J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Feb;37(6):e40. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e40.
Sequence Variations of 31 Y-Chromosomal Short Tandem Repeats Analyzed by Massively Parallel Sequencing in Three U.S. Population Groups and Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Graduate School of Medical Science and Brain Korea 21 Project, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e40
Abstract
- Background
Rapidly mutating (RM) Y-chromosomal short tandem repeats (Y-STRs) have been demonstrated to increase the possibility of distinguishing between male relatives due to a higher mutation rate than conventional Y-STRs. Massively parallel sequencing (MPS) can be useful for forensic DNA typing as it allows the detection of sequence variants of many forensic markers. Here, we present sequence variations of 31 Y-STRs including nine RM Y-STRs (DYF387S1, DYF399S1, DYF404S1, DYS449, DYS518, DYS570, DYS576, DYS612, and DYS627), their frequencies, distribution, and the gain in the number of alleles using MPS.
Methods
We constructed a multiplex MPS assay capable of simultaneously amplifying 32 Y-chromosomal markers, producing amplicons ranging from 85–274 bp. Barcoded libraries from 220 unrelated males from four populations—African Americans, Caucasians, Hispanics, and Koreans—were generated via two-step polymerase chain reaction and sequenced on a MiSeq system. Genotype concordance between the capillary electrophoresis (CE) and MPS method and sequence variation of Y-STRs were investigated.
Results
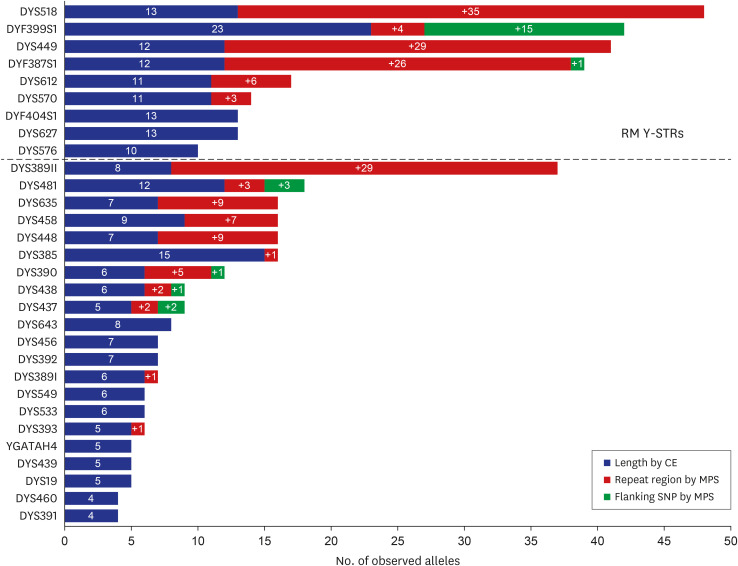
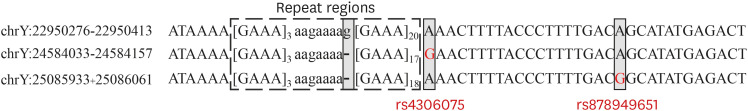
In total, 195 alleles were increased by MPS compared to CE-based alleles (261 to 456). The DYS518 marker showed the largest increase due to repeat region variation (a 3.69-fold increase). The highest increase in the number of alleles due to single nucleotide polymorphisms in the flanking region was found in DYF399S1. RM Y-STRs had more diverse sequences than conventional Y-STRs. Furthermore, null alleles were observed in DYS576 due to primer-binding site mutation, and allele drop-outs in DYS449 resulted from low marker coverage of less than the threshold.
Conclusion
The results suggest that the expanded and discriminative MPS assay could provide more genetic information for Y-STRs, especially for RM Y-STRs, and could advance male individualization. Compiling sequence-based Y-STR data for worldwide populations would facilitate the application of MPS in the field of forensic genetics and could be applicable in solving male-related forensic cases.
