Lab Med Online.
2021 Oct;11(4):275-282. 10.47429/lmo.2021.11.4.275.
Evaluation of Clinical and Analytical Performance of a Nucleocapsid Protein Antigenbased ELISA for Detecting Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangwon National University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 2Korea Clinical Medicine Center, Chuncheon, Korea
- 3SG Medical, Inc., Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Diagnostic Immunology, Seegene Medical Foundation, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526089
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2021.11.4.275
Abstract
- Background
As the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic evolves, the development of immunoassays that will help assess population exposure and potentially predict immunity has become a pressing priority.
Methods
We evaluated the performance of the R-FIND COVID-19 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (SG Medical. Inc., Korea) for semi-quantitative detection of IgG, IgM, and IgG/M/A total antibodies in serum samples, using the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein as antigen. Serum samples from 87 patients with COVID-19 were tested for IgG and IgG/M/A. Samples from 19 patients were tested for IgM. Specimens from 160 patients without COVID-19 served as negative controls. Analytical performance was evaluated according to Ministry of Food and Drug Safety guidelines. Sensitivity and specificity were the primary measures of clinical performance.
Results
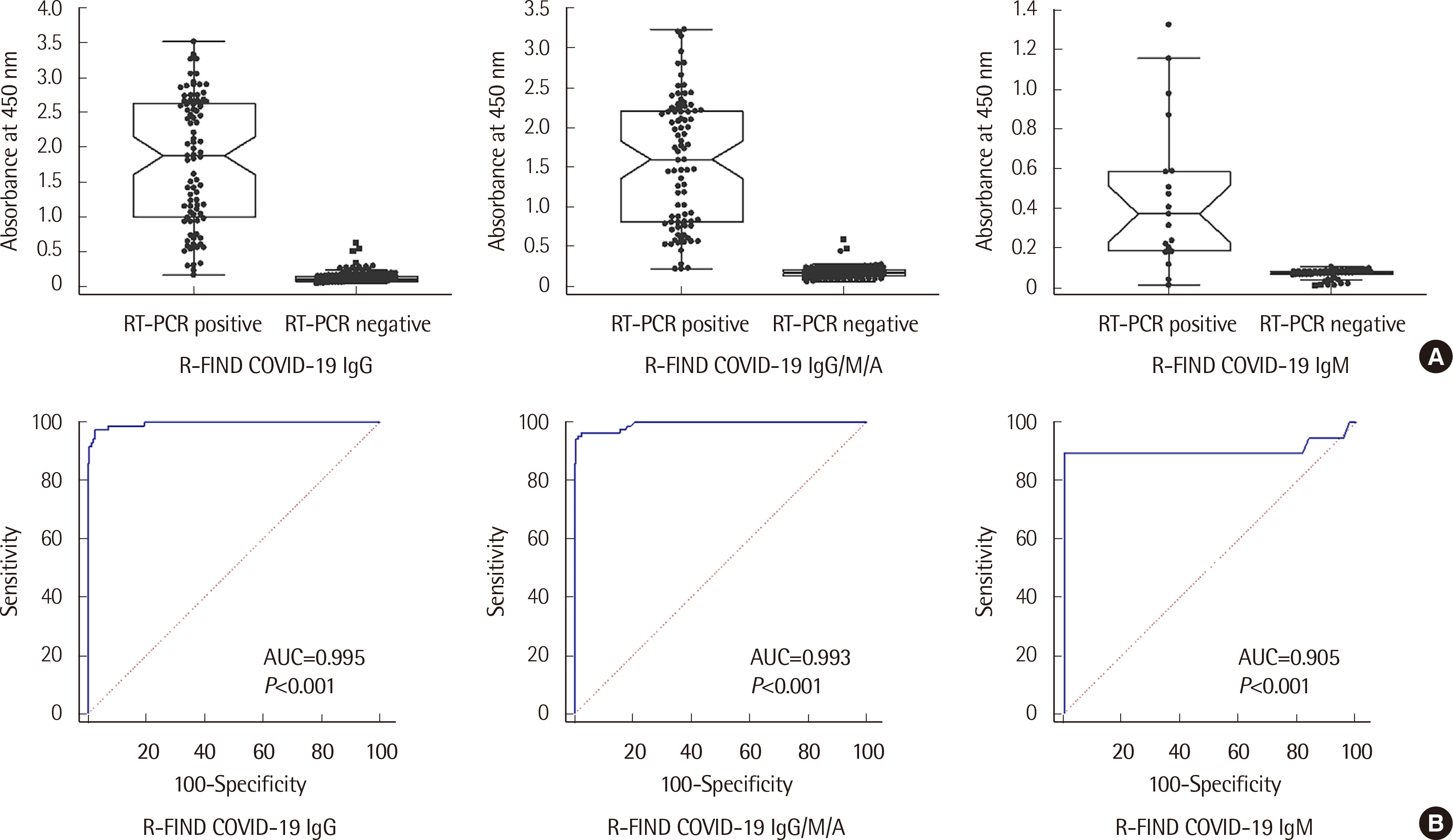
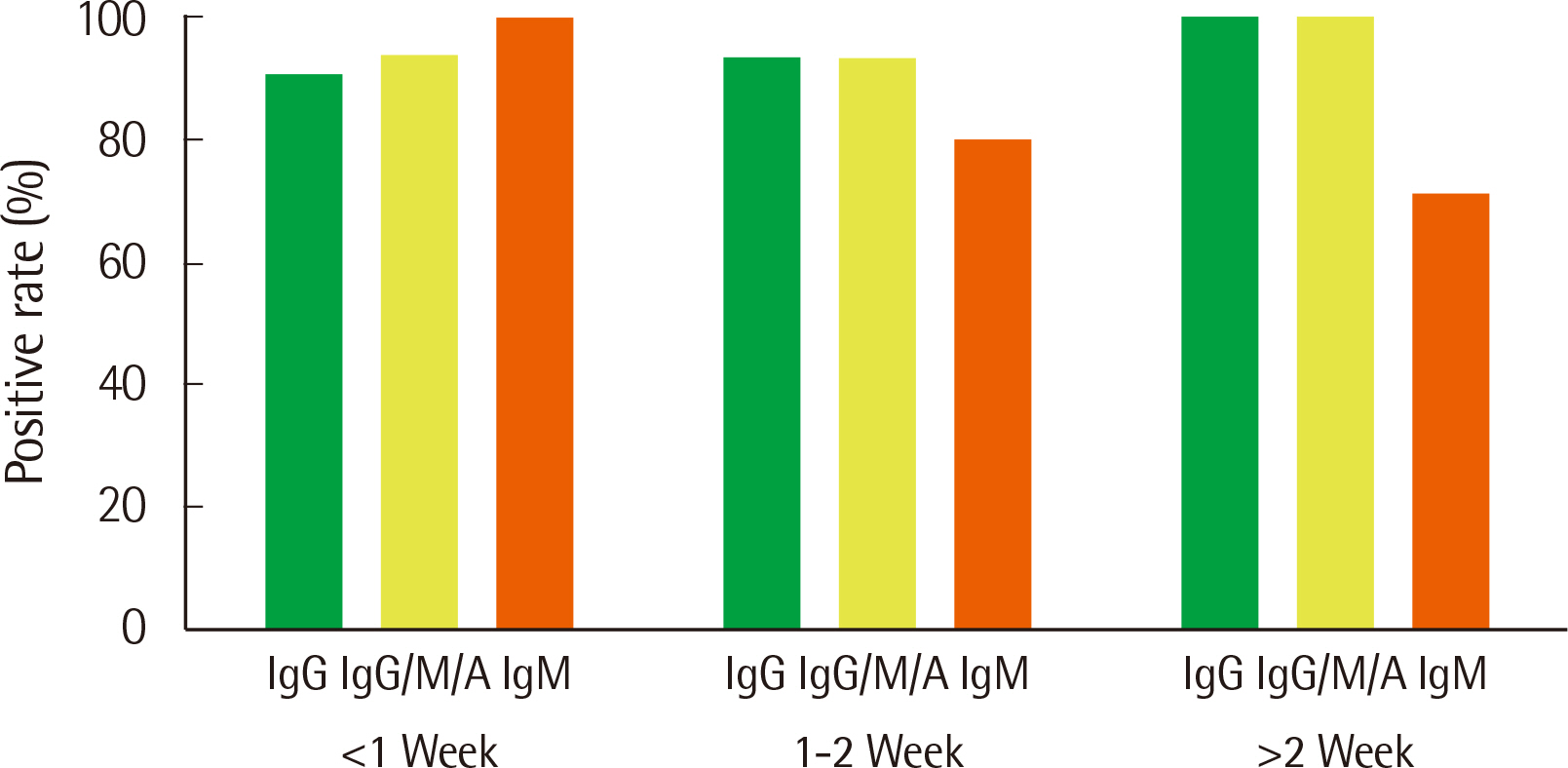
The analytical performance of the R-FIND COVID-19 ELISA met Ministry guidelines. Sensitivity and specificity were 94.25% and 98.13% for IgG, 95.40% and 98.13% for IgG/M/A, and 84.21% and 100% for IgM, respectively. IgM showed a 100% positive rate within 1 week of hospitalization, then decreased. IgG and IgG/M/A antibodies displayed 100% positivity after 2 weeks. IgG and IgG/M/A antibody titers steadily increased throughout patient hospitalization, but IgM titers gradually decreased.
Conclusions
The R-FIND COVID-19 ELISA detects IgG, IgM, and IgG/M/A and displays excellent analytical performance, sensitivity, and specificity. IgG titers increased steadily throughout hospitalization, but IgM titers peaked at one week post-hospitalization, and then steadily declined.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, de Groot RJ, Drosten C, Gulyaeva AA, et al. 2020; The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat Microbiol. 5:536–44. DOI: 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z. PMID: 32123347. PMCID: PMC7095448.
