Blood Res.
2021 Dec;56(4):279-284. 10.5045/br.2021.2021116.
Treatment of adult Burkitt lymphoma with the CALGB 1002 protocol: a single center experience in Jordan
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Oncology, King Hussein Cancer Center, Amman, Jordan
- KMID: 2524087
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2021.2021116
Abstract
- Background
The treatment of adult Burkitt lymphoma with pediatric-based chemotherapy protocols usually results in high cure rates, although with significant toxicity. We report our experience with the Cancer and Leukemia Group B1002 (CALGB 1002) protocol.
Methods
The files of adult patients diagnosed with Burkitt lymphoma and treated with the CALGB 1002 protocol at King Hussein Cancer Center between 2008 and 2017 were reviewed. Baseline demographics, clinical laboratory features, treatment details, and responses were collected. The correlations between clinical and laboratory variables with event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) were determined by univariate and multivariate analyses using backward stepwise Cox regression models. EFS and OS were plotted using Kaplan‒Meier curves.
Results
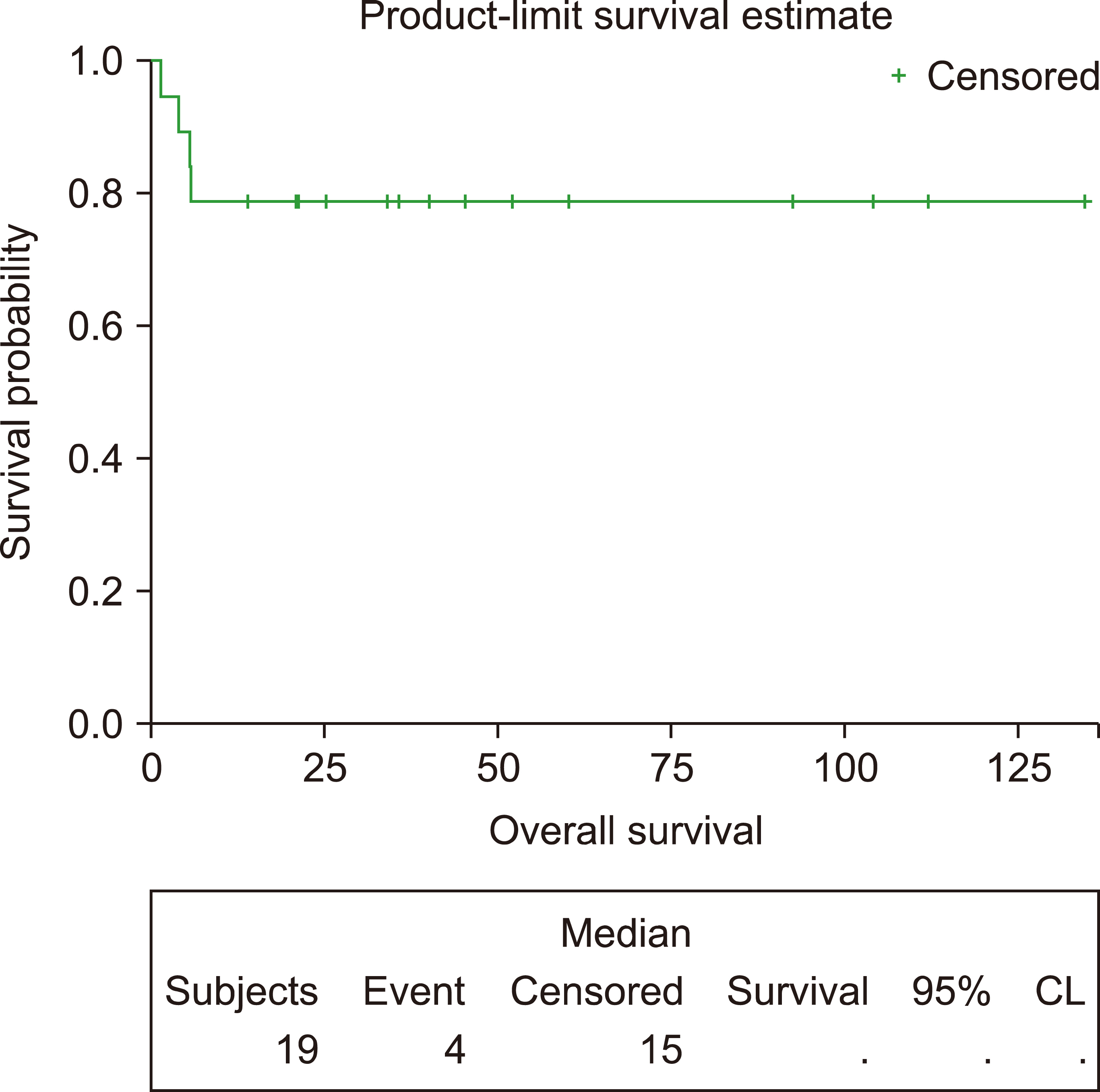
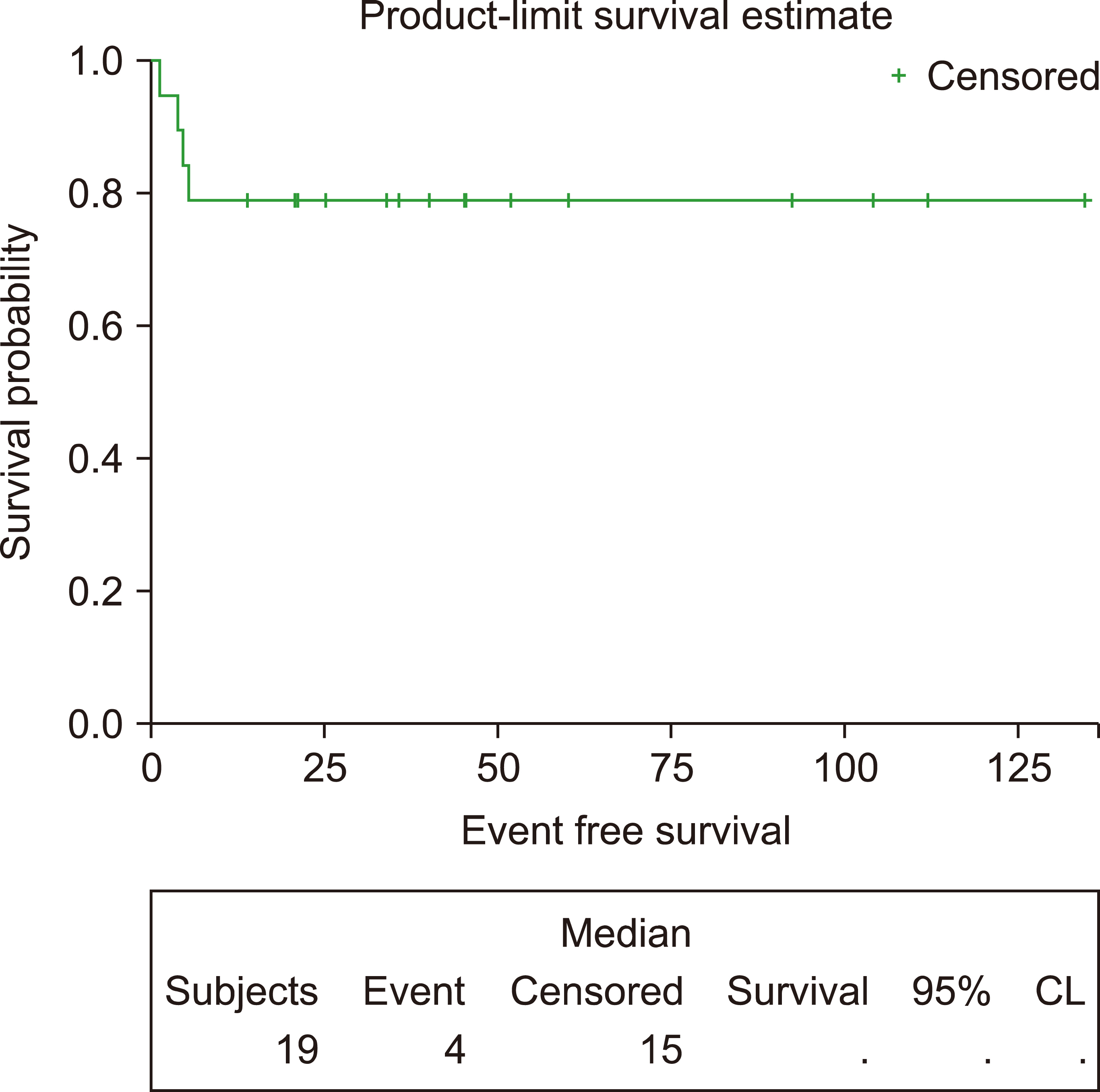
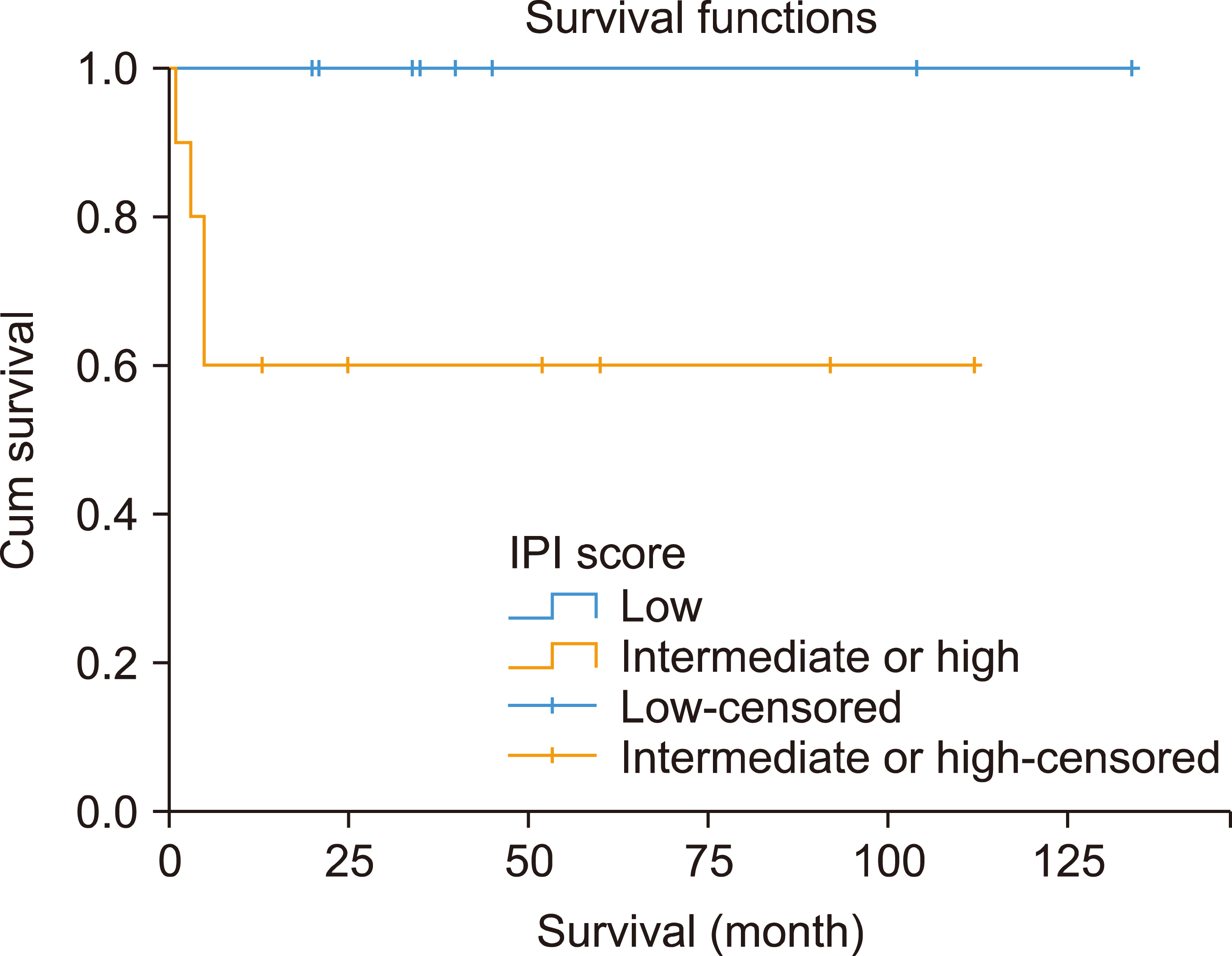
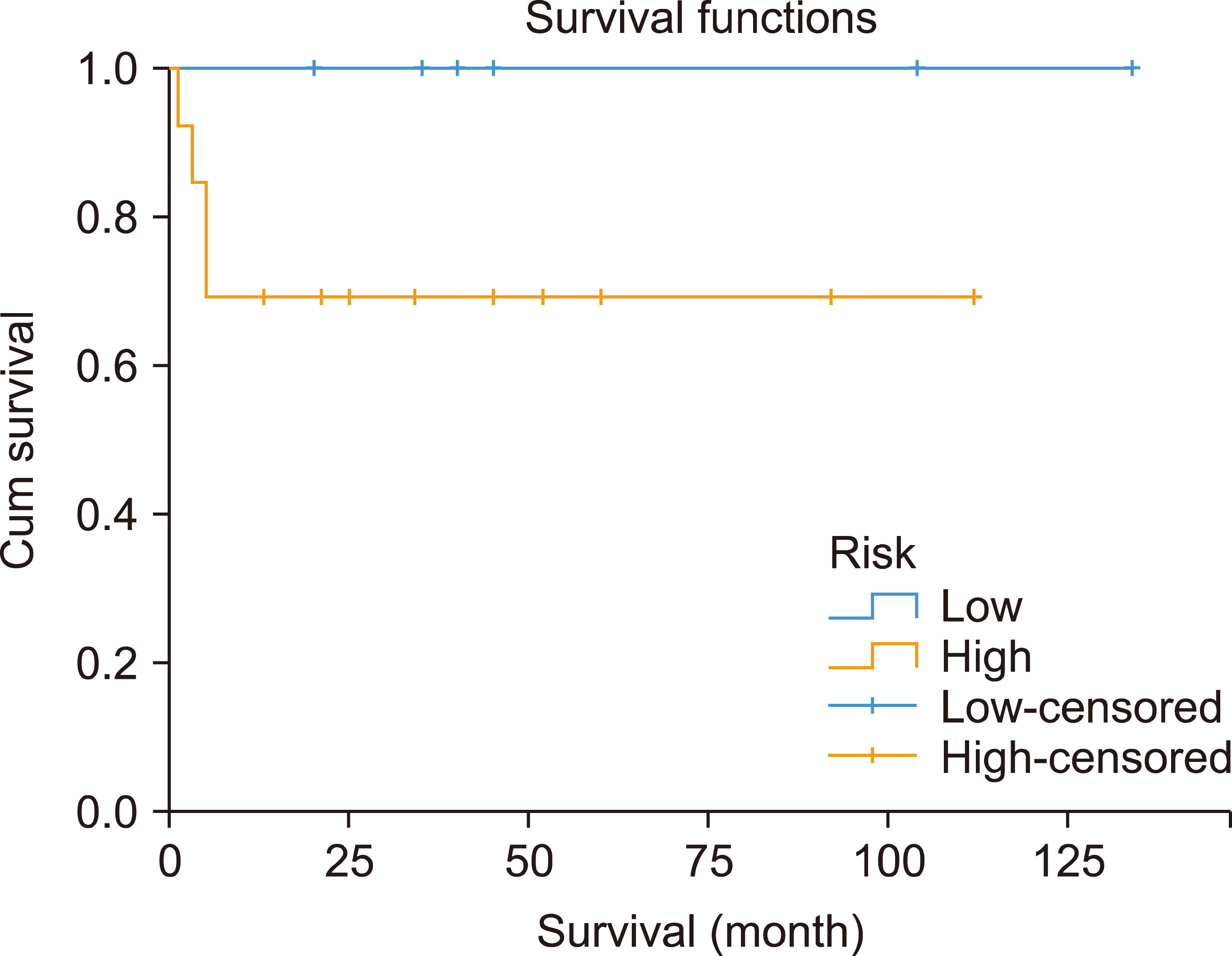
This study included 19 patients with a median age of 33 years (range, 19‒65). Eleven (58%) and two (10.5%) patients had advanced-stage and central nervous system disease, respectively. Among 106 administered cycles, the median interval between cycles was 23 days (range, 19‒84 days). Sixteen patients (84%) achieved a complete response. After a median follow-up of 40.8 months, the 3-year EFS and OS rates were 78.95%. Patients with a low-risk International Prognostic Index (IPI) had better survival than those with intermediate-or high-risk IPI. Grade III‒IV hematological toxicities occurred in 88% of patients, while 73% had grade III‒IV mucositis.
