Korean J Women Health Nurs.
2021 Nov;27(4):318-325. 10.4069/kjwhn.2021.12.12.
Abdominal skin subcutaneous fat thickness over the gestational period in Korean pregnant women: a descriptive observational study
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Woosuk University, Wanju, Korea
- KMID: 2524351
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2021.12.12
Abstract
- Purpose
Although insulin is usually injected into the abdominal subcutaneous fat, in pregnancy women tend to avoid abdominal injections due to concern about fetal damage. Prior studies have been limited to only measuring skin-subcutaneous fat thickness (S-ScFT) at one site at specific pregnancy points. This study aimed to measure S-ScFT across several abdominal sites and over the gestational period in Korean pregnant women. This can identify which site would be relatively safe for subcutaneous injection during pregnancy.
Methods
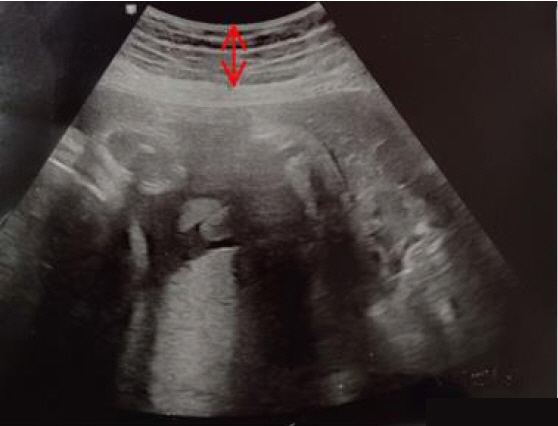
Healthy women over 24 weeks of pregnancy in Korea were invited to voluntarily participate in this descriptive study. For the 142 women, S-ScFT of 12 sites in the abdomen were measured by ultrasound, several times over the pregnancy. Each incidence was treated as a case and a total of 262 cases were analyzed.
Results
The mean S-ScFT during pregnancy was 1.14±0.47 cm (1.25±0.54 cm at 24+0–27+6 weeks; 1.17±0.48 cm at 28+0–31+6 weeks; 1.09+0.40 cm at 32+0–35+6 weeks; and 1.06±0.47 cm at 36+0–40 weeks of pregnancy). Most S-ScFT were thicker than 10 mm. But S-ScFTs in the lateral abdomen and some sites were suboptimal (<6 mm), especially in the pre-pregnancy underweight body mass index group, who had a high rate of suboptimal thickness (27.1% overall and 33.9% in the lateral side).
Conclusion
The whole abdomen seems to be appropriate for subcutaneous injection in most pregnant Korean women, with a 4 to 5-mm short needle. However, for the lateral abdomen, making the skin fold might be needed for fetal safety.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. American Diabetes Association. Management of diabetes in pregnancy: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43(Suppl 1):S183–S192. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-S014.2. Brawerman GM, Dolinsky VW. Therapies for gestational diabetes and their implications for maternal and offspring health: Evidence from human and animal studies. Pharmacol Res. 2018; 130:52–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.02.002.
Article3. Sim KH, Hwang MS, Kim SY, Lee HM, Chang JY, Lee MK. The appropriateness of the length of insulin needles based on determination of skin and subcutaneous fat thickness in the abdomen and upper arm in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38(2):120–133. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.2.120.
Article4. Berard L, Desrochers F, Hagerty D, MacNeill G, Roscoe R. FIT Forum for Injection Technique Canada: Recommendations for Best Practice in Injection Technique. 2nd ed. Franklin Lakes, NJ: Becton, Dickinson and Company;2015.5. Frid AH, Hirsch LJ, Menchior AR, Morel DR, Strauss KW. Worldwide injection technique questionnaire study: injecting complications and the role of the professional. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016; 91(9):1224–1230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.06.012.
Article6. Kennedy N, Quinton A, Brown C, Peek MJ, Benzie R, Nanan R. Changes in maternal abdominal subcutaneous fat layers using ultrasound: a longitudinal study. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2017; 11(6):655–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2017.10.003.
Article7. Hirsch L, Byron K, Gibney M. Intramuscular risk at insulin injection sites--measurement of the distance from skin to muscle and rationale for shorter-length needles for subcutaneous insulin therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014; 16(12):867–873. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2014.0111.
Article8. Hofman PL, Derraik JG, Pinto TE, Tregurtha S, Faherty A, Peart JM, et al. Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(9):1940–1944. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-0871.
