J Surg Ultrasound.
2021 May;8(1):6-18. 10.46268/jsu.2021.8.1.6.
Impact of 8-Week Bedside Ultrasound Training for Surgical Residents in the Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Care Hospital - a Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Trauma and Surgical Critical Care, Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.46268/jsu.2021.8.1.6
Abstract
- Purpose
Bedside ultrasound has become one of the most important non-invasive and readily available diagnostic tools, especially for critically ill patients. Despite the increasing usage and importance of bedside ultrasound, a standard and well-structured training program for surgical residents is still lacking. This study assessed and evaluated the effectiveness of our new 8-weeks ultrasound course for surgical residents.
Methods
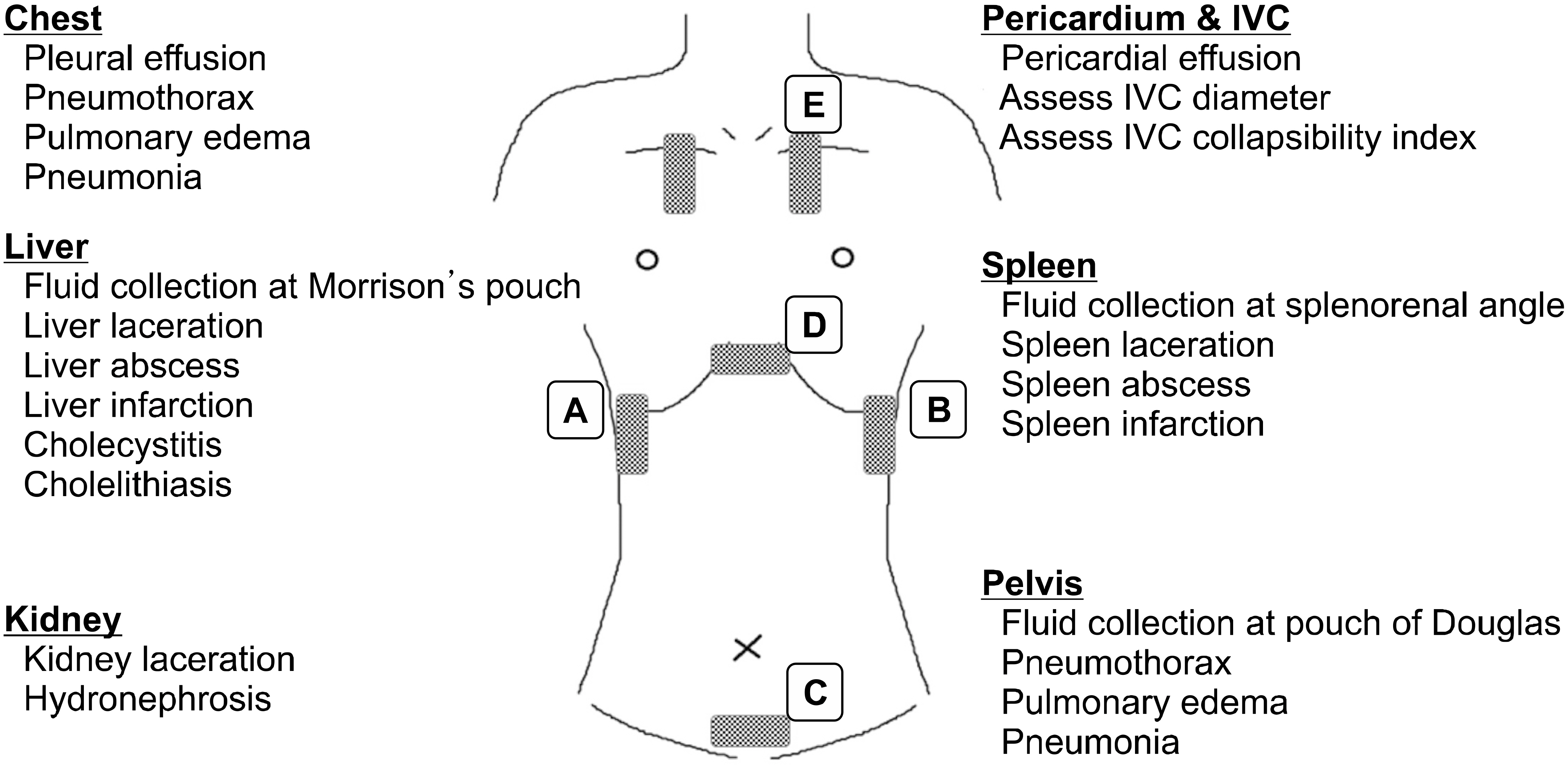
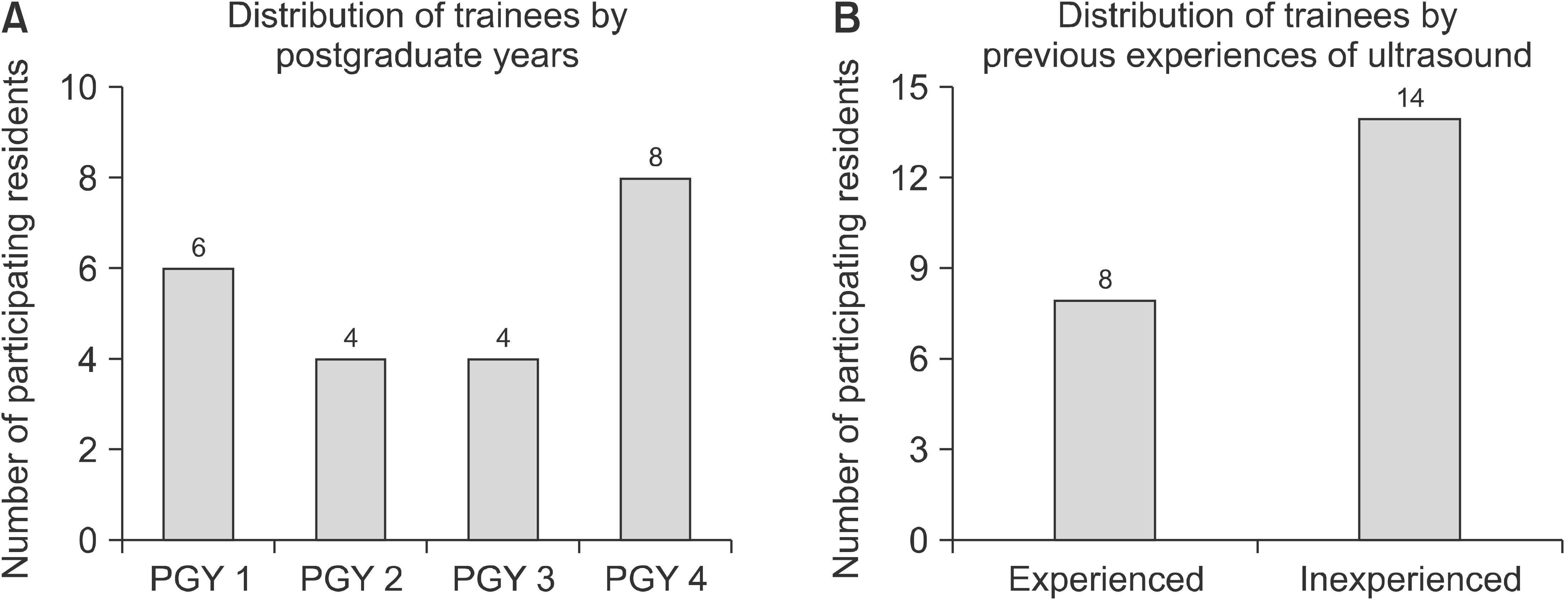
Twenty-two residents from the department of general surgery from a tertiary care hospital in Korea attended the newly designed 8-weeks of bedside ultrasound training course in the surgical intensive care unit. A multimodal approach was used including didactic lectures about the basics of ultrasound as well as daily hands-on ultrasound examinations of patients under the supervision of an instructor. Participants documented their ultrasound findings and determined self-proficiency in ultrasound techniques using a 5-point Likert scale.