Conclusion
In adult Burkitt lymphoma, the CALGB 1002 protocol provides high cure rates and can be administered promptly, but is associated with significant toxicity. Risk-adapted approaches and other, less toxic, chemotherapeutic regimens should be considered.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dunleavy K. 2018; Approach to the diagnosis and treatment of adult Burkitt's lymphoma. J Oncol Pract. 14:665–71. DOI: 10.1200/JOP.18.00148. PMID: 30423267.
Article2. Morton LM, Wang SS, Devesa SS, Hartge P, Weisenburger DD, Linet MS. 2006; Lymphoma incidence patterns by WHO subtype in the United States, 1992-2001. Blood. 107:265–76. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2508. PMID: 16150940. PMCID: PMC1895348.
Article3. Kalisz K, Alessandrino F, Beck R, et al. 2019; An update on Burkitt lymphoma: a review of pathogenesis and multimodality imaging assessment of disease presentation, treatment response, and recurrence. Insights Imaging. 10:56. DOI: 10.1186/s13244-019-0733-7. PMID: 31115699. PMCID: PMC6529494.
Article4. Kasamon YL, Swinnen LJ. 2004; Treatment advances in adult Burkitt lymphoma and leukemia. Curr Opin Oncol. 16:429–35. DOI: 10.1097/00001622-200409000-00003. PMID: 15314510.
Article5. Jacobson C, LaCasce A. 2014; How I treat Burkitt lymphoma in adults. Blood. 124:2913–20. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-06-538504. PMID: 25258344.
Article6. Rizzieri DA, Johnson JL, Niedzwiecki D, et al. 2004; Intensive chemotherapy with and without cranial radiation for Burkitt leukemia and lymphoma: final results of Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study 9251. Cancer. 100:1438–48. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.20143. PMID: 15042678.7. Rizzieri DA, Johnson JL, Byrd JC, et al. 2014; Improved efficacy using rituximab and brief duration, high intensity chemotherapy with filgrastim support for Burkitt or aggressive lymphomas: cancer and Leukemia Group B study 10 002. Br J Haematol. 165:102–11. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.12736. PMID: 24428673. PMCID: PMC3996561.8. Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, et al. 2014; Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol. 32:3059–68. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.8800. PMID: 25113753. PMCID: PMC4979083.
Article9. International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. 1993; A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 329:987–94. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199309303291402. PMID: 8141877.10. Mead GM, Sydes MR, Walewski J, et al. 2002; An international evaluation of CODOX-M and CODOX-M alternating with IVAC in adult Burkitt's lymphoma: results of United Kingdom Lymphoma Group LY06 study. Ann Oncol. 13:1264–74. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdf253. PMID: 12181251.
