Clinical presentation of COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- KMID: 2525080
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2020.00108
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is recognized to have variable clinical manifestations. The clinical presentation of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) having COVID-19 is unclear.
Methods
We identified articles reporting about the clinical presentation of COVID-19 in those with underlying IBD from PubMed and Embase. The studies, irrespective of design or language, were included. The overall pooled frequency of various symptoms was estimated. Joanna Briggs Institute Critical appraisal checklist was used to assess the quality of studies.
Results
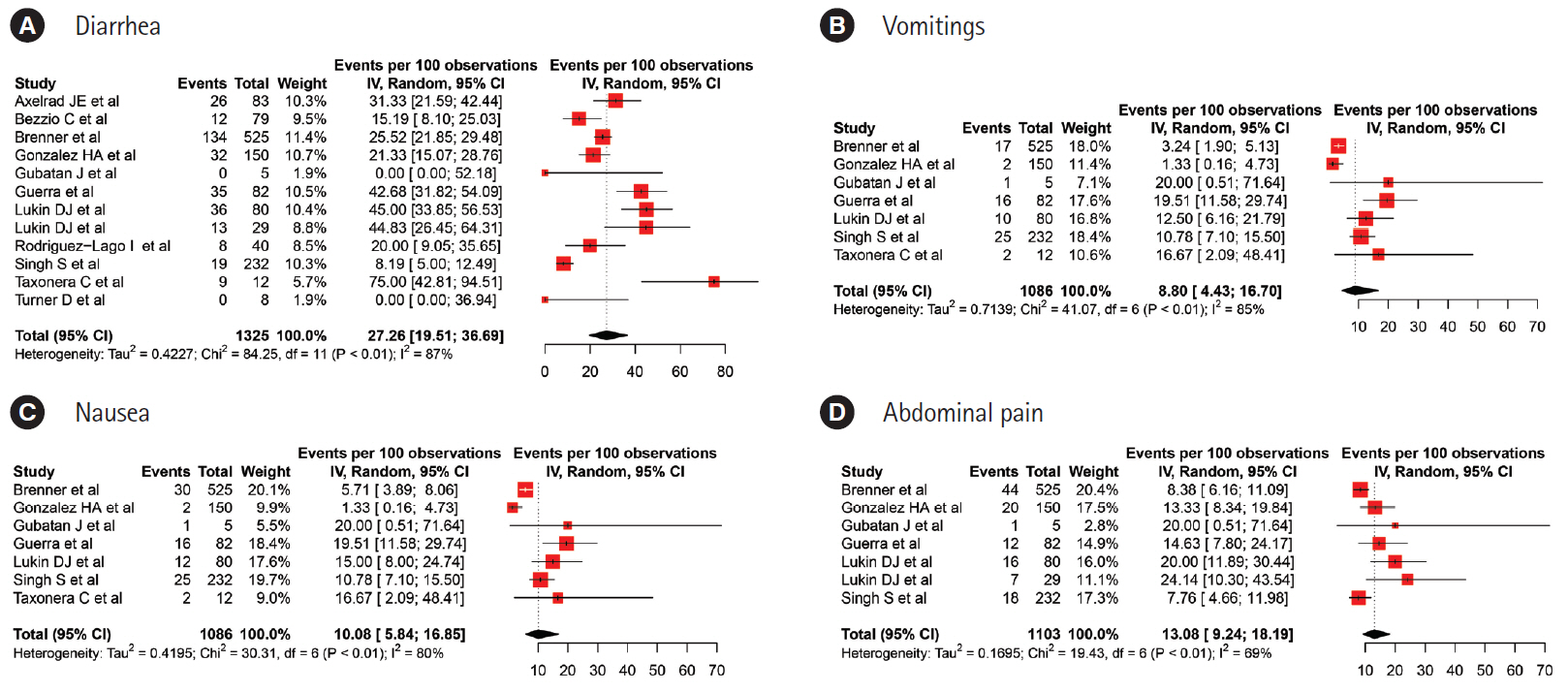
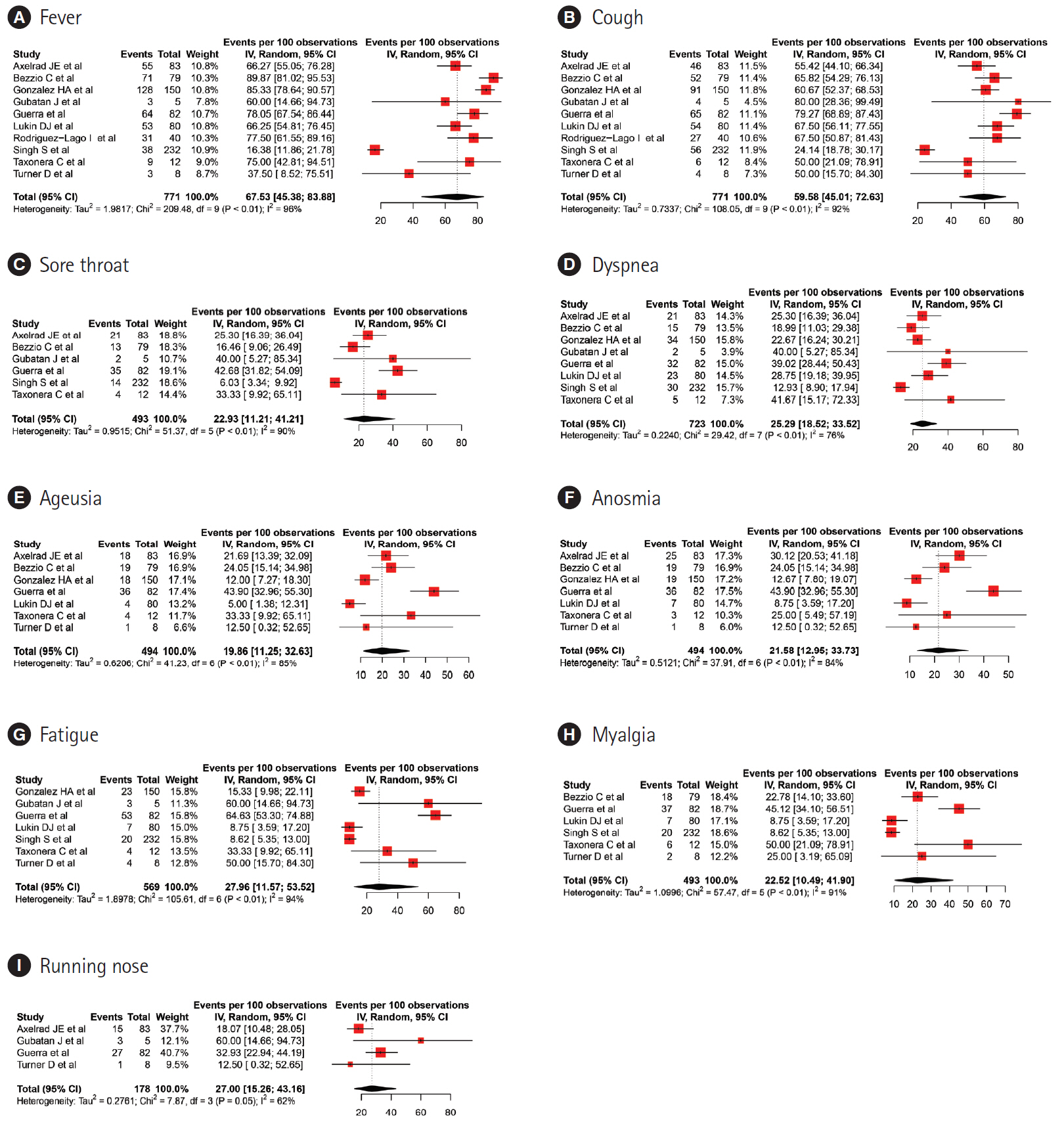
Eleven studies, including 1,325 patients, were included in the pooled analysis. The pooled estimates for clinical presentation were; fever: 67.53% (95% confidence interval [CI], 45.38–83.88), cough: 59.58% (95% CI, 45.01–72.63), diarrhea: 27.26% (95% CI, 19.51–36.69), running nose: 27% (95% CI, 15.26–43.19) and dyspnea: 25.29% (95% CI, 18.52–33.52). The pooled prevalence rates for abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting were 13.08% (95% CI, 9.24–18.19), 10.08% (95% CI, 5.84–16.85) and 8.80% (95% CI, 4.43–16.70) per 100 population, respectively.