Results
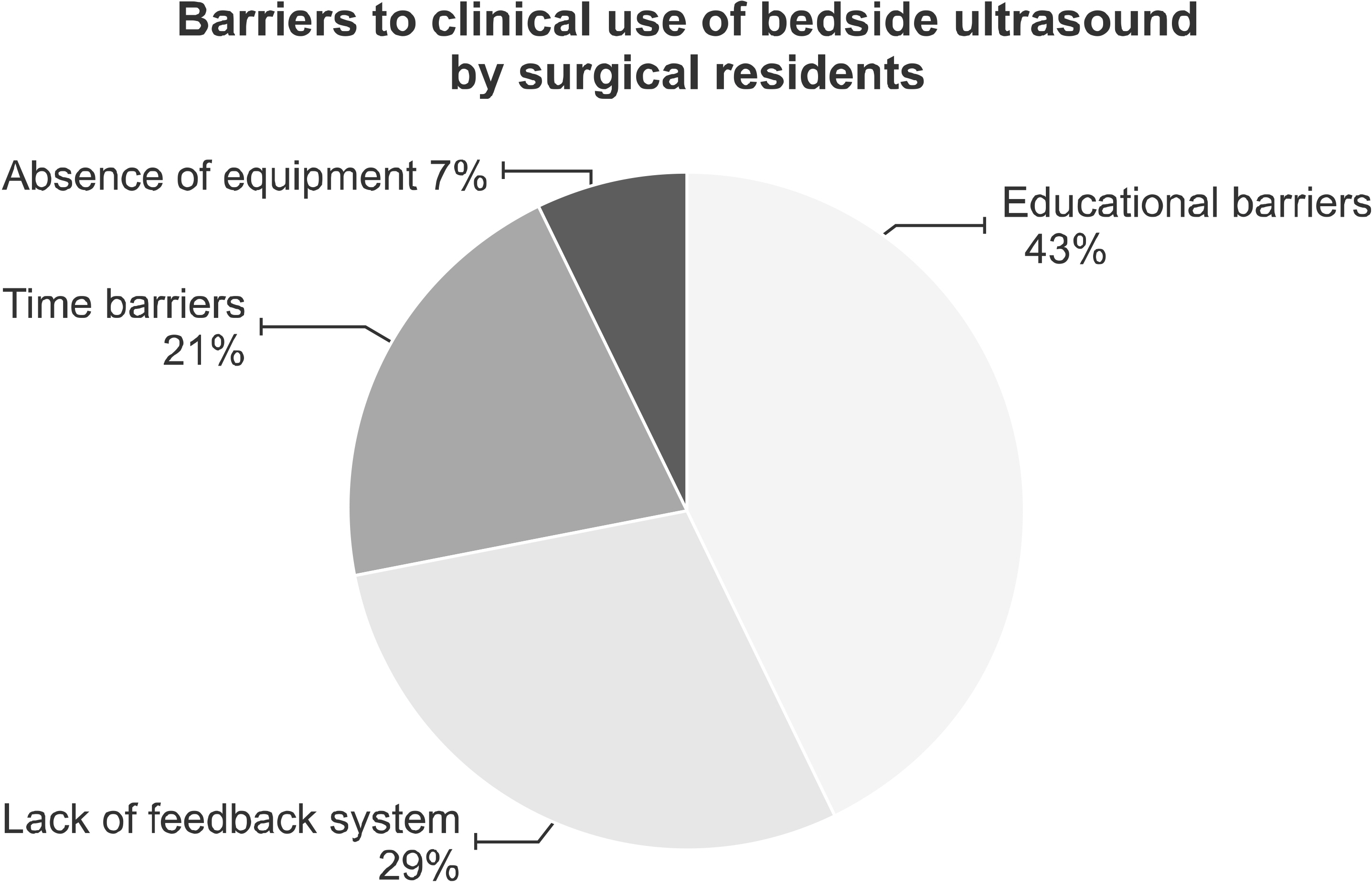
After the educational intervention, the proficiency scores of the residents showed a significant improvement in every element (P < 0.001). Proficiency scores also showed a significant improvement regardless of their previous exposure to ultrasound manipulation. Among the most perceived barriers in using bedside ultrasound were lack of education (43%) and lack of a feedback system (29%).
