Incidence comparison of adverse events in patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving different biologic agents: retrospective long-term evaluation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Surgery, Oncology and Gastroenterology (DISCOG), University of Padua, Padua, Italy
- 2NIHR Nottingham Biomedical Research Centre, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust and University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
- 3Nottingham Digestive Diseases Centre, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
- 4Division of Epidemiology and Public Health, School of Medicine, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
- 5Department of Cardio-Thoraco-Vascular Sciences and Public Health, University of Padua, Padua, Italy
- KMID: 2525078
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2021.00037
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Current literature is lacking in studies comparing the incidence of adverse events (AEs) in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) treated with adalimumab (ADA) or vedolizumab (VDZ) in a real-life scenario. Therefore, our primary aim was to compare the AEs occurring in patients taking ADA to those of patients taking VDZ.
Methods
In this single center study, data on AEs from IBD patients who underwent treatment with ADA and VDZ were retrospectively collected. AE rates per 100 person-years were calculated. A Cox regression model was used to estimate the hazard ratios of the AEs between the 2 drugs.
Results
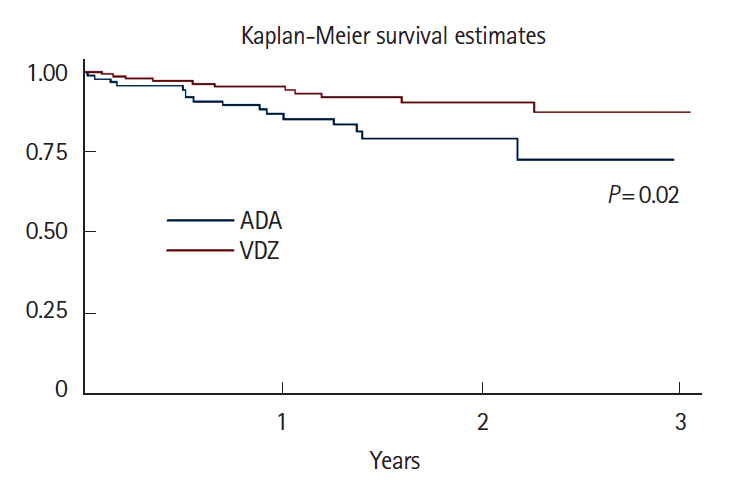
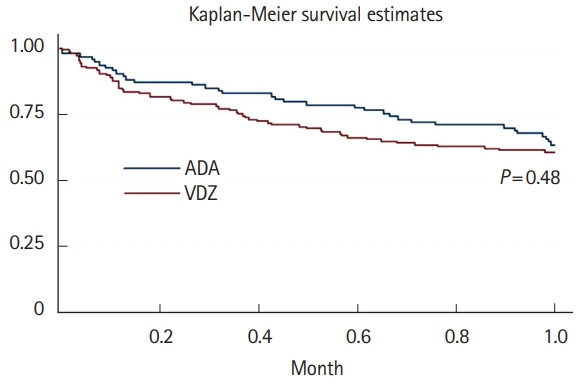
A total of 16 ADA patients (17.2%) and 11 VDZ patients (7.6%) had AEs causing drug interruption during the study period (P=0.02). Most of the AEs were noninfectious extraintestinal events (50% in ADA and 54.5% in VDZ) while infections accounted for 31.2% of the AEs in patients treated with ADA and 27.3% in those treated with VDZ. The incidence rate of AEs causing withdrawal of therapy was 13.2 per 100 person-years for ADA and 5.3 per 100 person-years for VDZ, corresponding to a 76% lower risk in patients in VDZ. Considering the first year of treatment, we observed 34 subjects treated with ADA (36.5%) having at least 1 AEs and 57 (39.3%) among those taking VDZ (P=0.67).
Conclusions
VDZ has a lower incidence rate of AEs causing withdrawal of treatment compared to ADA but a similar risk of AEs not causing drug interruption. Real-life head-to-head studies are still necessary to further explore the safety profile of these drugs.