Article2. Korea Centers of Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines in response to coronavirus disease 2019. 7-3rd ed (for local government). http://www.gidcc.or.kr/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/0315-%EC%BD%94%EB%A1%9C%EB%82%98%EB%B0%94%EC%9D%B4%EB%9F%AC%EC%8A%A4%EA%B0%90%EC%97%BC%EC%A6%9D-19-%EB%8C%80%EC%9D%91%EC%A7%80%EC%B9%A8%EC%A7%80%EC%9E%90%EC%B2%B4%EC%9A%A97-3%ED%8C%90.hwp. Updated on Mar 2020.3. Kim HS, Hong KH, Sung HS, Lee HM, Kim JS. 2020; Laboratory tests for diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JoHTA. 8:14–9.4. Tahamtan A, Ardebili A. 2020; Real-time RT-PCR in COVID-19 detection: issues affecting the results. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 20:453–4. DOI: 10.1080/14737159.2020.1757437. PMID: 32297805. PMCID: PMC7189409.
Article5. Guo L, Ren L, Yang S, Xiao M, Chang D, Yang F, et al. 2020; Proflling early humoral response to diagnose novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Clin Infect Dis. 71:778–85. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa310. PMID: 32198501. PMCID: PMC7184472.6. Gralinski LE, Menachery VD. 2020; Return of the coronavirus: 2019-nCoV. Viruses. 12:135. DOI: 10.3390/v12020135. PMID: 31991541. PMCID: PMC7077245.
Article7. Suresh MR, Bhatnagar PK, Das D. 2008; Molecular targets for diagnostics and therapeutics of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV). J Pharm Pharm Sci. 11:1s–13s. DOI: 10.18433/J3J019. PMID: 19203466. PMCID: PMC2678938.
Article8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2012. Evaluation of detection capability for clinical laboratory measurement procedures; Approved guideline-Second edition. CLSI document EP17-A2. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2014. Evaluation of precision of quantitative measurement procedures; Approved guideline-Third edition. CLSI document EP05-A3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2004. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; Approved guideline-Second edition. CLSI document EP05-A2. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:11. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2006. User veriflcation of performance for precision and trueness; Approved guideline-Second edition. CLSI document EP15-A2. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:12. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2018. Interference testing in clinical chemistry, 3rd Edition. CLSI guideline EP07. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:13. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administrations. 2013. Bioanalytical method validation; Guidance for industry. Docket No. FDA-2013-D-1020. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administrations;Silver Spring, MD: https://www.fda.gov/flles/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf. Updated on May 2018.14. Krüttgen A, Cornelissen CG, Dreher M, Hornef M, Imöhl M, Kleines M. 2020; Comparison of four new commercial serologic assays for determination of SARS-CoV-2 IgG. J Clin Virol. 128:104394. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104394. PMID: 32416599. PMCID: PMC7189838.
Article15. Seegmiller JC, Kokaisel EL, Story SJ, Zaun CP, Peters JM, Thomas SN, et al. 2020; Method comparison of SARS-CoV-2 serology assays involving three commercially available platforms and a novel in-house developed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Biochem. 86:34–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.08.004. PMID: 32791053. PMCID: PMC7417259.
Article16. Tré Hardy M, Wilmet A, Beukinga I, Favresse J, Dogné JM, Douxflls J, et al. 2021; Analytical and clinical validation of an ELISA for speciflc SARS CoV 2 IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies. J Med Virol. 93:803–11. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26303. PMID: 32667733. PMCID: PMC7405491.17. Liu X, Zheng X, Liu B, Wu M, Zhang Z, Zhang G, et al. 2020; Serum IgM against SARS-CoV-2 correlates with in-hospital mortality in severe/critical patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. Aging (Albany NY). 12:12432–40. DOI: 10.18632/aging.103417. PMID: 32628642. PMCID: PMC7377873.
Article18. Long QX, Deng HJ, Chen J, Hu J, Liu BZ, Liao P, et al. 2020. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients: the perspective application of serological tests in clinical practice. medRxiv. Updated on Mar 2020.
Article19. Vashist SK. 2020; In vitro diagnostic assays for COVID-19: recent advances and emerging trends. Diagnostics (Basel). 10:202. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10040202. PMID: 32260471. PMCID: PMC7235801.
Article20. Tuaillon E, Bolloré K, Pisoni A, Debiesse S, Renault C, Marie S, et al. 2020; Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies using commercial assays and seroconversion patterns in hospitalized patients. J Infect. 81:e39–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.077. PMID: 32504735. PMCID: PMC7834649.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Usefulness of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test
- Clinical Utility of Sero-Immunological Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein During Subsequent Prevalence of Wild-Type, Delta Variant, and Omicron Variant
- Performance comparison between Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S and Atellica IM SARS-CoV-2 Total and SARS-CoV-2 IgG assays
- Druggability for COVID-19: in silico discovery of potential drug compounds against nucleocapsid (N) protein of SARS-CoV-2
- The Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Children During Early COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study