Article9. Chen L, Xing Q, Li J, Zhou J, Yuan Y, Wan Y, et al. Injection technique education in patients with diabetes injecting insulin into areas of lipohypertrophy: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Ther. 2021; 12(3):813–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-021-01013-1.
Article10. Kim C, Yang SH, Kim JH. Evaluation of gestational diabetes mellitus risk factors using abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness for early pregnancy in the US imaging. J Radiol Sci Technol. 2017; 40(1):35–40. https://doi.org/10.17946/JRST.2017.40.1.06.
Article11. Eley V, Sekar R, Chin A, Donovan T, Krepska A, Lawrence M, et al. Increased maternal abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness and body mass index are associated with increased cesarean delivery: a prospective cohort study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019; 98(2):196–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/aogs.13486.
Article12. Yang SH, Kim C, An HS, An H, Lee JS. Prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant Korean women based on abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness as measured by ultrasonography. Diabetes Metab J. 2017; 41(6):486–491. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.486.
Article13. Selovic A, Sarac J, Missoni S. Changes in adipose tissue distribution during pregnancy estimated by ultrasonography. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016; 29(13):2131–2137. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2015.1077220.
Article14. Kilpatrick SJ; American Academy of Pediatrics; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Guidelines for perinatal care. 8th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; Washington, DC: The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; 2017.15. Seo MH, Lee WY, Kim SS, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim KK, et al. 2018 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guideline for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019; 28(1):40–45. https://doi.org/10.7570/jomes.2019.28.1.40.
Article16. A clinical & statistical study on the presentation & position of fetus. Korean Nurs. 1966; 5(5):35–39.17. Gibney MA, Arce CH, Byron KJ, Hirsch LJ. Skin and subcutaneous adipose layer thickness in adults with diabetes at sites used for insulin injections: implications for needle length recommendations. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010; 26(6):1519–1530. https://doi.org/10.1185/03007995.2010.481203.
Article18. Choi DW, Sohng KY, Kim BS. Prediction of optimal gluteal intramuscular needle length by skinfold thickness measurements in Korean adults. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2010; 40(6):844–851. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.6.844.
Article19. Jain SM, Pandey K, Lahoti A, Rao PK. Evaluation of skin and subcutaneous tissue thickness at insulin injection sites in Indian, insulin naïve, type-2 diabetic adult population. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 17(5):864–870. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.117249.
Article20. Ludescher B, Rommel M, Willmer T, Fritsche A, Schick F, Machann J. Subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness in adults - correlation with BMI and recommendations for pen needle lengths for subcutaneous self-injection. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2011; 75(6):786–790. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04132.x.
Article21. Choi HM. Perinatal outcomes associated with prepregnancy body mass index and weight gain during pregnancy. Korea J Obstet Gynecol. 2010; 53(11):981–987. https://doi.org/10.5468/kjog.2010.53.11.981.
Article22. Kim MJ, Lee SK, Lee JA, Lee PR, Park HS. Risk factors for gestational diabetes mellitus in Korean women. Korean J Obes. 2013; 22(2):85–93. https://doi.org/10.7570/kjo.2013.22.2.85.
Article23. Kim YK, Han MS. The usefulness of visceral fat thickness measured by ultrasonography as an abdominal obesity index. J Radiol Sci Technol. 2008; 31(3):249–257.24. Yun SH, Han SW, Lee SH, Jeong YW, Kim EH. Comparison of obstetric and neonatal outcomes according to oral glucose challenge test in Korean pregnant women. Korean J Perinatol. 2013; 24(3):180–186. https://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2013.24.3.180.
Article25. Park YJ, Ahn YJ, Han SH, Park JS, Kim TH. Is a maternal prepregnancy weight effective in the pattern of labor progression of nulliparous women? Korean J Obes. 2008; 17(3):117–123.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thickness of Rectus Abdominis Muscle and Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Tissue in Adult Women: Correlation with Age, Pregnancy, Laparotomy, and Body Mass Index
- Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Korean Women Based on Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness as Measured by Ultrasonography
- Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness Measured by Ultrasonography Correlates with Hyperlipidemia and Steatohepatitis in Obese Children
- Fetal Hyperinsulinemia and Ultrasonographic Measurement of Fetal Growth in Pregnancy Complicated by Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Comparative Analysis of Subcutaneous Thickness of Each Compartment of Abdomen & the Selection of Cannula Insertion Site in Liposuction