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Vedolizumab Is Safe and Efficacious for the Treatment of Pediatric-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Who Fail a Primary Biologic Agent
Sujin Choi, Eun Sil Kim, Yiyoung Kwon, Mi Jin Kim, Yon Ho Choe, Byung-Ho Choe, Ben Kang
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(37):e282. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e282.Which biologic agents increase perioperative complications in patients with inflammatory bowel disease?
Jihye Park
Intest Res. 2022;20(1):1-2. doi: 10.5217/ir.2021.00170.Infectious complications in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in Asia: the results of a multinational web-based survey in the 8th Asian Organization for Crohn’s and Colitis meeting
Yu Kyung Jun, Seong-Joon Koh, Dae Seong Myung, Sang Hyoung Park, Choon Jin Ooi, Ajit Sood, Jong Pil Im
Intest Res. 2023;21(3):353-362. doi: 10.5217/ir.2023.00013.Beyond the survey, to the ideal therapy for Asian
Ki Jae Jo, Jong Pil Im
Intest Res. 2023;21(3):280-282. doi: 10.5217/ir.2023.00075.
Reference
-
1. Maaser C, Sturm A, Vavricka SR, et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J Crohns Colitis. 2019; 13:144–164.
Article2. Pineton de Chambrun G, Blanc P, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Current evidence supporting mucosal healing and deep remission as important treatment goals for inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 10:915–927.3. Torres J, Bonovas S, Doherty G, et al. ECCO guidelines on therapeutics in Crohn’s disease: medical treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2020; 14:4–22.
Article4. Barberio B, Black CJ, Savarino EV, Ford AC. Ciclosporin or infliximab as rescue therapy in acute glucorticosteroid-refractory ulcerative colitis: systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis. 2021; 15:733–741.
Article5. Dignass A, Lindsay JO, Sturm A, et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2012; 6:991–1030.
Article6. Nielsen OH, Ainsworth MA. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:754–762.
Article7. Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:2462–2476.
Article8. Sandborn WJ, van Assche G, Reinisch W, et al. Adalimumab induces and maintains clinical remission in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142:257–265.
Article9. Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Marano C, et al. Subcutaneous golimumab maintains clinical response in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:96–109.
Article10. Barberio B, Zingone F, D’Incà R, et al. Infliximab originator, infliximab biosimilar, and adalimumab are more effective in Crohn’s disease than ulcerative colitis: a real-life cohort study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020; 11:e00177.
Article11. Barberio B, Zingone F, Frazzoni L, et al. Real-life comparison of different anti-TNF biologic therapies for ulcerative colitis treatment: a retrospective cohort study. Dig Dis. 2021; 39:16–24.
Article12. Marinelli C, Savarino E, Inferrera M, et al. Factors influencing disability and quality of life during treatment: a cross-sectional study on IBD patients. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019; 2019:5354320.13. Marinelli C, Zingone F, Inferrera M, et al. Factors associated with disability in patients with ulcerative colitis: a cross-sectional study. J Dig Dis. 2020; 21:81–87.14. Marinelli C, Savarino EV, Marsilio I, et al. Sleep disturbance in inflammatory bowel disease: prevalence and risk factors-a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:507.15. Barberio B, Zingone F, Savarino EV. Inflammatory bowel disease and sleep disturbance: as usual, quality matters. Dig Dis Sci. 2021; 66:3–4.
Article16. Bodini G, Giannini EG, De Maria C, et al. Anti-TNF therapy is able to stabilize bowel damage progression in patients with Crohn’s disease: a study performed using the Lémann Index. Dig Liver Dis. 2017; 49:175–180.
Article17. Barberio B, Zamani M, Black CJ, Savarino EV, Ford AC. Prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021; 6:359–370.
Article18. Zingone F, Barberio B, Compostella F, et al. Good efficacy and safety of vedolizumab in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in a real-world scenario. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020; 13:1756284820936536.
Article19. Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Sands BE, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:699–710.
Article20. Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:711–721.21. Scribano ML. Vedolizumab for inflammatory bowel disease: from randomized controlled trials to real-life evidence. World J Gastroenterol. 2018; 24:2457–2467.
