Korean J Gastroenterol.
2022 Feb;79(2):83-86. 10.4166/kjg.2022.019.
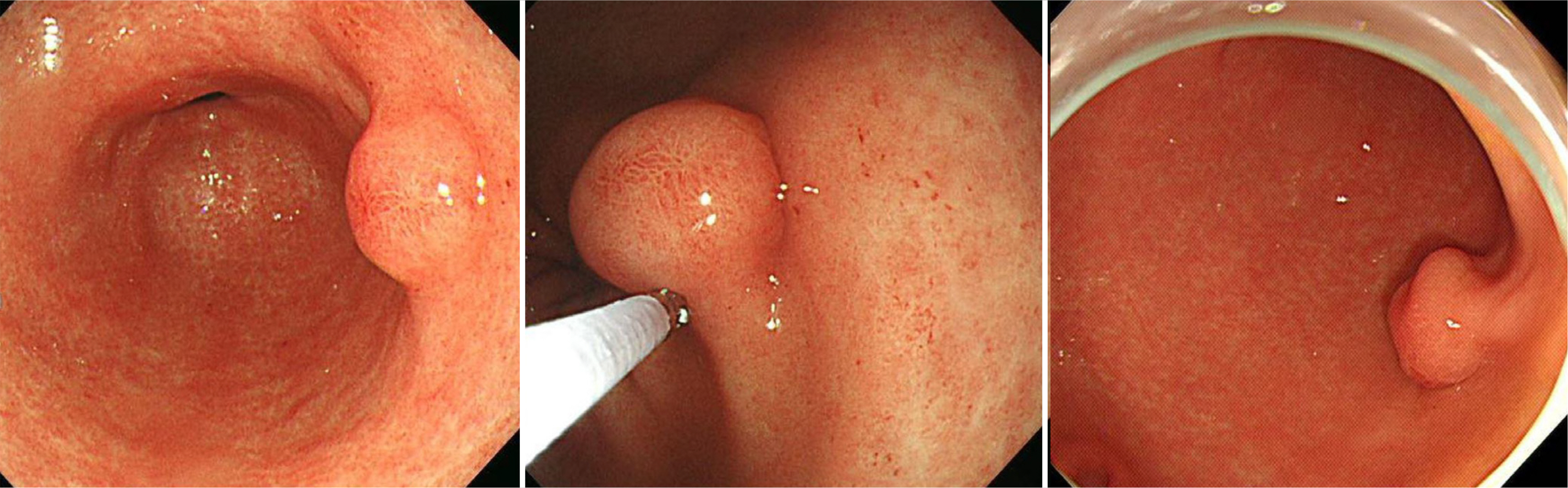
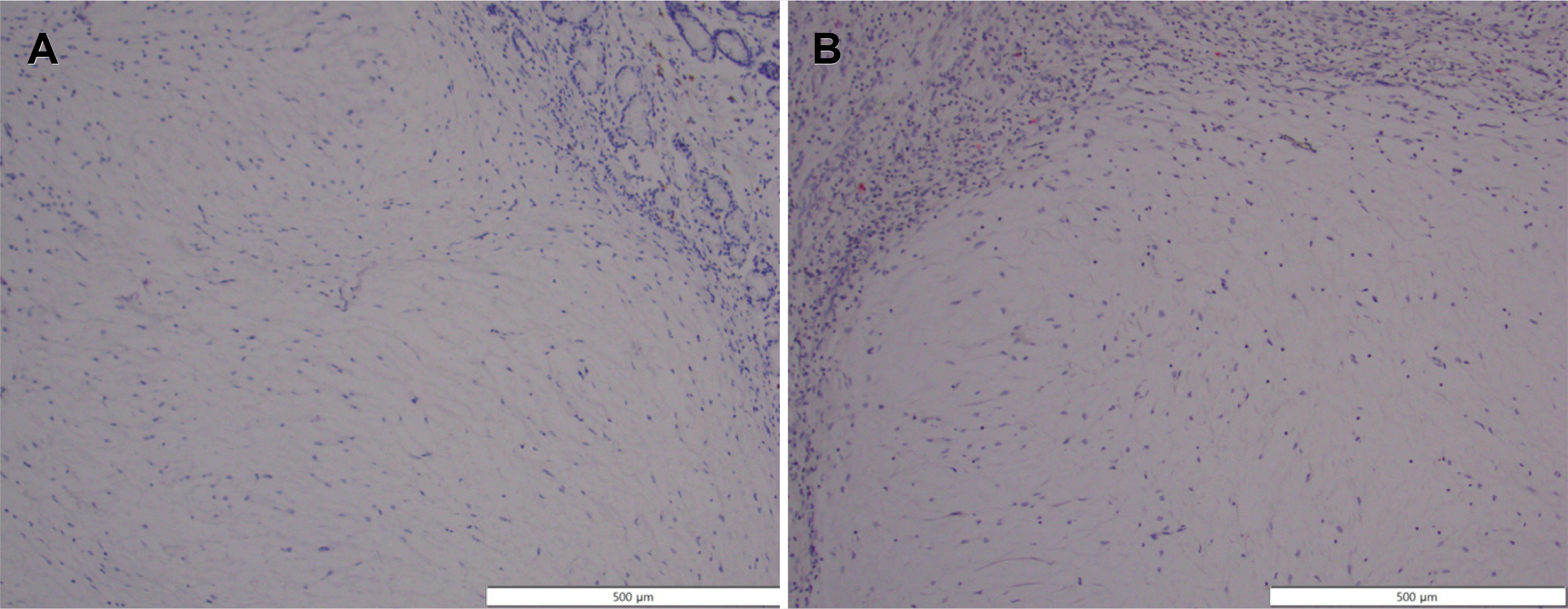
Gastric Plexiform Fibromyxoma Incidentally Found in the Routine Checkup
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 3Department of Pathology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2526787
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2022.019
Abstract
- no abstract available
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arslan ME, Li H, Jennings TA, Lee EC, Nigam A, Lee H. 2020; Frequency of plexiform fibromyxoma relative to gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a single center study. Ann Diagn Pathol. 48:151568. DOI: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2020.151568. PMID: 32717659.
Article2. Miettinen M, Fletcher CDM, Kindblom LG, Tsui WMS. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND, editors. 2010. Mesenchymal tumors of the stomach. WHO classification of tumors of the digestive system. 4th ed. IARC;Lyon: p. 74–79.3. Takahashi Y, Shimizu S, Ishida T, et al. 2007; Plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor of the stomach. Am J Surg Pathol. 31:724–728. DOI: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213448.54643.2f. PMID: 17460456.
