Lab Med Online.
2021 Apr;11(2):106-114. 10.47429/lmo.2021.11.2.106.
Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Levels and Thrombin Generation in Hemorrhagic Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525792
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2021.11.2.106
Abstract
- Background
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) regulates blood coagulation. To treat hemorrhagic disease, studies have been conducted to achieve a hemostatic effect by inhibiting TFPI. In this study, blood TFPI levels of healthy and hemorrhagic disease groups were compared, and the effects of blood TFPI level and its activity on coagulation were investigated.
Methods
The blood TFPI levels of the healthy, chronic liver disease (CLD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and hemophilia groups were measured and compared. Thrombin generation assay (TGA) was performed to investigate the effects of TFPI level and its activity on coagulation.
Results
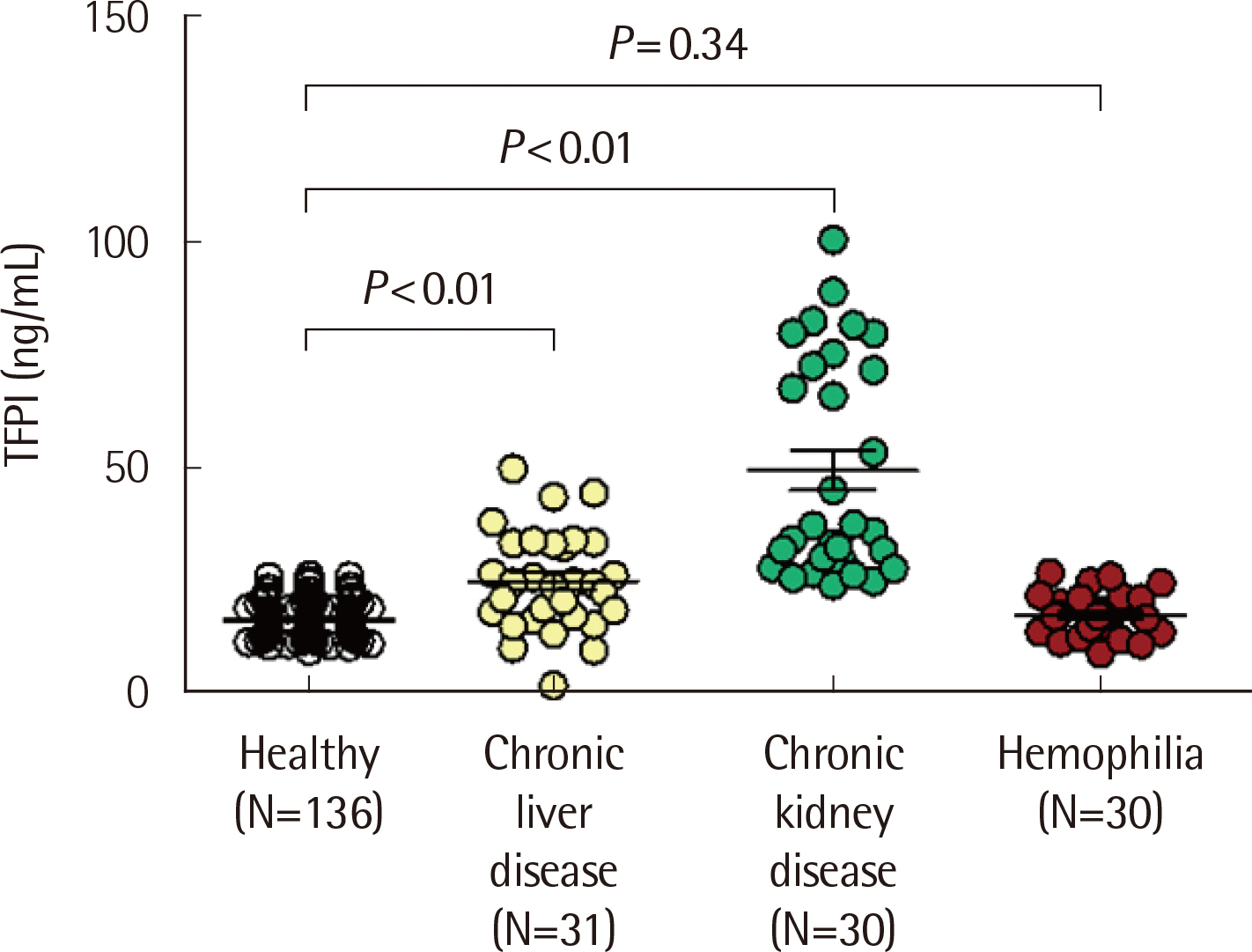
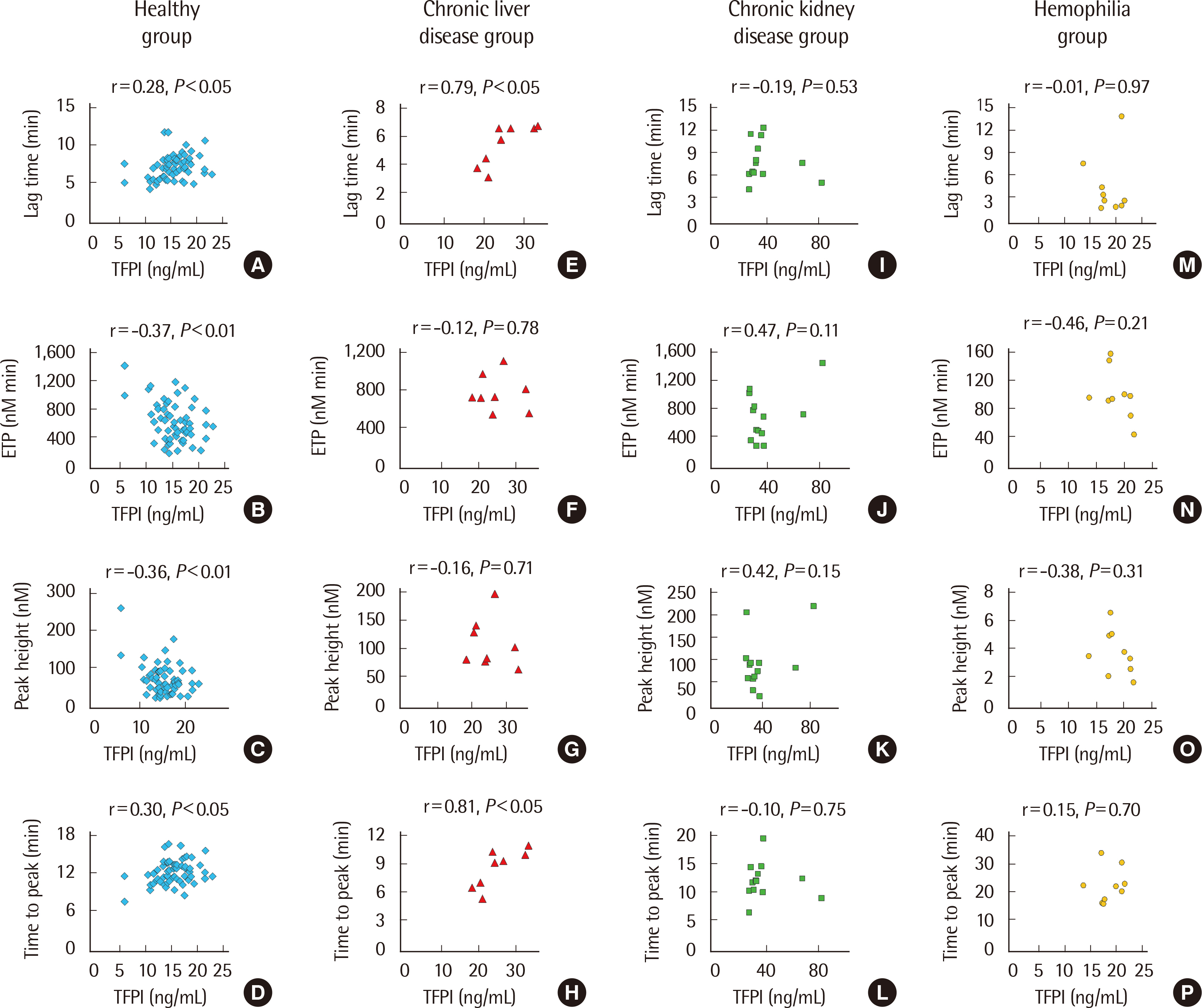
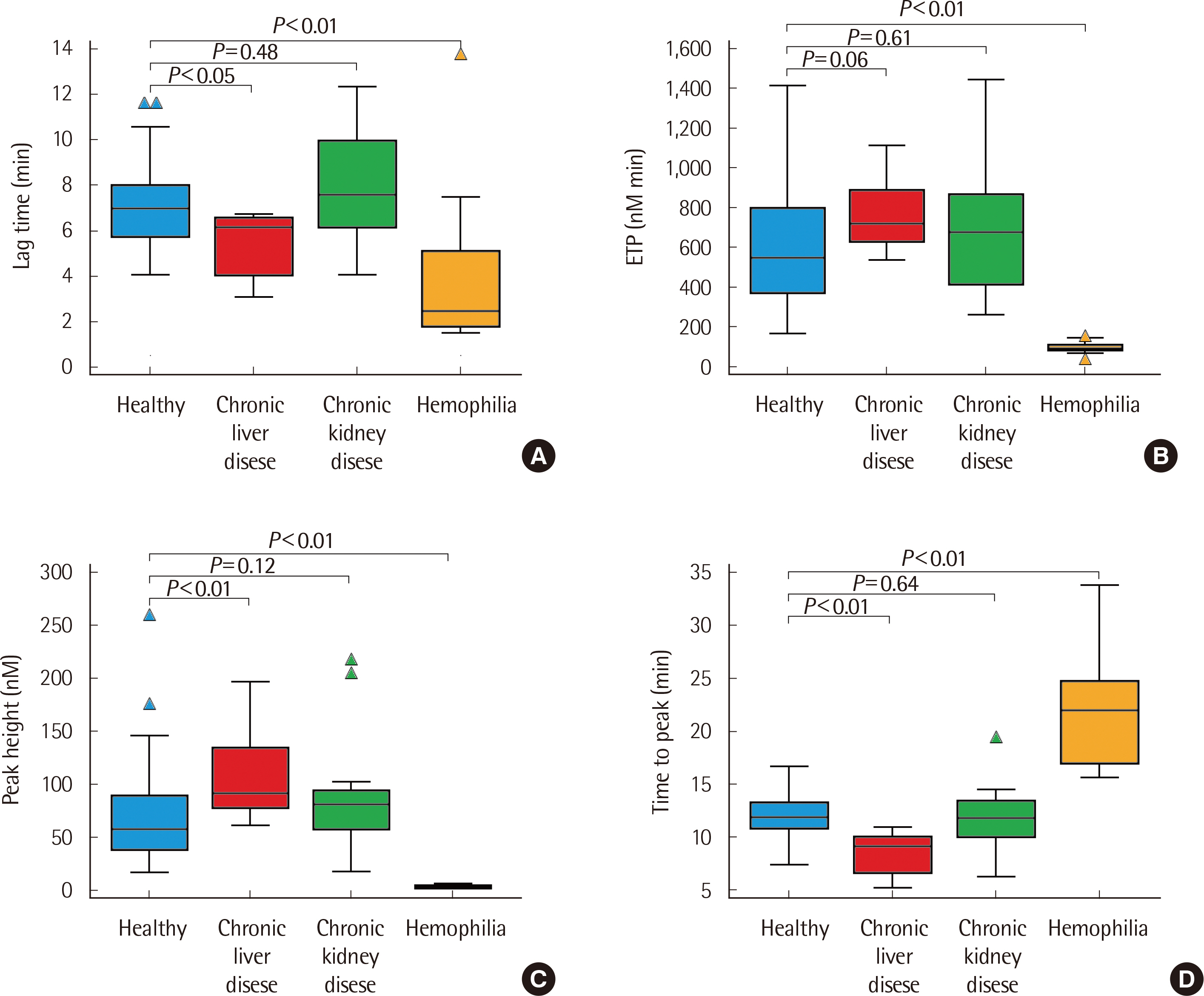
The mean blood TFPI levels of the healthy, CLD, CKD, and hemophilia groups were 16.47 ng/mL, 24.90 ng/mL, 49.47 ng/mL, and 17.35 ng/mL, respectively. The healthy and CLD groups showed correlations between their blood TFPI levels and TGA parameters (P < 0.05). The TGA parameters of the CLD and hemophilia groups showed significant differences compared with those of the healthy group (P < 0.05). In FVIII-deficient plasma with anti-TFPI antibodies, the TGA parameters tended to be normalized according to anti-TFPI antibody levels. However, the differences in TGA parameters caused by FVIII concentration were unclear.
Conclusions
Although the TFPI level was related to bleeding in the disease groups, it is difficult to interpret its effects independently because of the various factors that affect the coagulation process. However, TFPI is worth studying to facilitate the development of a treatment strategy for bleeding due to lack of FVIII.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Crawley JT, Lane DA. 2008; The haemostatic role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:233–42. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.141606. PMID: 17951326.
Article2. Chelle P, Montmartin A, Damien P, Piot M, Cournil M, Lienhart A, et al. 2019; Tissue factor pathway inhibitor is the main determinant of thrombin generation in haemophilic patients. Haemophilia. 25:343–8. DOI: 10.1111/hae.13679. PMID: 30690836.
