J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2021 Dec;37(4):268-273. 10.14368/jdras.2021.37.4.268.
Non-surgical root canal treatment of maxillary second premolar fused paramolar tubercle
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Dental Science Research Institute, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Dental Science Research Institute, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2526002
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2021.37.4.268
Abstract
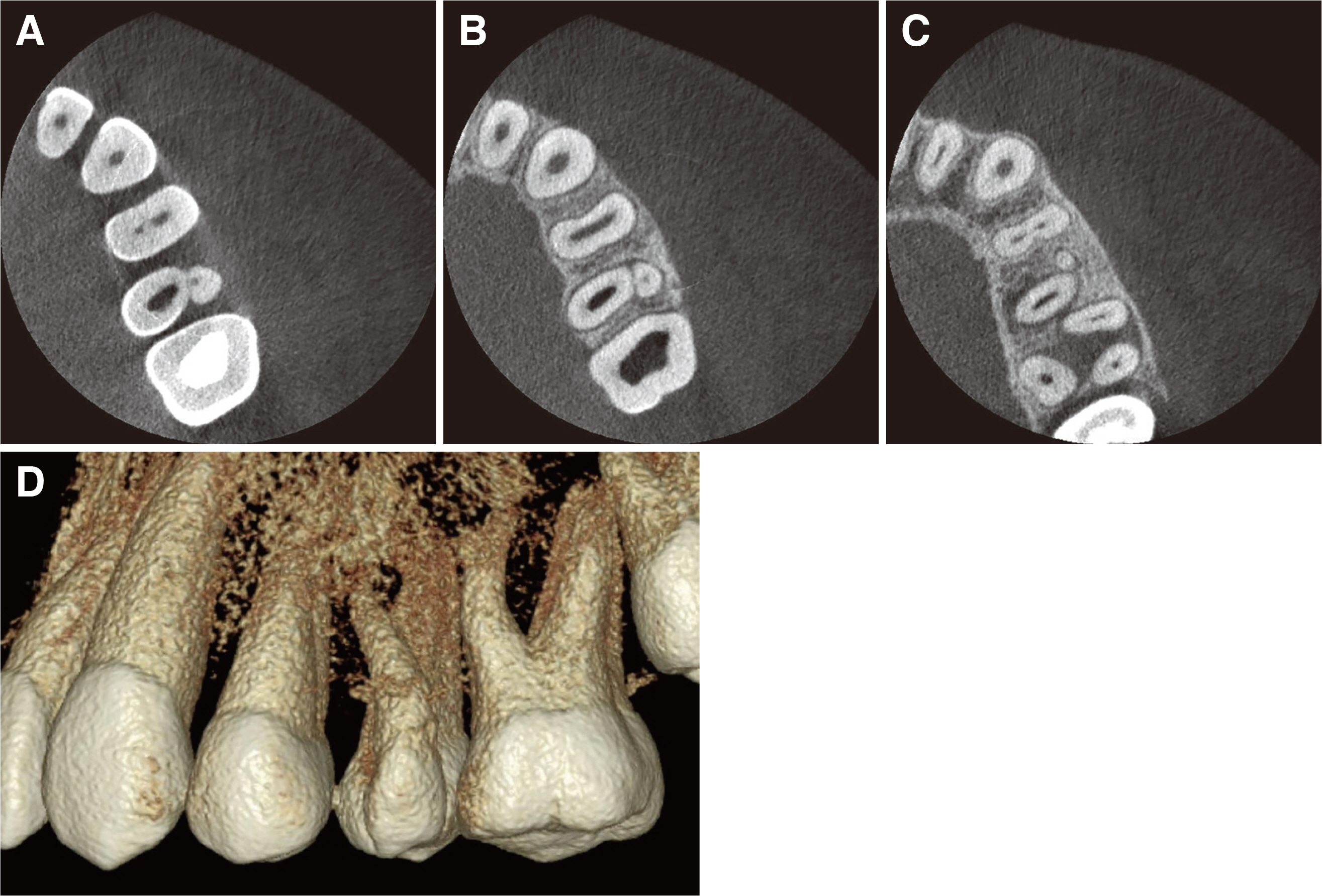
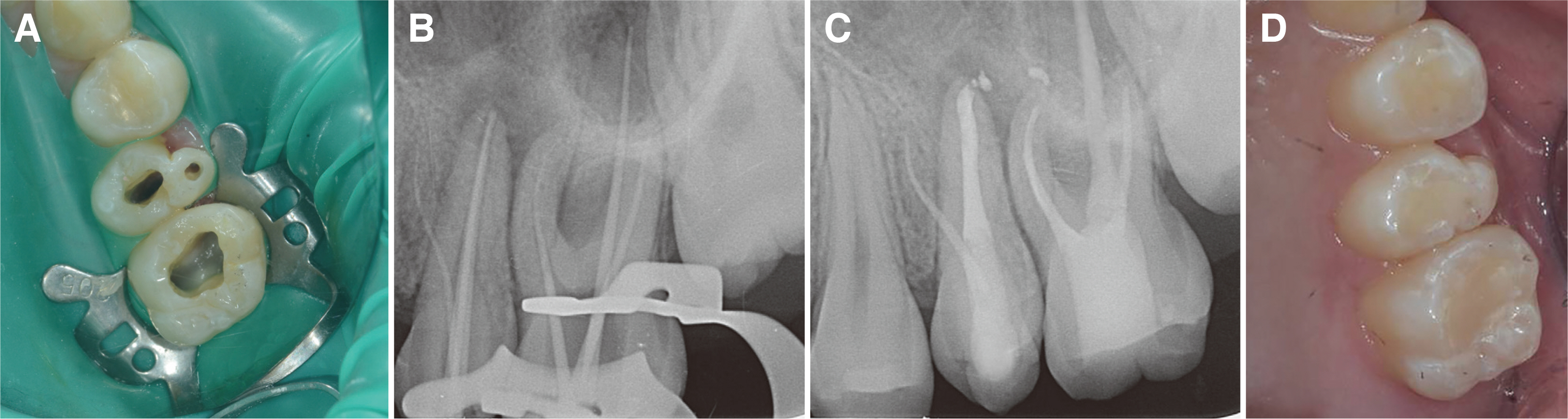
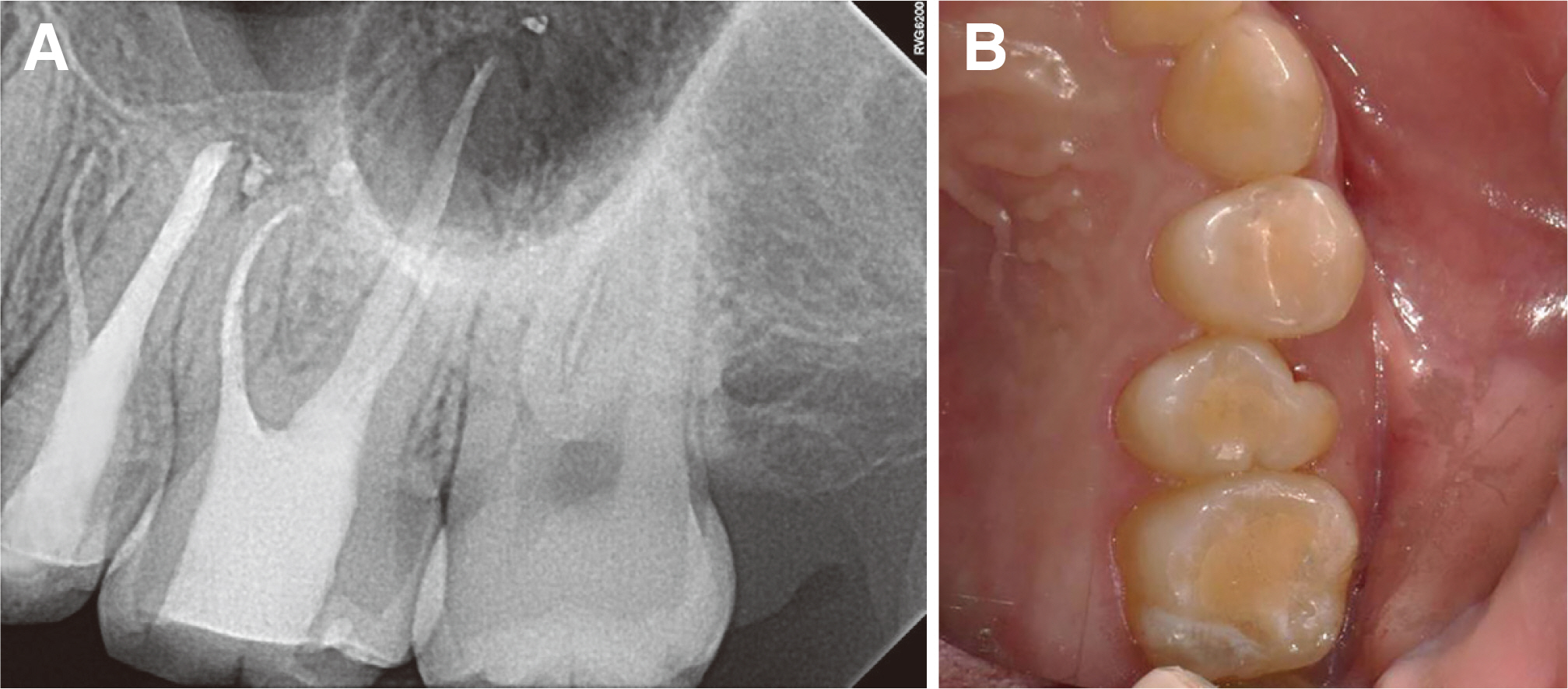
- Paramolar tubercle is a rare developmental dental anomaly defined as an additional cusp occurring on the buccal or lingual sur-faces of the molar. Permanent molar fused with paramolar tubercles can be a cause of difficulty in root canal treatment. Therefore, proper understanding of these variations is important in order to ensure successful endodontic treatment. Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) can be helpful to understand anatomy of complicated cases. This case report describes nonsurgical endodontic treatment of maxillary second premolar fused with paramolar tubercle.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Dahlberg AA. 1950; The evolutionary significance of the protostylid. Am J Phys Anthropol. 8:15–25. DOI: 10.1002/ajpa.1330080110. PMID: 15410861.2. Bolk L. 1916; Problems of human dentition. Am J Ant. 19:91–148. DOI: 10.1002/aja.1000190106.3. Dahlberg AA. 1945; The paramolar tubercle (Bolk). Am J Phys Anthropol. 