Lab Med Online.
2021 Jul;11(3):177-182. 10.47429/lmo.2021.11.3.177.
Performance Evaluation of Aptima HBV and HCV Quant Assays in the Panther System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526064
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2021.11.3.177
Abstract
- Background
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections remain a serious health problem despite advancements in their prevention and treatment. Guidelines on their management recommend using viral DNA/RNA titers. Thus, accurate measurement and prompt reporting are crucial.
Methods
The performances of the Aptima HBV and HCV Quant assays (Hologic Inc., USA) were analyzed. The results were compared with those of Cobas 4800 (Roche Molecular Systems, USA). Linearity, limit of detection (LoD), and precision were evaluated as recommended in each corresponding CLSI guideline.
Results
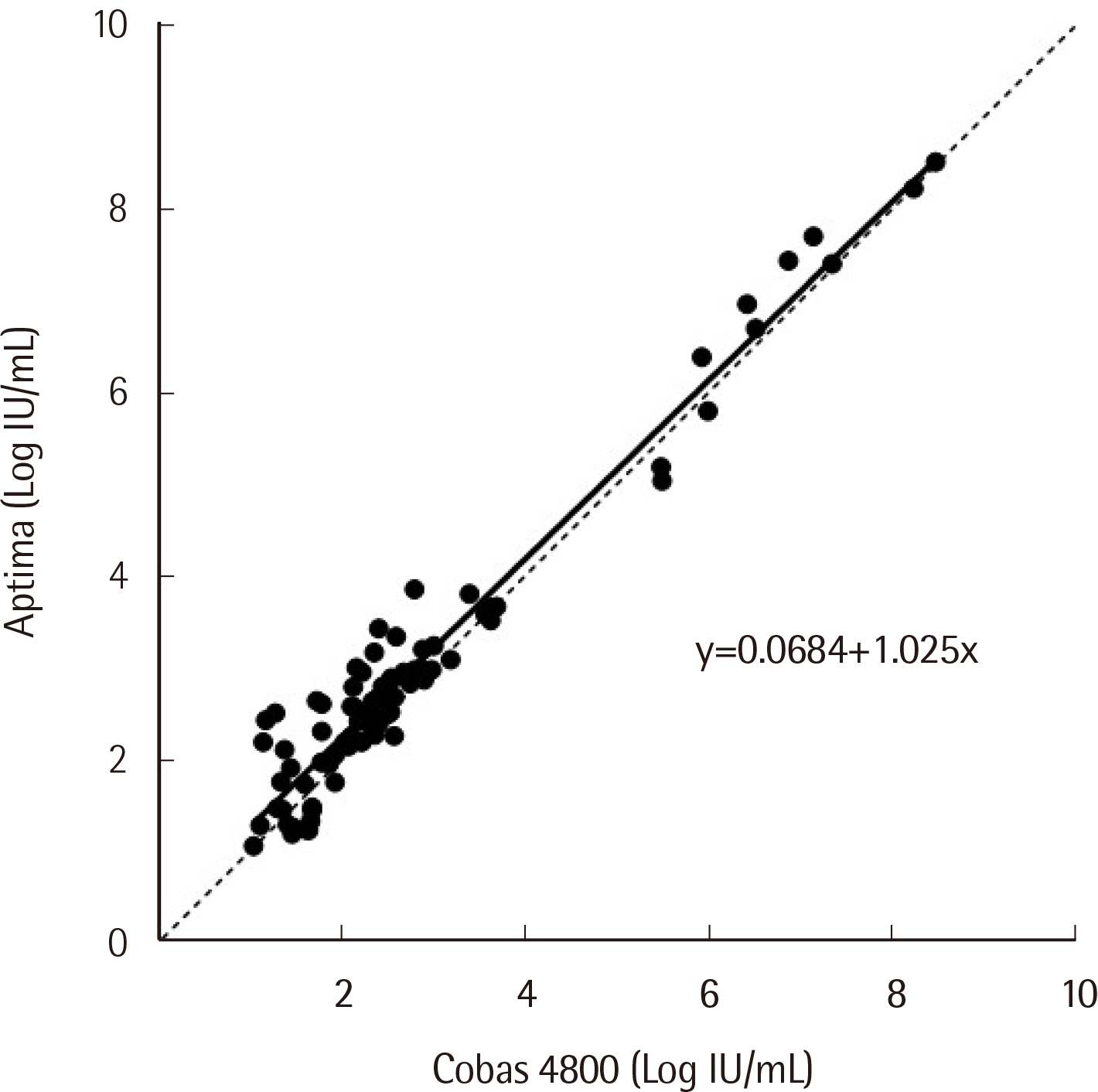
