bioadhesives with high wet strength for sutureless wound closure. Biomaterials. 33:7972–7983. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.07.055. PMID: 22902057. PMCID: PMC3432175.
Article16. Fan C, Fu J, Zhu W, Wang DA. 2016; A mussel-inspired double-crosslinked tissue adhesive intended for internal medical use. Acta Biomater. 33:51–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.02.003. PMID: 26850148.
Article17. Kim K, Ryu JH, Koh MY, Yun SP, Kim S, Park JP, et al. 2021; Coagulopathy-independent, bioinspired hemostatic materials: a full research story from preclinical models to a human clinical trial. Sci Adv. 7:eabc9992. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc9992. PMID: 33762330. PMCID: PMC7990328.
Article18. Burks S, Spotnitz W. 2014; Safety and usability of hemostats, sealants, and adhesives. AORN J. 100:160–176. DOI: 10.1016/j.aorn.2014.01.026. PMID: 25080417.
Article19. Emilia M, Luca S, Francesca B, Luca B, Paolo S, Giuseppe F, et al. 2011; Topical hemostatic agents in surgical practice. Transfus Apher Sci. 45:305–311. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2011.10.013. PMID: 22040778.
Article20. Mehdizadeh M, Yang J. 2013; Design strategies and applications of tissue bioadhesives. Macromol Biosci. 13:271–288. DOI: 10.1002/mabi.201200332. PMID: 23225776. PMCID: PMC3660144.
Article21. Samudrala S. 2008; Topical hemostatic agents in surgery: a surgeon's perspective. AORN J. 88:S2–S11. DOI: 10.1016/S0001-2092(08)00586-3.
Article22. Albes JM, Krettek C, Hausen B, Rohde R, Haverich A, Borst HG. 1993; Biophysical properties of the gelatin-resorcin-formaldehyde/glutaraldehyde adhesive. Ann Thorac Surg. 56:910–915. DOI: 10.1016/0003-4975(93)90354-K. PMID: 8215668.
Article23. Brennan M. 1991; Fibrin glue. Blood Rev. 5:240–244. DOI: 10.1016/0268-960X(91)90015-5. PMID: 1782483.
Article24. Tomizawa Y. 2005; Clinical benefits and risk analysis of topical hemostats: a review. J Artif Organs. 8:137–142. DOI: 10.1007/s10047-005-0296-x. PMID: 16235029.
Article25. Lewis KM, Spazierer D, Urban MD, Lin L, Redl H, Goppelt A. 2013; Comparison of regenerated and non-regenerated oxidized cellulose hemostatic agents. Eur Surg. 45:213–220. DOI: 10.1007/s10353-013-0222-z. PMID: 23950762. PMCID: PMC3739866.
Article26. Schwartz M, Madariaga J, Hirose R, Shaver TR, Sher L, Chari R, et al. 2004; Comparison of a new fibrin sealant with standard topical hemostatic agents. Arch Surg. 139:1148–1154. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.139.11.1148. PMID: 15545559.
Article27. Frilling A, Stavrou GA, Mischinger HJ, de Hemptinne B, Rokkjaer M, Klempnauer J, et al. 2005; Effectiveness of a new carrier-bound fibrin sealant versus argon beamer as haemostatic agent during liver resection: a randomised prospective trial. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 390:114–120. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-005-0543-x. PMID: 15723234.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A multicenter, prospective, randomized clinical trial of marine mussel-inspired adhesive hemostatic materials, InnoSEAL Plus
- Animal models of hemorrhage, parameters, and development of hemostatic methods
- The use of green mussel as bioindicator of heavy metal pollution in Indonesia: a review
- The influence of hemostatic agent contamination on bond strengths on dentin bonding agents
- The Frequency of Reexpansion Pulmonary Edema after Trocar and Hemostat Assisted Thoracostomy in Patients with Spontaneous Pneumothorax