Conclusion
The confidence of surgical residents in their use of bedside ultrasound could be improved with a well-structured training program. In addition, a short and intense program may help them to overcome the barriers that they may perceive to using bedside ultrasound. The authors believe such programs should be encouraged in all surgical residencies so that residents can competently use bedside ultrasound for the primary care of critically ill patients
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moore CL, Copel JA. 2011; Point-of-care ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 364:749–57. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra0909487. PMID: 21345104.
Article2. Schnittke N, Damewood S. 2019; Identifying and overcoming barriers to resident use of point-of-care ultrasound. West J Emerg Med. 20:918–25. DOI: 10.5811/westjem.2019.8.43967. PMID: 31738719. PMCID: PMC6860390.
Article3. Kim DY, Lee JH, Jung JY, Kwon HS, Chang IW, Kim DK, et al. 2017; Re-evaluation of pediatric emergency ultrasound education for emergency medicine residents. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 28:650–8.4. Beggs AD, Thomas PR. 2013; Point of use ultrasound by general surgeons: review of the literature and suggestions for future practice. Int J Surg. 11:12–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2012.11.014. PMID: 23207511.5. Ghane MR, Gharib M, Ebrahimi A, Saeedi M, Akbari-Kamrani M, Rezaee M, et al. 2015; Accuracy of early rapid ultrasound in shock (RUSH) examination performed by emergency physician for diagnosis of shock etiology in critically ill patients. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 8:5–10. DOI: 10.4103/0974-2700.145406. PMID: 25709245. PMCID: PMC4335159.
Article6. Cevik AA, Noureldin A, El Zubeir M, Abu-Zidan FM. 2018; Assessment of EFAST training for final year medical students in emergency medicine clerkship. Turk J Emerg Med. 18:100–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.tjem.2018.05.004. PMID: 30191188. PMCID: PMC6107923.
Article7. Helling TS, Wilson J, Augustosky K. 2007; The utility of focused abdominal ultrasound in blunt abdominal trauma: a reappraisal. Am J Surg. 194:728–32. discussion 732–3. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.08.012. PMID: 18005762.
Article8. Nassour I, Spalding MC, Hynan LS, Gardner AK, Williams BH. 2017; The surgeon-performed ultrasound: a curriculum to improve residents’ basic ultrasound knowledge. J Surg Res. 213:51–9.
Article9. Rempell JS, Saldana F, DiSalvo D, Kumar N, Stone MB, Chan W, et al. 2016; Pilot point-of-care ultrasound curriculum at Harvard Medical School: early experience. West J Emerg Med. 17:734–40. DOI: 10.5811/westjem.2016.8.31387. PMID: 27833681. PMCID: PMC5102600.
Article10. Lee JH, Kang B, Kwon H, Kim S, Kim JY, Lee JH, et al. 2014; The experience of emergency pediatric ultrasound education course. Pediatr Emerg Med J. 1:34–41. DOI: 10.22470/pemj.2014.1.1.34.
Article11. Kim JS, Cho YS, Kim YS, Ha YR, Kang BS, Chung HS, et al. 2010; Development of an emergency abdominal ultrasound course in Korea: 1-year experience. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 21:382–7.12. Kim BK, Cha JM, Song DS. 2019; How to revitalize the abdominal ultrasonography education program. Korean J Gastroenterol. 73:66–9. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.2.66.
Article13. Choi BI. 2015. Ultrasound Diagnosis of the Abdomen. 3rd ed. Ilchokak;Seoul:14. Martin JA, Regehr G, Reznick R, MacRae H, Murnaghan J, Hutchison C, et al. 1997; Objective structured assessment of technical skill (OSATS) for surgical residents. Br J Surg. 84:273–8. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1997.02502.x. PMID: 9052454.
Article15. Crouch AK, Dawson M, Long D, Allred D, Madsen T. 2010; Perceived confidence in the FAST exam before and after an educational intervention in a developing country. Int J Emerg Med. 3:49–52. DOI: 10.1007/s12245-009-0144-5. PMID: 20414382. PMCID: PMC2850974.
