J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Jan;37(2):e16. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e16.
Impact of Social Distancing on Intussusception Incidence in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2524289
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e16
Abstract
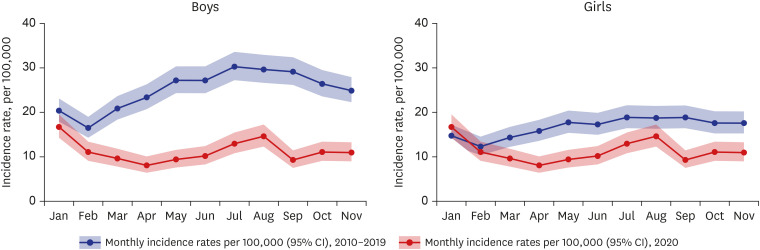
- Following nonpharmaceutical intervention (NPI) to mitigate coronavirus disease 2019 has led to drastic reduction in incidence of communicable disease. Intussusception is commonly preceded by infectious pathogens. Indirect effect from NPI implementation on incidence of intussusception has not been understood fully. We conducted a cohort study to estimate the impact of NPI on incidence of intussusception in Korean children. The net risk ratio of intussusception incidence for 2020 compared to 2010–2019 was 0.53 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.43–0.64) for boys and 0.56 (95% CI, 0.44–0.71) for girls (P for difference = 0.017). Our study showed an association between NPI implementation and reduction of intussusception incidence, with more profound reduction in boys compared to girls.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Impact of COVID-19 on Clinicopathological Spectrum of Pityriasis Rosea in Korea
Dai Hyun Kim, Jun Hyuk Cho, Sung Jin Park, Soo Hong Seo, Hyo Hyun Ahn
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(24):e190. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e190.
Reference
-
1. Burnett E, Parashar UD, Tate JE. Associations of intussusception with adenovirus, rotavirus, and other pathogens: a review of the literature. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020; 39(12):1127–1130. PMID: 33060518.
Article2. Zheng J, Ye Y, Liao Y, Wang B. Fewer paediatric intussusception cases during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Paediatr Child Health. 2020; 56(7):1165.
Article3. Brown CM, Vostok J, Johnson H, Burns M, Gharpure R, Sami S, et al. Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 infections, including COVID-19 vaccine breakthrough infections, associated with large public gatherings - Barnstable County, Massachusetts, July 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021; 70(31):1059–1062. PMID: 34351882.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes in the Incidence of Intussusception and Infectious Diseases After the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea
- Decrease in Incidence of Febrile Seizure following Social Distancing Measures: A National Cohort Study in South Korea
- Changes in cardiovascular-related health behaviors after the end of social distancing: the 2023 Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Awareness Survey
- Impact of COVID-19 on the Incidence of Fragility Fracture in South Korea
- A Comparison of the Perception of and Adherence to the COVID-19 Social Distancing Behavior Guidelines among Health Care Workers, Patients, and General Public