Article11. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, et al. 2007; Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 25:579–86. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2403. PMID: 17242396.12. National Cancer Institute. Division of cancer treatment and diagnosis. 2020. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0. National Cancer Institute;Bethesda, MD: at https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_8.5x11.pdf. Accessed May 20, 2021.13. Lee D, Kim S, Ko OB, et al. 2005; Burkitt's lymphoma in Korea: clinical manifestations and efficacy of modified CALGB 9251 regimen (BNHL). Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 106(Suppl):4661. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V106.11.4661.4661.
Article14. Blum KA, Lozanski G, Byrd JC. 2004; Adult Burkitt leukemia and lymphoma. Blood. 104:3009–20. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0405. PMID: 15265787.
Article15. Roschewski M, Dunleavy K, Abramson JS, et al. 2020; Multicenter study of risk-adapted therapy with dose-adjusted EPOCH-R in adults with untreated Burkitt lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 38:2519–29. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.00303. PMID: 32453640. PMCID: PMC7392744.
Article16. Evens AM, Carson KR, Kolesar J, et al. 2013; A multicenter phase II study incorporating high-dose rituximab and liposomal doxorubicin into the CODOX-M/IVAC regimen for untreated Burkitt's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 24:3076–81. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdt414. PMID: 24146219. PMCID: PMC3841019.
Article17. Hoelzer D, Walewski J, Döhner H, et al. 2014; Improved outcome of adult Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia with rituximab and chemo-therapy: report of a large prospective multicenter trial. Blood. 124:3870–9. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-563627. PMID: 25359988. PMCID: PMC4271177.
Article18. Intermesoli T, Rambaldi A, Rossi G, et al. 2013; High cure rates in Burkitt lymphoma and leukemia: a Northern Italy Leukemia Group study of the German short intensive rituximab-chemotherapy program. Haematologica. 98:1718–25. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.086827. PMID: 23753030. PMCID: PMC3815172.
Article19. McMillan AK, Phillips EH, Kirkwood AA, et al. 2020; Favourable outcomes for high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (IPI 3-5) treated with front-line R-CODOX-M/R-IVAC chemotherapy: results of a phase 2 UK NCRI trial. Ann Oncol. 31:1251–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.05.016. PMID: 32464282. PMCID: PMC7487775.
Article20. Barnes JA, Lacasce AS, Feng Y, et al. 2011; Evaluation of the addition of rituximab to CODOX-M/IVAC for Burkitt's lymphoma: a retrospective analysis. Ann Oncol. 22:1859–64. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdq677. PMID: 21339382.
Article21. Diviné M, Casassus P, Koscielny S, et al. 2005; Burkitt lymphoma in adults: a prospective study of 72 patients treated with an adapted pediatric LMB protocol. Ann Oncol. 16:1928–35. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdi403. PMID: 16284057.
Article22. Patekar M, Gogia A, Tiwari A, et al. 2018; Adult Burkitt lymphoma: an institutional experience with a uniform chemotherapy protocol. South Asian J Cancer. 7:195–9. DOI: 10.4103/sajc.sajc_230_17. PMID: 30112340. PMCID: PMC6069339.
Article23. Zayac AS, Evens AM, Danilov A, et al. 2021; Outcomes of Burkitt lymphoma with central nervous system involvement: evidence from a large multicenter cohort study. Haematologica. 106:1932–42. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2020.270876. PMID: 33538152. PMCID: PMC8252937.
Article24. Sun P, Wang Y, Chen C, et al. 2021; R-split-EPOCH plus high dose methotrexate in untreated diffuse large B cell lymphoma with MYC rearrangement or double expression of MYC and BCL-2. J Cancer. 12:2059–64. DOI: 10.7150/jca.52958. PMID: 33754004. PMCID: PMC7974535.25. Chihara D, Fowler NH, Oki Y, et al. 2017; Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R and mid-cycle high dose methotrexate for patients with systemic lymphoma and secondary CNS involvement. Br J Haematol. 179:851–4. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.14267. PMID: 27502933. PMCID: PMC6063086.
Article