Article3. Waters EK, Sigh J, Friedrich U, Hilden I, Sørensen BB. 2017; Concizumab, an anti-tissue factor pathway inhibitor antibody, induces increased thrombin generation in plasma from haemophilia patients and healthy subjects measured by the thrombin generation assay. Haemophilia. 23:769–76. DOI: 10.1111/hae.13260. PMID: 28594458.
Article4. Waters EK, Genga RM, Schwartz MC, Nelson JA, Schaub RG, Olson KA, et al. 2011; Aptamer ARC19499 mediates a procoagulant hemostatic effect by inhibiting tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood. 117:5514–22. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-311936. PMID: 21389323.
Article5. Erhardtsen E, Ezban M, Madsen MT, Diness V, Glazer S, Hedner U, et al. 1995; Blocking of tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) shortens the bleeding time in rabbits with antibody induced haemophilia A. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 6:388–94. DOI: 10.1097/00001721-199507000-00004. PMID: 8589204.6. Choi S, Lee S, Kwak H, Song J, Hwang S. 2016; MG1113, Anti-TFPI antibody, efficiently recovers coagulation efficacy through blocking the Kunitz 2 domain of human TFPI. Blood. 128:1406. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V128.22.1406.1406.
Article7. Molnar AO, Bota SE, Garg AX, Harel Z, Lam N, McArthur E, et al. 2016; The risk of major hemorrhage with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:2825–32. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015050535. PMID: 26823554. PMCID: PMC5004646.
Article8. Tripodi A, Mannucci PM. 2011; The coagulopathy of chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 365:147–56. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1011170. PMID: 21751907.
Article9. Magnusson M, Berndtsson M, Fischler B, Petrini P, Schulman S, Renne T, et al. 2015; Thrombin generation test in children and adolescents with chro-nic liver disease. Thromb Res. 135:382–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.11.040. PMID: 25541032.
Article10. Lane DA, Caso R. 1989; Antithrombin: structure, genomic organization, function and inherited deficiency. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 2:961–98. DOI: 10.1016/S0950-3536(89)80054-X. PMID: 2688761.11. Dahlbäck B. 2004; Progress in the understanding of the protein C anticoagulant pathway. Int J Hematol. 79:109–16. DOI: 10.1532/IJH97.03149. PMID: 15005336.
Article12. Mann KG. 2003; Thrombin formation. Chest. 124:4S–10S. DOI: 10.1378/chest.124.3_suppl.4S. PMID: 12970118.
Article13. Kario K, Matsuo T, Yamada T, Matsuo M. 1994; Increased tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels in uremic patients on regular hemodialysis. Thromb Haemost. 71:275–9. DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1642429. PMID: 8029788.
Article14. Gäckler A, Rohn H, Lisman T, Benkö T, Witzke O, Kribben A, et al. 2019; Evaluation of hemostasis in patients with end-stage renal disease. PLoS One. 14:e0212237. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212237. PMID: 30785941. PMCID: PMC6382154.
Article15. Ocak G, van Stralen KJ, Rosendaal FR, Verduijn M, Ravani P, Palsson R, et al. 2012; Mortality due to pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke among incident dialysis patients. J Thromb Haemost. 10:2484–93. DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04921.x. PMID: 22970891.
Article16. Ocak G, Lijfering WM, Verduijn M, Dekker FW, Rosendaal FR, Cannegieter SC, et al. 2013; Risk of venous thrombosis in patients with chronic kidney disease: identification of high-risk groups. J Thromb Haemost. 11:627–33. DOI: 10.1111/jth.12141. PMID: 23433091.
Article17. Gu JM, Patel C, Kauser K. Plasma Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI) Levels in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Hemophilia A and B. https://www.postersessiononline.eu/173580348_eu/congresos/WFH2016/aula/-PP-T_101_WFH2016.pdf.Updated on Jul 2016.18. Haghpanah S, Bazrafshan A, Silavizadeh S, Dehghani J, Afrasiabi A, Karimi M. 2016; Evaluation of thrombin generation assay in patients with hemophilia. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 22:322–6. DOI: 10.1177/1076029614555903. PMID: 25354749.
Article19. Broze GJ Jr, Girard TJ. 2012; Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: structure-function. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:262–80. DOI: 10.2741/3926. PMID: 22201743. PMCID: PMC3692300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Low Molecular Weight Heparin on Plasma Thrombin-Antithrombin Complex and Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
- Thrombin Induced Apoptosis through Calcium-Mediated Activation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in Intestinal Myofibroblasts
- Back to basics: the coagulation pathway
- Activation of the Intrinsic Coagulation Pathway in Patients With Chronic Urticaria
- Optimal Concentration of Thrombin to Activate Platelet for Wound Healing