Figure
Reference
-
1. de Knijff P, Kayser M, Caglià A, Corach D, Fretwell N, Gehrig C, et al. Chromosome Y microsatellites: population genetic and evolutionary aspects. Int J Legal Med. 1997; 110(3):134–149. PMID: 9228564.2. Jobling MA, Pandya A, Tyler-Smith C. The Y chromosome in forensic analysis and paternity testing. Int J Legal Med. 1997; 110(3):118–124. PMID: 9228562.3. Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C. The human Y chromosome: an evolutionary marker comes of age. Nat Rev Genet. 2003; 4(8):598–612. PMID: 12897772.4. Ballantyne KN, Goedbloed M, Fang R, Schaap O, Lao O, Wollstein A, et al. Mutability of Y-chromosomal microsatellites: rates, characteristics, molecular bases, and forensic implications. Am J Hum Genet. 2010; 87(3):341–353. PMID: 20817138.5. Ballantyne KN, Keerl V, Wollstein A, Choi Y, Zuniga SB, Ralf A, et al. A new future of forensic Y-chromosome analysis: rapidly mutating Y-STRs for differentiating male relatives and paternal lineages. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2012; 6(2):208–218. PMID: 21612995.6. Ballantyne KN, Ralf A, Aboukhalid R, Achakzai NM, Anjos MJ, Ayub Q, et al. Toward male individualization with rapidly mutating Y-chromosomal short tandem repeats. Hum Mutat. 2014; 35(8):1021–1032. PMID: 24917567.7. Bredemeyer S, Roewer L, Willuweit S. Next generation sequencing of Y-STRs in father-son pairs and comparison with traditional capillary electrophoresis. Forensic Sci Res. Forthcoming. 2021; DOI: 10.1080/20961790.2021.1898078.8. Alghafri R, Goodwin W, Ralf A, Kayser M, Hadi S. A novel multiplex assay for simultaneously analysing 13 rapidly mutating Y-STRs. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2015; 17:91–98. PMID: 25884342.9. Adnan A, Ralf A, Rakha A, Kousouri N, Kayser M. Improving empirical evidence on differentiating closely related men with RM Y-STRs: a comprehensive pedigree study from Pakistan. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016; 25:45–51. PMID: 27497645.10. Park MJ, Lee HY, Chung U, Kang SC, Shin KJ. Y-STR analysis of degraded DNA using reduced-size amplicons. Int J Legal Med. 2007; 121(2):152–157. PMID: 17106735.11. Fattorini P, Previderé C, Carboni I, Marrubini G, Sorçaburu-Cigliero S, Grignani P, et al. Performance of the ForenSeqTM DNA Signature Prep kit on highly degraded samples. Electrophoresis. 2017; 38(8):1163–1174. PMID: 28078776.12. Müller P, Sell C, Hadrys T, Hedman J, Bredemeyer S, Laurent FX, et al. Inter-laboratory study on standardized MPS libraries: evaluation of performance, concordance, and sensitivity using mixtures and degraded DNA. Int J Legal Med. 2020; 134(1):185–198. PMID: 31745634.13. Churchill JD, Schmedes SE, King JL, Budowle B. Evaluation of the Illumina® Beta Version ForenSeq™ DNA Signature Prep Kit for use in genetic profiling. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016; 20:20–29. PMID: 26433485.14. Gettings KB, Borsuk LA, Steffen CR, Kiesler KM, Vallone PM. Sequence-based U.S. population data for 27 autosomal STR loci. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2018; 37:106–115. PMID: 30144646.15. Huszar TI, Jobling MA, Wetton JH. A phylogenetic framework facilitates Y-STR variant discovery and classification via massively parallel sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2018; 35:97–106. PMID: 29679929.16. Kim SY, Lee HC, Chung U, Ham SK, Lee HY, Park SJ, et al. Massive parallel sequencing of short tandem repeats in the Korean population. Electrophoresis. 