J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Jan;37(4):e30. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e30.
Clinical Characteristics of Atopic Dermatitis in Korean School-Aged Children and Adolescents According to Onset Age and Severity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Childhood Asthma Atopy Center, Humidifier Disinfectant Health Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 7Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- 8Department of Pediatrics, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 9Department of Pediatrics, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 10Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 11Department of Pediatrics, Busan St. Mary’s Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 12Department of Pediatrics, Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Sejong, Korea
- 13Department of Pediatrics, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin, Korea
- 14Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea
- 15Department of Pediatrics, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 16Department of Pediatrics, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 17Department of Pediatrics, CHA Ilsan Hospital, CHA University School of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 18Department of Pediatrics, Inha University Hospital, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2525011
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e30
Abstract
- Background
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a heterogeneous disease with different age of onset, disease course, clinical symptoms, severity, and risk of comorbidity. The characteristics of children with AD also vary by age or country. However, little is known about the clinical characteristics of AD in Korean school-aged children and adolescents. Furthermore, there are few studies on phenotypic differences according to onset age. This study aimed to explore the clinical characteristics and phenotypes according to onset age and severity of AD in children and adolescents in Korea.
Methods
AD patients aged 6–18 years who presented to 18 hospitals nationwide were surveyed. The patients were examined for disease severity by pediatric allergy specialists, and data on history of other allergic diseases, familial allergy history, onset age, trigger factors, lesion sites,treatment history and quality of life were collected. The results of the patient’s allergy test were also analyzed. The patients were classified into infancy-onset (< 2 years of age), preschoolonset (2–5 years of age), and childhood-onset (≥ 6 years of age) groups. Study population was analyzed for clinical features according to onset-age groups and severity groups.
Results
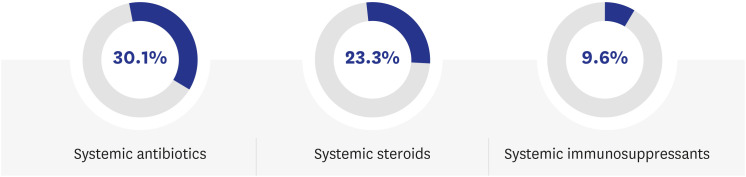
A total of 258 patients with a mean age of 10.62 ± 3.18 years were included in the study. Infancy-onset group accounted for about 60% of all patients and presented significantly more other allergic diseases, such as allergic rhinitis and asthma (P = 0.002 and P = 0.001, respectively). Food allergy symptoms and diagnoses were highly relevant to both earlier onset and more severe group. Inhalant allergen sensitization was significantly associated with both infancy-onset group and severe group (P = 0.012 and P = 0.024, respectively). A family history of food allergies was significantly associated with infancyonset group (P = 0.036). Severe group was significantly associated with a family history of AD, especially a paternal history of AD (P = 0.048 and P = 0.004, respectively). Facial (periorbital, ear, and cheek) lesions, periauricular fissures, hand/foot eczema, and xerosis were associated with infancy-onset group. The earlier the onset of AD, the poorer the quality of life (P = 0.038). Systemic immunosuppressants were used in only 9.6% of the patients in the severe group.
Conclusion
This study analyzed the clinical features of AD in Korean children and adolescents through a multicenter nationwide study and demonstrated the phenotypic differences according to onset age and severity. Considering the findings that the early-onset group is more severe and accompanied by more systemic allergic diseases, early management should be emphasized in young children and infants.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Associations Between Phthalate, Eosinophil, and Aeroallergen Sensitization in Schoolchildren
Jeongsik Yi, Ho-Sang Shin, Man Yong Han, Hee Jin Choi, Mi Seon Lee, Myongsoon Sung
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(45):e391. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e391.
Reference
-
1. Weidinger S, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2016; 387(10023):1109–1122. PMID: 26377142.
Article2. Yang G, Seok JK, Kang HC, Cho YY, Lee HS, Lee JY. Skin barrier abnormalities and immune dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(8):2867.
Article3. Schmidt SA, Olsen M, Schmidt M, Vestergaard C, Langan SM, Deleuran MS, et al. Atopic dermatitis and risk of atrial fibrillation or flutter: A 35-year follow-up study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020; 83(6):1616–1624. PMID: 31442537.
Article4. Jung HJ, Lee DH, Park MY, Ahn J. Cardiovascular comorbidities of atopic dermatitis: using National Health Insurance data in Korea. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021; 17(1):94. PMID: 34551806.
Article5. Abuabara K, Yu AM, Okhovat JP, Allen IE, Langan SM. The prevalence of atopic dermatitis beyond childhood: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Allergy. 2018; 73(3):696–704. PMID: 28960336.
Article6. Ha J, Lee SW, Yon DK. Ten-year trends and prevalence of asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis among the Korean population, 2008–2017. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020; 63(7):278–283. PMID: 32023407.
Article7. Hanifin JM. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980; 92:44–47.8. Roduit C, Frei R, Depner M, Karvonen AM, Renz H, Braun-Fahrländer C, et al. Phenotypes of atopic dermatitis depending on the timing of onset and progression in childhood. JAMA Pediatr. 2017; 171(7):655–662. PMID: 28531273.
Article9. Lewis-Jones MS, Finlay AY. The Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI): initial validation and practical use. Br J Dermatol. 1995; 132(6):942–949. PMID: 7662573.
Article10. Bieber T, D’Erme AM, Akdis CA, Traidl-Hoffmann C, Lauener R, Schäppi G, et al. Clinical phenotypes and endophenotypes of atopic dermatitis: Where are we, and where should we go? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 139(4):4S. S58–S64. PMID: 28390478.