Article16. Pulijala Y, Ma M, Pears M, Peebles D, Ayoub A. 2018; Effectiveness of immersive virtual reality in surgical training- a randomized control trial. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 76:1065–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2017.10.002. PMID: 29104028.17. Fonseca AL, Reddy V, Yoo PS, Gusberg RJ, Longo WE. 2016; Senior surgical resident confidence in performing flexible endoscopy: what can we do differently? J Surg Educ. 73:311–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2015.09.014. PMID: 26531744.
Article18. Happel CS, Lease MA, Nishisaki A, Braga MS. 2015; Evaluating simulation education via electronic surveys immediately following live critical events: a pilot study. Hosp Pediatr. 5:96–100. DOI: 10.1542/hpeds.2014-0091. PMID: 25646203.
Article19. Schroll R, Smith A, Martin MS, Zeoli T, Hoof M, Duchesne J, et al. 2020; Stop the bleed training: rescuer skills, knowledge, and attitudes of hemorrhage control techniques. J Surg Res. 245:636–42. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.08.011. PMID: 31525629.
Article20. Carver TW. 2018; Ultrasound training in surgical critical care fellowship: a survey of program directors. J Surg Educ. 75:1250–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2018.01.017. PMID: 29449161.
Article21. Tolsgaard MG, Todsen T, Sorensen JL, Ringsted C, Lorentzen T, Ottesen B, et al. 2013; International multispecialty consensus on how to evaluate ultrasound competence: a Delphi consensus survey. PLoS One. 8:e57687. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057687. PMID: 23469051. PMCID: PMC3585207.
Article22. Tolsgaard MG. 2018; Assessment and learning of ultrasound skills in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Dan Med J. 65:B5445.23. Celebi N, Griewatz J, Malek NP, Hoffmann T, Walter C, Muller R, et al. 2019; Outcomes of three different ways to train medical students as ultrasound tutors. BMC Med Educ. 19:125. DOI: 10.1186/s12909-019-1556-4. PMID: 31046757. PMCID: PMC6498570.
Article24. Knudsen L, Nawrotzki R, Schmiedl A, Mühlfeld C, Kruschinski C, Ochs M. 2018; Hands-on or no hands-on training in ultrasound imaging: a randomized trial to evaluate learning outcomes and speed of recall of topographic anatomy. Anat Sci Educ. 11:575–91. DOI: 10.1002/ase.1792. PMID: 29683560.
Article25. LoPresti CM, Schnobrich DJ, Dversdal RK, Schembri F. 2019; A road map for point-of-care ultrasound training in internal medicine residency. Ultrasound J. 11:10. DOI: 10.1186/s13089-019-0124-9. PMID: 31359161. PMCID: PMC6638610.
Article26. Williams RJ, Windsor AC, Rosin RD, Mann DV, Crofton M. 1994; Ultrasound scanning of the acute abdomen by surgeons in training. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 76:228–33. PMID: 8074382. PMCID: PMC2502236.27. Trajkovski T, Veillette C, Backstein D, Wadey VM, Kraemer B. 2012; Resident self-assessment of operative experience in primary total knee and total hip arthroplasty: is it accurate? Can J Surg. 55:S153–7. DOI: 10.1503/cjs.035510. PMID: 22854152. PMCID: PMC3432254.
Article28. Arora S, Miskovic D, Hull L, Moorthy K, Aggarwal R, Johannsson H, et al. 2011; Self vs expert assessment of technical and non-technical skills in high fidelity simulation. Am J Surg. 202:500–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.01.024. PMID: 21943950.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bedside ultrasound-guided percutaneous cystostomy in an infant in the neonatal intensive care unit
- Bedside Echocardiography-Based Hemodynamic Assessment in the Intensive Care Unit
- Development of the role of teaching hospitalists in the education of residents
- Factors Influencing Intensive Care Unit Nurses’ Competency in Delirium Care in A Tertiary General Hospital
- Successful neural modulation of bedside modified thoracic epidural anesthesia for ventricular tachycardia electrical storm