2018; 39(21):2702–2707. PMID: 30084488.17. Kwon SY, Lee HY, Kim EH, Lee EY, Shin KJ. Investigation into the sequence structure of 23 Y chromosomal STR loci using massively parallel sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016; 25:132–141. PMID: 27591816.18. Kwon YL, Kim BM, Lee EY, Shin KJ. Massively parallel sequencing of 25 autosomal STRs including SE33 in four population groups for forensic applications. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1):4701. PMID: 33633141.19. Phillips C, Devesse L, Ballard D, van Weert L, de la Puente M, Melis S, et al. Global patterns of STR sequence variation: sequencing the CEPH human genome diversity panel for 58 forensic STRs using the Illumina ForenSeq DNA Signature Prep Kit. Electrophoresis. 2018; 39(21):2708–2724. PMID: 30101987.20. Purps J, Siegert S, Willuweit S, Nagy M, Alves C, Salazar R, et al. A global analysis of Y-chromosomal haplotype diversity for 23 STR loci. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014; 12(100):12–23. PMID: 24854874.21. Woerner AE, King JL, Budowle B. Fast STR allele identification with STRait Razor 3.0. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2017; 30:18–23. PMID: 28605651.22. Lee EY, Lee HY, Kwon SY, Oh YN, Yang WI, Shin KJ. A multiplex PCR system for 13 RM Y-STRs with separate amplification of two different repeat motif structures in DYF403S1a. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2017; 26:85–90. PMID: 27816850.23. Phillips C, Gettings KB, King JL, Ballard D, Bodner M, Borsuk L, et al. “The devil’s in the detail”: release of an expanded, enhanced and dynamically revised forensic STR sequence guide. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2018; 34:162–169. PMID: 29486434.24. Novroski NM, King JL, Churchill JD, Seah LH, Budowle B. Characterization of genetic sequence variation of 58 STR loci in four major population groups. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2016; 25:214–226. PMID: 27697609.25. Watahiki H, Fujii K, Fukagawa T, Mita Y, Kitayama T, Mizuno N. Polymorphisms and microvariant sequences in the Japanese population for 25 Y-STR markers and their relationships to Y-chromosome haplogroups. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2019; 41:e1–e7. PMID: 30948258.26. Park MJ, Lee HY, Yang WI, Shin KJ. Understanding the Y chromosome variation in Korea--relevance of combined haplogroup and haplotype analyses. Int J Legal Med. 2012; 126(4):589–599. PMID: 22569803.27. Lang M, Liu H, Song F, Qiao X, Ye Y, Ren H, et al. Forensic characteristics and genetic analysis of both 27 Y-STRs and 143 Y-SNPs in Eastern Han Chinese population. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2019; 42:e13–e20. PMID: 31353318.28. Yin C, Su K, He Z, Zhai D, Guo K, Chen X, et al. Genetic reconstruction and forensic analysis of Chinese Shandong and Yunnan Han populations by co-analyzing Y chromosomal STRs and SNPs. Genes (Basel). 2020; 11(7):743.29. Verogen. ForenSeq DNA signature prep reference guide. Updated 2020. Accessed August 2, 2021. https://verogen.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/forenseq-dna-signature-prep-reference-guide-VD2018005-c.pdf .30. Promega. PowerSeq® 46GY system. Updated 2021. Accessed August 2, 2021. https://promega.widen.net/s/zwjslklfvk/alternate-powerseq-46gy-protocol-application-note-an365 .
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Population Genetics of the Hypervariable Locus D12S391 in Korean
- Entire Mitochondrial DNA Sequencing on Massively Parallel Sequencing for the Korean Population
- Instability at Short Tandem Repeats in Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines
- The Study of Epidemiological investigation of Leprosy by Using Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Allele-related Variation in Minisatellite Repeats Involved in Transcription of the ABO Gene in Korean Blood Donors