Conclusions
The clinical presentation of COVID-19 in IBD patients is similar to the general population.
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
KASID Guidance for Clinical Practice Management of Adult Inflammatory Bowel Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Expert Consensus Statement
Yong Eun Park, Yoo Jin Lee, Ji Young Chang, Hyun Joo Song, Duk Hwan Kim, Young Joo Yang, Byung Chang Kim, Jae Gon Lee, Hee Chan Yang, Miyoung Choi, Seong-Eun Kim, Seung-Jae Myung, The Clinical Practice Guideline Committee of the K Diseases
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2021;78(2):105-116. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2021.112.Clinical Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Korea: a KASID Multicenter Study
Jin Wook Lee, Eun Mi Song, Sung-Ae Jung, Sung Hoon Jung, Kwang Woo Kim, Seong-Joon Koh, Hyun Jung Lee, Seung Wook Hong, Jin Hwa Park, Sung Wook Hwang, Dong-Hoon Yang, Byong Duk Ye, Jeong-Sik Byeon, Seung-Jae Myung, Suk-Kyun Yang, Sang Hyoung Park,
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(48):e336. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e336.Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases guidance for clinical practice of adult inflammatory bowel disease during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: expert consensus statements
Yong Eun Park, Yoo Jin Lee, Ji Young Chang, Hyun Joo Song, Duk Hwan Kim, Young Joo Yang, Byung Chang Kim, Jae Gon Lee, Hee Chan Yang, Miyoung Choi, Seong-Eun Kim, Seung-Jae Myung
Intest Res. 2022;20(4):431-444. doi: 10.5217/ir.2021.00111.
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020 [Internet]. c2020 [cited 2020 Nov 29]. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020.2. Rubin R. COVID-19’s crushing effects on medical practices, some of which might not survive. JAMA. 2020; 324:321–323.
Article3. Bezzio C, Saibeni S, Variola A, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 in 79 patients with IBD in Italy: an IG-IBD study. Gut. 2020; 69:1213–1217.
Article4. Brenner EJ, Ungaro RC, Gearry RB, et al. Corticosteroids, but not TNF antagonists, are associated with adverse COVID-19 outcomes in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: results from an international registry. Gastroenterology. 2020; 159:481–491.
Article5. Axelrad JE, Malter L, Hong S, Chang S, Bosworth B, Hudesman D. From the American Epicenter: coronavirus disease 2019 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in the New York City metropolitan area. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021; 27:662–666.
Article6. Effenberger M, Grabherr F, Mayr L, et al. Faecal calprotectin indicates intestinal inflammation in COVID-19. Gut. 2020; 69:1543–1544.
Article7. Aguila EJT, Cua IHY, Fontanilla JAC, Yabut VLM, Causing MFP. Gastrointestinal manifestations of COVID-19: impact on nutrition practices. Nutr Clin Pract. 2020; 35:800–805.
Article8. Gulati A, Pomeranz C, Qamar Z, et al. A comprehensive review of manifestations of novel coronaviruses in the context of deadly COVID-19 global pandemic. Am J Med Sci. 2020; 360:5–34.
Article9. Munn Z, Moola S, Lisy K, Riitano D, Tufanaru C. Methodological guidance for systematic reviews of observational epidemiological studies reporting prevalence and cumulative incidence data. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2015; 13:147–153.
Article10. Gubatan J, Levitte S, Balabanis T, Patel A, Sharma A, Habtezion A. SARS-CoV-2 testing, prevalence, and predictors of COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in northern California. Gastroenterology. 2020; 159:1141–1144.
Article11. Guerra I, Algaba A, Jiménez L, et al. Incidence, clinical characteristics, and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a single-center study in Madrid, Spain. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021; 27:25–33.
Article12. Lukin DJ, Kumar A, Hajifathalian K, et al. Baseline disease activity and steroid therapy stratify risk of COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2020; 159:1541–1544.
Article13. Rodríguez-Lago I, Ramírez de la Piscina P, Elorza A, Merino O, Ortiz de Zárate J, Cabriada JL. Characteristics and prognosis of patients with inflammatory bowel disease during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in the Basque Country (Spain). Gastroenterology. 2020; 159:781–783.