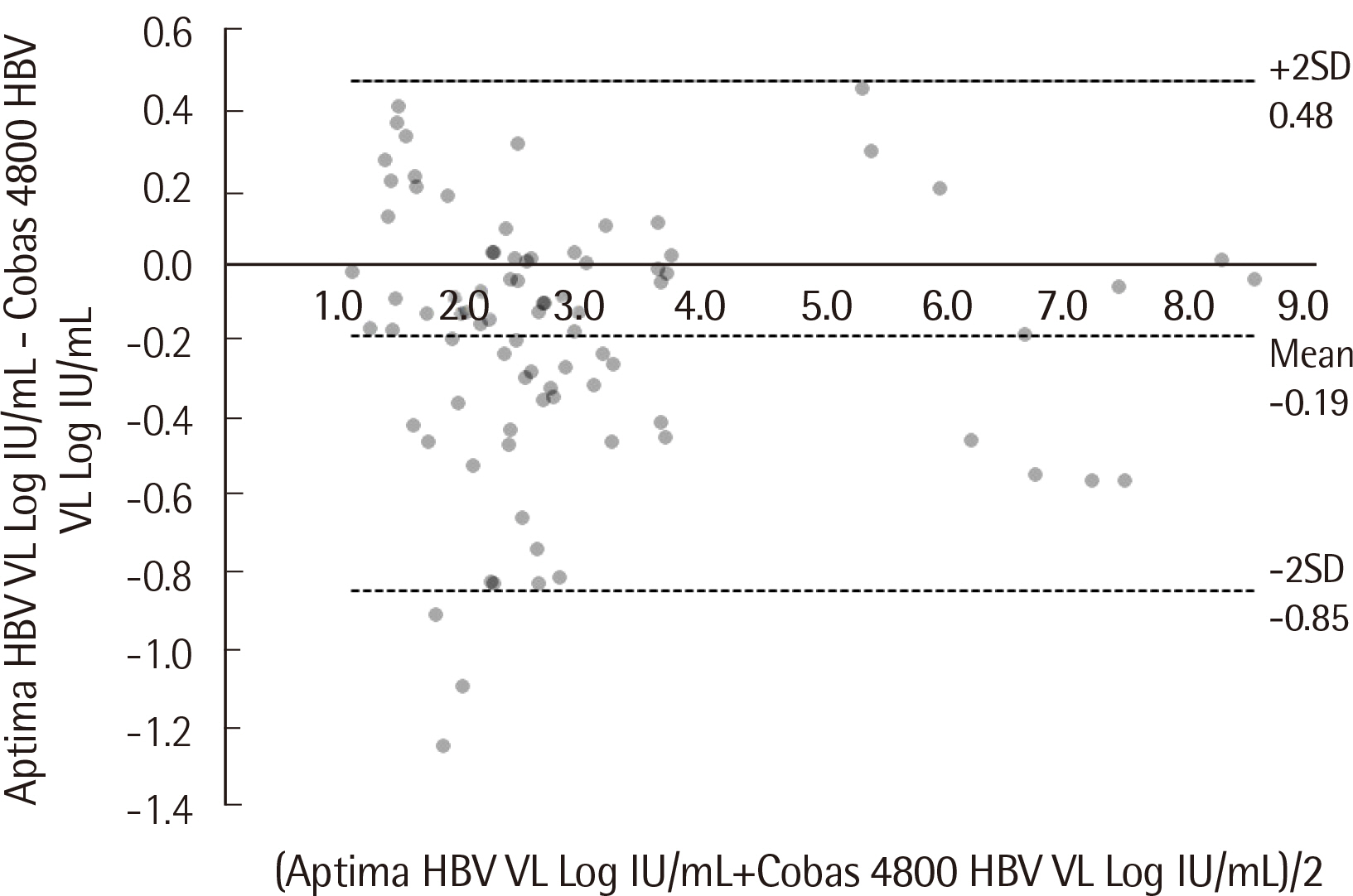
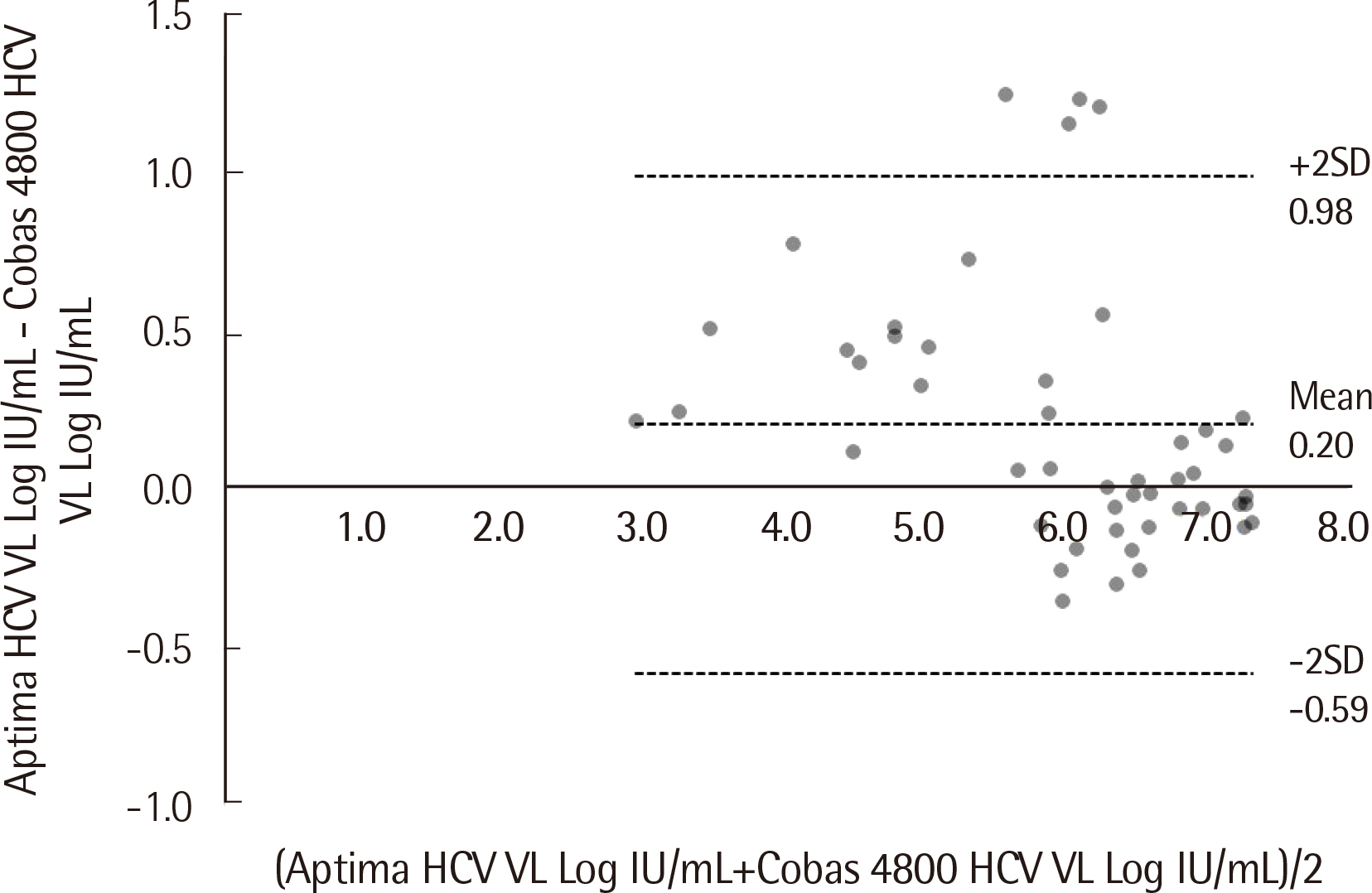
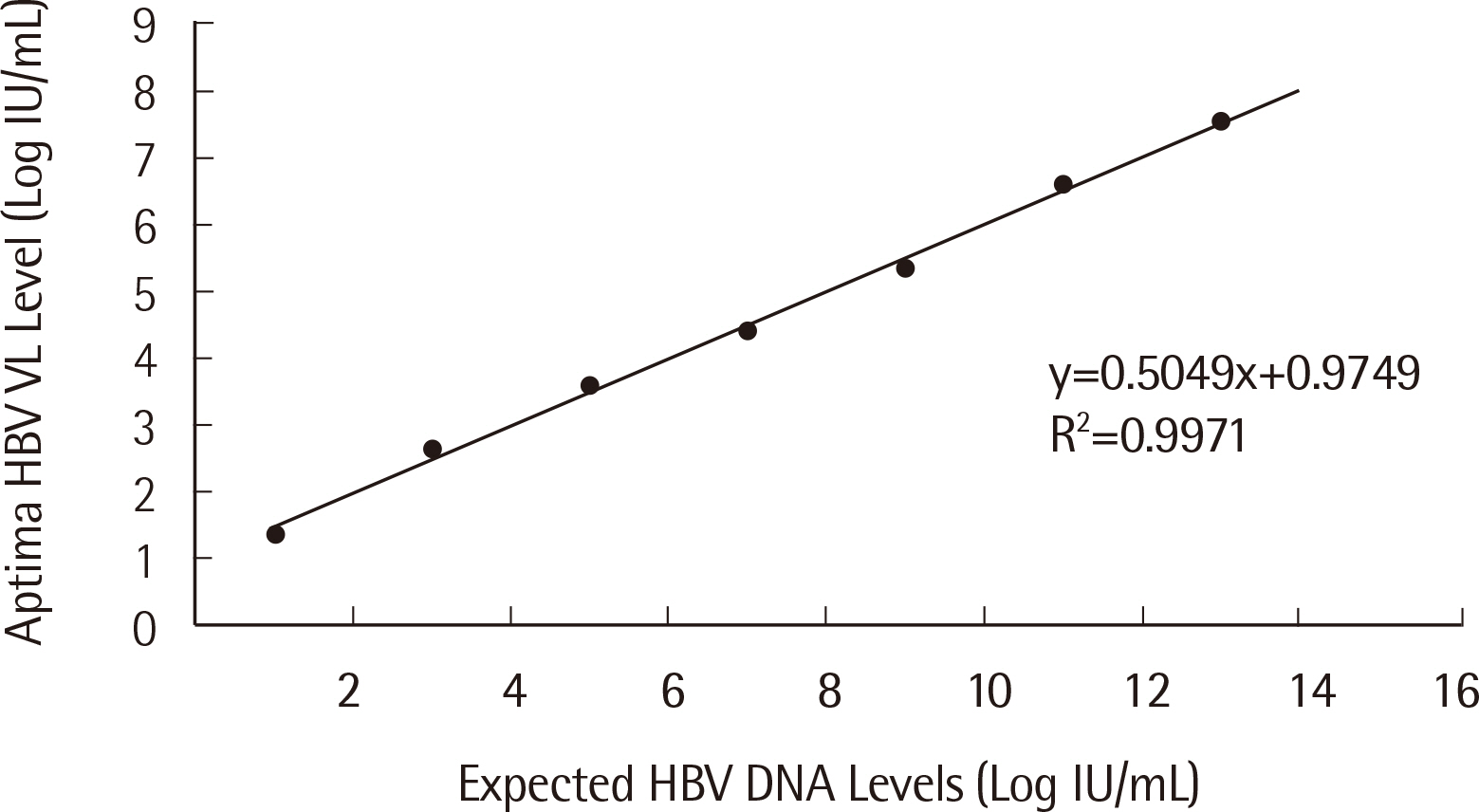
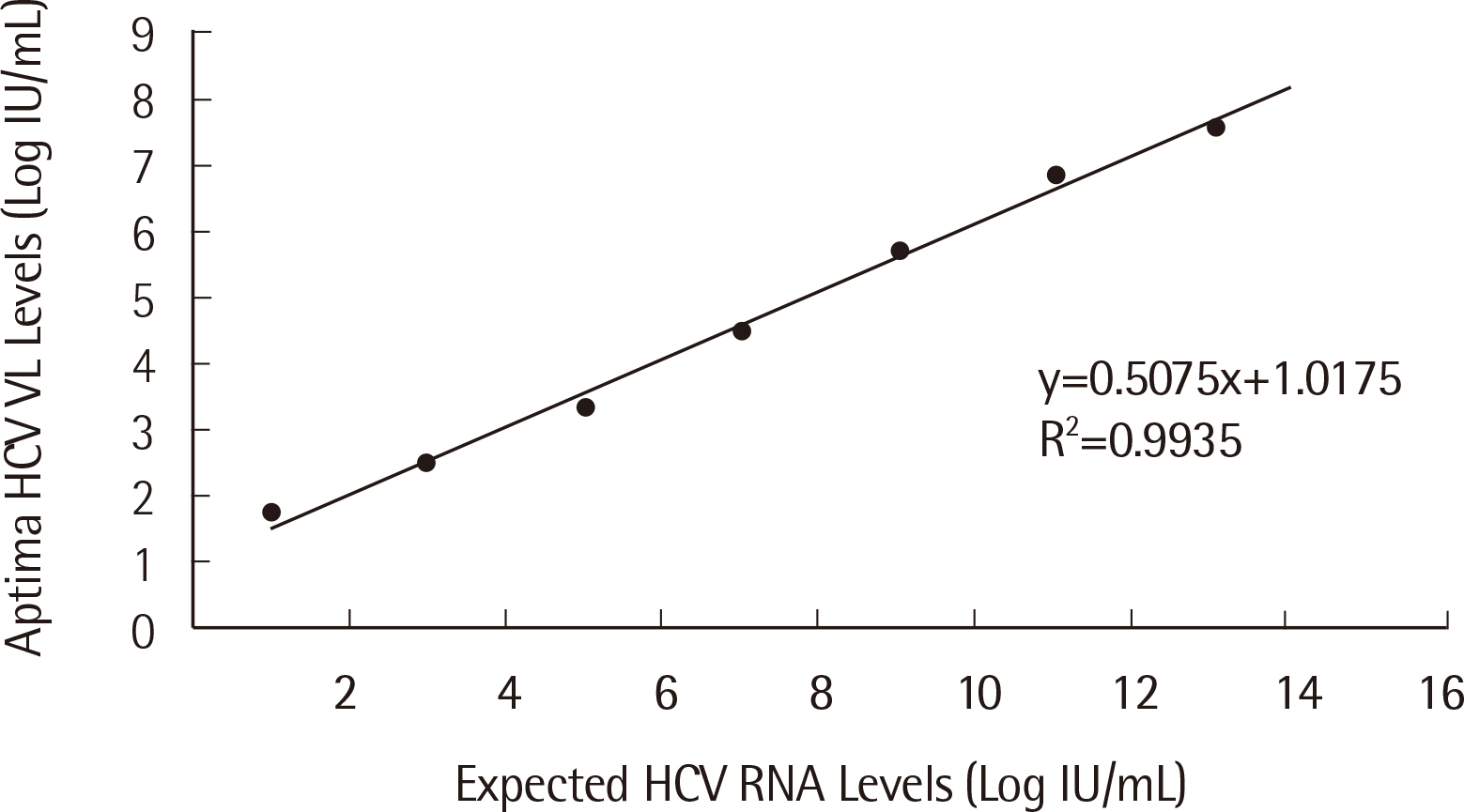
Passing-Bablok regression analysis showed a high correlation between the two assays: regression line was y = 0.0684+1.025x (95% CI: 0.9604-1.092) for HBV and y = -0.9650+1.141x (95% CI: 1.071-1.226) for HCV. Agreement between the assays’ qualitative results based on categorical analysis was 82.30% (185/224) (κ: 0.738, 95% CI: 0.701-0.775) for HBV and 94.52% (69/73) (κ: 0.855, 95% CI: 0.796-0.914) for HCV. The LoD values for HBV and HCV were 4.448 IU/mL and 6.166 IU/mL, respectively. The percent coefficient of variation (%CV) for the HBV assay for both low and high positive controls was less than 2%, whereas for the HCV assay, %CV for low positive control was 3.20%.
Conclusions
Overall, the Aptima HBV and HCV Quant assays demonstrated a high correlation with Cobas 4800. These tests were both sensitive and precise. Therefore, we conclude that the Aptima assay is a practical tool in the management of HBV- and HCV-infected patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schweitzer A, Horn J, Mikolajczyk RT, Krause G, Ott JJ. 2015; Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet. 386:1546–55. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61412-X.