Article11. Saunes M, Øien T, Dotterud CK, Romundstad PR, Storrø O, Holmen TL, et al. Early eczema and the risk of childhood asthma: a prospective, population-based study. BMC Pediatr. 2012; 12(1):168. PMID: 23095804.
Article12. von Kobyletzki LB, Bornehag CG, Hasselgren M, Larsson M, Lindström CB, Svensson Å. Eczema in early childhood is strongly associated with the development of asthma and rhinitis in a prospective cohort. BMC Dermatol. 2012; 12(1):11. PMID: 22839963.
Article13. Carlsten C, Dimich-Ward H, Ferguson A, Watson W, Rousseau R, Dybuncio A, et al. Atopic dermatitis in a high-risk cohort: natural history, associated allergic outcomes, and risk factors. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 110(1):24–28. PMID: 23244654.
Article14. Tran MM, Lefebvre DL, Dharma C, Dai D, Lou WYW, Subbarao P, et al. Predicting the atopic march: Results from the Canadian Healthy Infant Longitudinal Development Study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141(2):601–607 e8. PMID: 29153857.
Article15. Tran MM, Sears MR. Can the atopic march be predicted? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018; 120(2):115–116. PMID: 29413331.
Article16. Brough HA, Nadeau KC, Sindher SB, Alkotob SS, Chan S, Bahnson HT, et al. Epicutaneous sensitization in the development of food allergy: what is the evidence and how can this be prevented? Allergy. 2020; 75(9):2185–2205. PMID: 32249942.
Article17. Beck LA, Leung DY. Allergen sensitization through the skin induces systemic allergic responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 106(5):Suppl. S258–S263. PMID: 11080741.
Article18. Boralevi F, Hubiche T, Léauté-Labrèze C, Saubusse E, Fayon M, Roul S, et al. Epicutaneous aeroallergen sensitization in atopic dermatitis infants - determining the role of epidermal barrier impairment. Allergy. 2008; 63(2):205–210. PMID: 18186810.
Article19. Tham EH, Rajakulendran M, Lee BW, Van Bever HP. Epicutaneous sensitization to food allergens in atopic dermatitis: What do we know? Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2020; 31(1):7–18. PMID: 31541586.
Article20. Deckers J, Sichien D, Plantinga M, Van Moorleghem J, Vanheerswynghels M, Hoste E, et al. Epicutaneous sensitization to house dust mite allergen requires interferon regulatory factor 4-dependent dermal dendritic cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 140(5):1364–1377.e2. PMID: 28189772.
Article21. Schoos AM, Chawes BL, Bønnelykke K, Stokholm J, Rasmussen MA, Bisgaard H. Increasing severity of early-onset atopic dermatitis, but not late-onset, associates with development of aeroallergen sensitization and allergic rhinitis in childhood. Allergy. 2021; 00:1–9.
Article22. Zhang Z, Li H, Zhang H, Cheng R, Li M, Huang L, et al. Factors associated with persistence of early-onset atopic dermatitis up to the age of 12 years: a prospective cohort study in China. Eur J Dermatol. 2021; 31(3):403–408. PMID: 34309525.
Article23. Tham EH, Leung DY. Mechanisms by which atopic dermatitis predisposes to food allergy and the atopic march. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019; 11(1):4–15. PMID: 30479073.
Article24. Jun M, Wang HY, Lee S, Choi E, Lee H, Choi EH. Differences in genetic variations between treatable and recalcitrant atopic dermatitis in Korean. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10(3):244–252. PMID: 29676071.
Article25. Güngör D, Nadaud P, LaPergola CC, Dreibelbis C, Wong YP, Terry N, et al. Infant milk-feeding practices and food allergies, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and asthma throughout the life span: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019; 109(Suppl 7):772S–799S. PMID: 30982870.
Article26. Silverberg JI, Vakharia PP, Chopra R, Sacotte R, Patel N, Immaneni S, et al. Phenotypical differences of childhood- and adult-onset atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018; 6(4):1306–1312. PMID: 29133223.
Article27. Yew YW, Thyssen JP, Silverberg JI. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the regional and age-related differences in atopic dermatitis clinical characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019; 80(2):390–401. PMID: 30287309.
Article28. Silverberg JI, Margolis DJ, Boguniewicz M, Fonacier L, Grayson MH, Ong PY, et al. Distribution of atopic dermatitis lesions in United States adults. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019; 33(7):1341–1348. PMID: 30883885.
Article29. Son JH, Chung BY, Kim HO, Park CW. Clinical features of atopic dermatitis in adults are different according to onset. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32(8):1360–1366. PMID: 28665074.
Article30. Kim KH, Hwang JH, Park KC. Periauricular eczematization in childhood atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996; 13(4):278–280. PMID: 8844743.
Article31. Kim DH, Li K, Seo SJ, Jo SJ, Yim HW, Kim CM, et al. Quality of life and disease severity are correlated in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27(11):1327–1332. PMID: 23166413.
Article32. Ferrucci SM, Tavecchio S, Angileri L, Surace T, Berti E, Buoli M. Factors associated with affective symptoms and quality of life in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021; 101(11):adv00590. PMID: 34518893.
Article33. Maksimović N, Janković S, Marinković J, Sekulović LK, Zivković Z, Spirić VT. Health-related quality of life in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol. 2012; 39(1):42–47. PMID: 22044078.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Effect of Topical Diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP) Therapy in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis in Children and Adolescents
- Update on management of pediatric atopic dermatitis
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability
- Relationship between Allergen Sensitization and Frequency of Asthma in Preschool Atopic Dermatitis Children
- The Effect of Antigen Sensitization and Development of Respiratory Allergy Disease on Severity of Atopic Dermatitis