3:97–103. DOI: 10.1002/ajpa.1330030119.4. Kustaloglu OA. 1962; Paramolar structures of the upper dentition. J Dent Res. 41:75–83. DOI: 10.1177/00220345620410015001.5. Turner RA, Harris EF. 2004; Maxillary second premolars with paramolar tubercles. Dent Anthropol. 17:75–8. DOI: 10.26575/daj.v17i3.150.6. Maglee RE, Kramer S. 1984; The paramolar tubercle: a morphological anomaly with clinical considerations. N Y State Dent J. 50:564–6. PMID: 6594633.7. Friedman S, Stabholz A, Rotstein I. 1986; Endodontic management of molars with developmental anomalies. Int Endod J. 19:267–76. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.1986.tb00490.x. PMID: 3466863.8. Zidan O, El-Deeb M. 1991; Restorative and endodontic management of an anomalous mandibular molar. Quintessence Int. 22:189–92. PMID: 2068257.9. Desai VD, Gaurav I, Das S, Kumar MS. 2014; Paramolar complex-the microdental variations: case series with review of literature. Ann Bioanthropol. 2:65. DOI: 10.4103/2315-7992.153820.10. Patel S, Dawood A, Ford TP, Whaites E. 2017; The potential applications of cone beam computed tomography in the management of endodontic problems. Int Endod J. 40:818–30. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01299.x. PMID: 17697108.11. Scarfe WC, Farman AG. 2008; What is cone-beam CT and how does it work? Dent Clin North Am. 52:707–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.cden.2008.05.005. PMID: 18805225.12. Thomposn BH. 1988; Endodontic theraphy of an unusual maxillary second molar. J Endod. 14:143–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0099-2399(88)80216-4.13. Ohishi K, Ohishi M, Takahashi A, Kido J, Uemura S, Nagata T. 1999; Examination of the roots of paramolar tubercles with computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 88:479–83. DOI: 10.1016/S1079-2104(99)70066-1. PMID: 10519759.14. Jain P, Ananthnarayan K, Ballal S, Natanasabapathy V. 2014; Endodontic management of maxillary second molars fused with paramolar tubercles diagnosed by cone beam computed tomography-two case reports. J Dent (Tehran). 11:726–32. PMID: 25628705. PMCID: PMC4281197.15. Nayak G, Shetty S, Singh I. 2013; Paramolar tubercle: A diversity in canal configuration identified with the aid of spiral computed tomography. Eur J Dent. 7:139–44. PMID: 23408249. PMCID: PMC3571523.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study of Root Canals Morphology in Primary Molars using Computerized Tomography
- Root canal treatment of a mandibular second premolar with three separate root canals
- Fused roots of maxillary molars: characterization and prevalence in a Latin American sub-population: a cone beam computed tomography study
- Cone-beam computed tomography observation of maxillary first premolar canal shapes
- Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of fused teeth with transposition: a case report