Article22. Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, et al. Adalimumab for maintenance of clinical response and remission in patients with Crohn’s disease: the CHARM trial. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:52–65.
Article23. Murdaca G, Spanò F, Puppo F. Selective TNF-α inhibitor-induced injection site reactions. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2013; 12:187–193.
Article24. Cantini F, Niccoli L, Goletti D. Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, and the risk of tuberculosis: data from clinical trials, national registries, and postmarketing surveillance. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2014; 91:47–55.
Article25. Osterman MT, Sandborn WJ, Colombel JF, et al. Increased risk of malignancy with adalimumab combination therapy, compared with monotherapy, for Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:941–949.26. Barberio B, Gubbiotti A, Albertoni L, Ghisa M, Savarino E. Gastrointestinal: an unusual rectal finding in a patient with ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 35:179.
Article27. Shah ED, Farida JP, Siegel CA, Chong K, Melmed GY. Risk for overall infection with anti-TNF and anti-integrin agents used in IBD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017; 23:570–577.
Article28. Card T, Ungaro R, Bhayat F, Blake A, Hantsbarger G, Travis S. Vedolizumab use is not associated with increased malignancy incidence: GEMINI LTS study results and post-marketing data. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020; 51:149–157.29. Kirchgesner J, Lemaitre M, Carrat F, Zureik M, Carbonnel F, Dray-Spira R. Risk of serious and opportunistic infections associated with treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2018; 155:337–346.30. Loftus EV Jr, Feagan BG, Panaccione R, et al. Long-term safety of vedolizumab for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020; 52:1353–1365.
Article31. Sands BE, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Loftus EV Jr, et al. Vedolizumab versus adalimumab for moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:1215–1226.
Article32. Harbord M, Eliakim R, Bettenworth D, et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2017; 11:769–784.
Article33. Renna S, Mocciaro F, Ventimiglia M, et al. A real life comparison of the effectiveness of adalimumab and golimumab in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis, supported by propensity score analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2018; 50:1292–1298.
Article34. Luthra P, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Ford AC. Systematic review and meta-analysis: opportunistic infections and malignancies during treatment with anti-integrin antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 41:1227–1236.
Article35. Chupin A, Perduca V, Meyer A, Bellanger C, Carbonnel F, Dong C. Systematic review with meta-analysis: comparative risk of lymphoma with anti-tumour necrosis factor agents and/or thiopurines in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020; 52:1289–1297.
Article36. Suzuki Y, Motoya S, Hanai H, et al. Four-year maintenance treatment with adalimumab in Japanese patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol. 2017; 52:1031–1040.
Article37. Colombel JF, Jharap B, Sandborn WJ, et al. Effects of concomitant immunomodulators on the pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who had failed conventional therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017; 45:50–62.
Article38. Loftus EV, Reinisch W, Panaccione R, et al. Adalimumab effectiveness up to six years in adalimumab-naïve patients with Crohn’s disease: results of the PYRAMID registry. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019; 25:1522–1531.
Article39. Ogata H, Watanabe M, Matsui T, et al. Safety of adalimumab and predictors of adverse events in 1693 Japanese patients with Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016; 10:1033–1041.
Article40. Moćko P, Kawalec P, Smela-Lipińska B, Pilc A. Effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab for treatment of Crohn’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Med Sci. 2016; 12:1088–1096.
Article41. Colombel JF, Sands BE, Rutgeerts P, et al. The safety of vedolizumab for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2017; 66:839–851.
Article42. Moćko P, Kawalec P, Pilc A. Safety profile of biologic drugs in the therapy of Crohn disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pharmacol Rep. 2016; 68:1237–1243.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases: focusing on biologic agents and new therapies
- Long-Term Response Durability of Infliximab for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Japan: A Single Center Experience
- Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Golimumab for Ulcerative Colitis in a Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center in Japan
- Natural Course of Crohn's Disease and Novel Treatment Drugs
- Biosimilars: concept, current status, and future perspectives in inflammatory bowel diseases