Article14. Singh S, Khan A, Chowdhry M, Bilal M, Kochhar GS, Clarke K. Risk of severe coronavirus disease 2019 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in the United States: a multicenter research network study. Gastroenterology. 2020; 159:1575–1578.
Article15. Taxonera C, Sagastagoitia I, Alba C, Mañas N, Olivares D, Rey E. 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020; 52:276–283.
Article16. Turner D, Huang Y, Martín-de-Carpi J, et al. Corona virus disease 2019 and paediatric inflammatory bowel diseases: global experience and provisional guidance (March 2020) from the paediatric IBD porto group of European society of paediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020; 70:727–733.
Article17. Luo S, Zhang X, Xu H. Don’t overlook digestive symptoms in patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 18:1636–1637.
Article18. Pan L, Mu M, Yang P, et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020; 115:766–773.
Article19. Zhao Y, Cao Y, Wang S, Cai K, Xu K. COVID-19 and gastrointestinal symptoms. Br J Surg. 2020; 107:e382–e383.
Article20. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020; 323:1061–1069.
Article21. D’Amico F, Baumgart DC, Danese S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Diarrhea during COVID-19 infection: pathogenesis, epidemiology, prevention, and management. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 18:1663–1672.
Article22. D’Amico F, Danese S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Systematic review on inflammatory bowel disease patients with coronavirus disease 2019: it is time to take stock. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 18:2689–2700.
Article23. Mao R, Qiu Y, He JS, et al. Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 5:667–678.
Article24. Cheung KS, Hung IFN, Chan PPY, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hong Kong cohort: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2020; 159:81–95.
Article25. Li LQ, Huang T, Wang YQ, et al. COVID-19 patients’ clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020; 92:577–583.
Article26. Suresh Kumar VC, Mukherjee S, Harne PS, et al. Novelty in the gut: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the gastrointestinal manifestations of COVID-19. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020; 7:e000417.
Article27. Parasa S, Desai M, Thoguluva Chandrasekar V, et al. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal viral shedding in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020; 3:e2011335.28. Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020; 94:91–95.
Article29. Tariq R, Saha S, Furqan F, Hassett L, Pardi D, Khanna S. Prevalence and mortality of COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020; 95:1632–1648.
Article30. Ghayda RA, Lee J, Lee JY, et al. Correlations of clinical and laboratory characteristics of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17:5026.
Article31. Wang H, Qiu P, Liu J, Wang F, Zhao Q. The liver injury and gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with coronavirus disease 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2020; 44:653–661.
Article32. Liu J, Cui M, Yang T, Yao P. Correlation between gastrointestinal symptoms and disease severity in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020; 7:e000437.
Article33. Kumar A, Arora A, Sharma P, et al. Gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations of corona virus disease-19 and their relationship to severe clinical course: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2020; 39:268–284.
Article34. Borges do Nascimento IJ, von Groote TC, O’Mathúna DP, et al. Clinical, laboratory and radiological characteristics and outcomes of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection in humans: a systematic review and series of meta-analyses. PLoS One. 2020; 15:e0239235.
Article35. Qiu P, Zhou Y, Wang F, et al. Clinical characteristics, laboratory outcome characteristics, comorbidities, and complications of related COVID-19 deceased: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020; 32:1869–1878.
Article36. Pormohammad A, Ghorbani S, Baradaran B, et al. Clinical characteristics, laboratory findings, radiographic signs and outcomes of 61,742 patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb Pathog. 2020; 147:104390.
Article37. Zhu J, Zhong Z, Ji P, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of 8697 patients with COVID-19 in China: a meta-analysis. Fam Med Community Health. 2020; 8:e000406.
Article38. Wang F, Wang H, Fan J, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhao Q. Pancreatic injury patterns in patients with coronavirus disease 19 pneumonia. Gastroenterology. 2020; 159:367–370.
Article39. Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT, Navis G, van Goor H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus: a first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J Pathol. 2004; 203:631–637.
Article40. Wu Y, Guo C, Tang L, et al. Prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in faecal samples. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 5:434–435.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How to Cope with COVID-19 in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Predictors of Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- The Prevalence of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in the General Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Single-Arm Meta-Analysis
- Clinical and Laboratory Features of Pediatric Patients with COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Depression in pregnant and postpartum women during COVID-19 pandemic: systematic review and meta-analysis