Article4. Miettinen M, Makhlouf HR, Sobin LH, Lasota J. 2009; Plexiform fibromyxoma: a distinctive benign gastric antral neoplasm not to be confused with a myxoid GIST. Am J Surg Pathol. 33:1624–1632. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181ae666a. PMID: 19675452.5. Baek SH, Yoon JH, Kim JY. 2014; Plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor of the stomach: report of a case and review of the literature. J Korean Soc Radiol. 70:47–52. DOI: 10.3348/jksr.2014.70.1.47.
Article6. Su HA, Yen HH, Chen CJ. 2019; An update on clinicopathological and molecular features of plexiform fibromyxoma. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019:3960920. DOI: 10.1155/2019/3960920. PMID: 31360694. PMCID: PMC6642755.
Article7. Akai H, Kiryu S, Shinozaki M, et al. 2017; Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of a plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor: a case report. BMC Med Imaging. 17:7. DOI: 10.1186/s12880-017-0180-1. PMID: 28103839. PMCID: PMC5244533.
Article8. Spans L, Fletcher CD, Antonescu CR, et al. 2016; Recurrent MALAT1-GLI1 oncogenic fusion and GLI1 up-regulation define a subset of plexiform fibromyxoma. J Pathol. 239:335–343. DOI: 10.1002/path.4730. PMID: 27101025. PMCID: PMC5586099.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastric Plexiform Fibromyxoma with Two Different Growth Patterns on Histological Images: a Case Report
- A Case of Fibromyxoma of the Maxilla
- Plexiform Angiomyxoid Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Stomach: A Case Report
- Two Cases of Plexiform Schwannoma
- A Case of Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma Showing Erythronychia