Article2. Yim SY, Kim JH. 2019; The epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 34:945–53. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2019.007. PMID: 30919608. PMCID: PMC6718747.
Article3. Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan HL, Chen CJ, et al. 2016; Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: a 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 10:1–98. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-015-9675-4. PMID: 26563120. PMCID: PMC4722087.
Article4. Petruzziello A, Marigliano S, Loquercio G, Cozzolino A, Cacciapuoti C. 2016; Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: An up-date of the distribution and circulation of hepatitis C virus genotypes. World J Gastroenterol. 22:7824–40. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7824. PMID: 27678366. PMCID: PMC5016383.
Article5. Jeong SH, Jang ES, Choi HY, Kim KA, Chung W, Ki M. 2017; Current status of hepatitis C virus infection and countermeasures in South Korea. Epidemiol Health. 39:e2017017. DOI: 10.4178/epih.e2017017. PMID: 28774165. PMCID: PMC5543292.
Article6. Chung RT, Ghany MG, Kim AY, Marks KM, Naggie S, Vargas HE, et al. 2018; Hepatitis C Guidance 2018 Update: AASLD-IDSA Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 67:1477–92. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciy585. PMID: 30215672. PMCID: PMC7190892.7. Aretzweiler G, Leuchter S, Simon CO, Marins E, Frontzek A. 2019; Generating timely molecular diagnostic test results: workflow comparison of the cobas® 6800/8800 to Panther. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 19:951–7. DOI: 10.1080/14737159.2019.1665999. PMID: 31526152.8. May S, Adamska E, Tang JW. 2018; Evaluating the aptima HIV-1 quant Dx, HCV quant Dx and HBV quant assays against the Abbott HIV-1, HCV and HBV RealTime assays. J Clin Virol. 106:7–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2018.06.015. PMID: 30007139.
Article9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2020. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures. CLSI guideline EP06. 2nd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2012. Evaluation of detection capability for clinical laboratory measurement procedures. CLSI guideline EP17-A2. Approved guideline. 2nd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:11. Schønning K, Johansen K, Nielsen LG, Weis N, Westh H. 2018; Analytical performance of the Hologic Aptima HBV Quant Assay and the COBAS Ampliprep/COBAS TaqMan HBV test v2.0 for the quantification of HBV DNA in plasma samples. J Clin Virol. 104:83–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2018.05.007. PMID: 29783147.
Article12. Worlock A, Blair D, Hunsicker M, Le-Nguyen T, Motta C, Nguyen C, et al. 2017; Analytical characteristics and comparative evaluation of Aptima HCV quant Dx assay with the Abbott RealTime HCV assay and Roche COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HCV quantitative test v2.0. Virol J. 14:66. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-017-0727-3. PMID: 28372576. PMCID: PMC5379753.
Article13. Hologic. Inc. Aptima HBV Quant Assay. https://www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/2019-03/AW-15644_002_01_0.pdf. Last accessed on September 2020.14. Hologic. Inc. Aptima HCV Quant Dx Assay. https://www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/2019-03/AW-14498_002_01_0.pdf. Last accessed on September 2020.15. Roche Diagnostics. Cobas® HCV GT for use on the cobas® 4800 System. https://diagnostics.roche.com/global/en/products/params/cobas-hcv-gt-for-use-on-thecobas-4800-system.html. Last accessed on September 2020.16. Braun P, Delgado R, Drago M, Fanti D, Fleury H, Gismondo MR, et al. 2017; European multicenter study on analytical performance of DxN veris system HCV assay. J Clin Microbiol. 55:1186–92. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02163-16. PMID: 28151405. PMCID: PMC5377846.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance Evaluation of Hologic Panther Aptima System to Detect HBV, HCV, and HIV-1 Infections: A Comparison with Abbott Alinity m System
- Performance Evaluations of the Abbott Alinity m Assay in Comparison with the Abbott m2000 Assay for Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Viruses
- Comparison of the Diagnostic Performance of Elecsys Anti-HCV II and Elecsys and Vitros Anti-HCV Assays
- Performance Evaluation of the Roche Cobas 5800 HBV and HCV Tests: Comparison of the 200 and 500 μL Protocols
- TT Virus Detection Using Different PCR Primer Sets in Healthy and Infected Individuals with Hepatitis B or C Viruses