J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2022 Jan;65(1):74-83. 10.3340/jkns.2021.0105.
Do Obliquity and Position of the Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cage Influence the Degree of Indirect Decompression of Foraminal Stenosis?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedics, Naresuan University Hospital, Phitsanulok, Thailand
- 2Department of Orthopaedics, Queen Savang Vadhana Memorial Hospital, Sri Racha, Thailand
- 3Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 5Spine Center, Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Orthopaedics, Burapha University Hospital, Chonburi, Thailand
- KMID: 2523915
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0105
Abstract
Objective
: Oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) is a surgical technique that utilizes a large interbody cage to indirectly decompress neural elements. The position of the cage relative to the vertebral body could affect the degree of foraminal decompression. Previous studies determined the position of the cage using plain radiographs, with conflicting results regarding the influence of the position of the cage to the degree of neural foramen decompression. Because of the cage obliquity, computed tomography (CT) has better accuracy than plain radiograph for the measurement of the obliquely inserted cage. The objective of this study is to find the correlation between the position of the OLIF cage with the degree of indirect decompression of foraminal stenosis using CT and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods
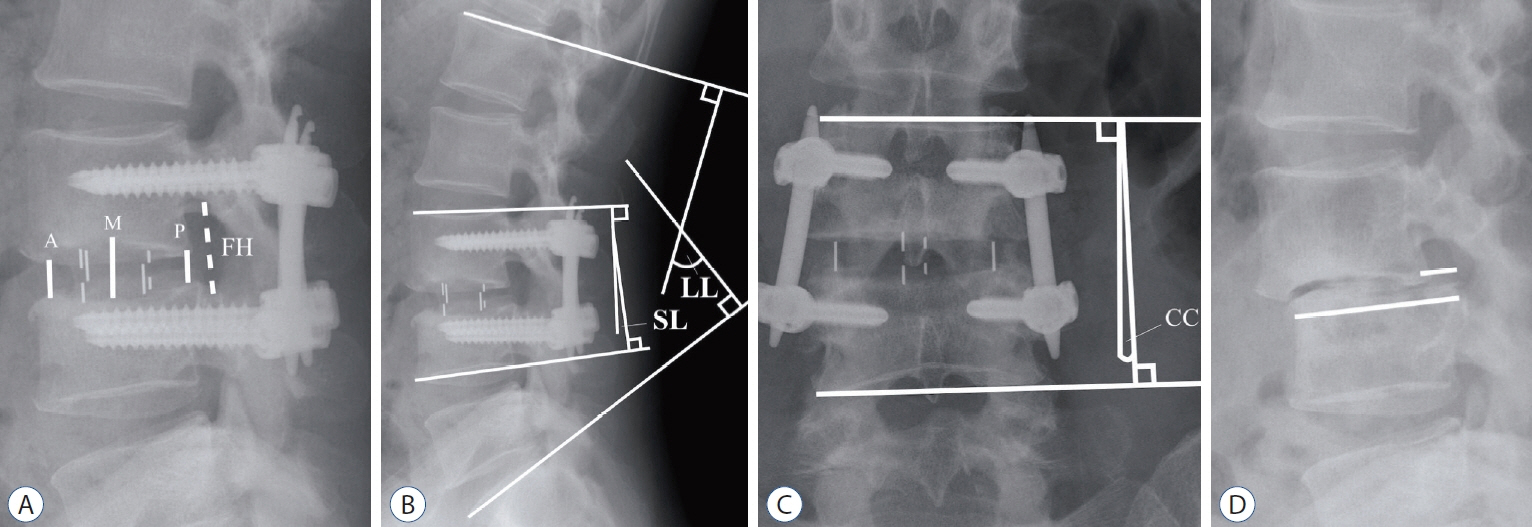
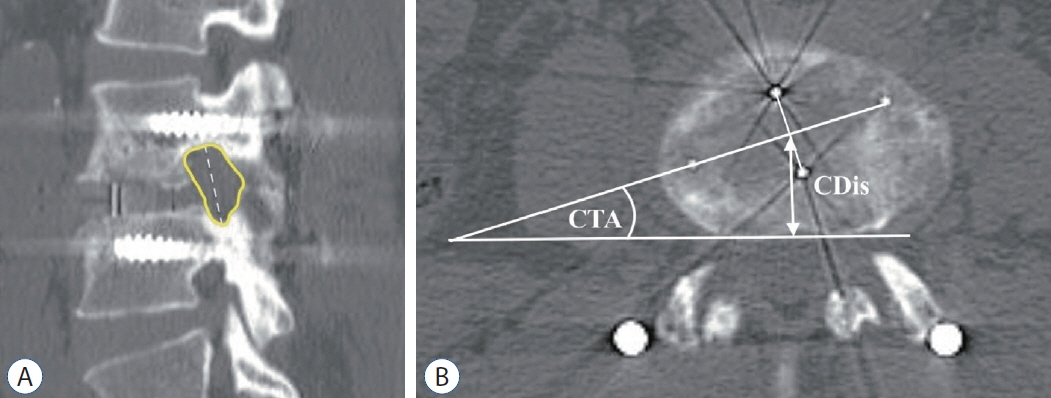
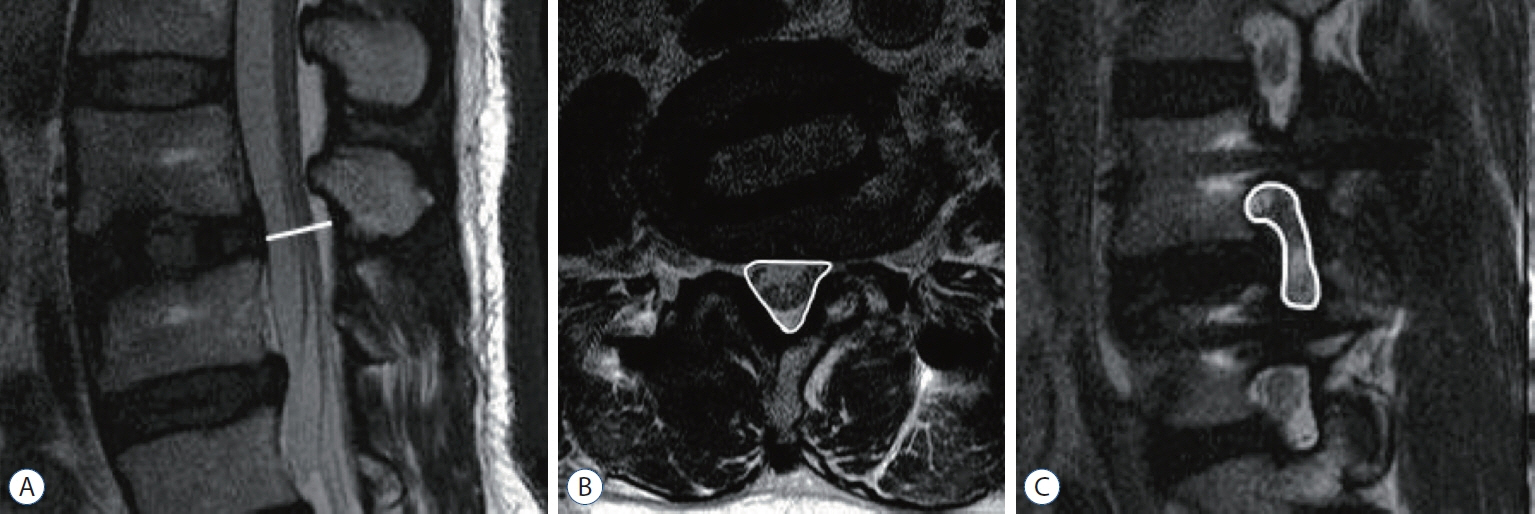
: We review imaging of 46 patients who underwent OLIF from L2-L5 for 68 levels. Segmental lordosis (SL) was measured in a plain radiograph. The positions of the cage were measured in CT. Spinal canal cross-sectional area (SCSA), and foraminal crosssectional area (FSCA) measurements using MRI were taken into consideration.
Results
: Patients’ mean age was 69.7 years. SL increases 3.0±5.1 degrees. Significant increases in SCSA (33.3%), FCSA (43.7% on the left and 45.0% on the right foramen) were found (p<0.001). Multiple linear regression analysis shows putting the cage in the more posterior position correlated with more increase of FSCA and decreases SL correction. The position of the cage does not affect the degree of the central spinal canal decompression. Obliquity of the cage does not result in different degrees of foraminal decompression between right and left side neural foramen.
Conclusion
: Cage position near the posterior part of the vertebral body increases the decompression effect of the neural foramen while putting the cage in the more anterior position correlated with increases SL.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Factors Affecting Cage Obliquity and the Relationship between Cage Obliquity and Radiological Outcomes in Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion at the L4-L5 Level
CheolWon Jang, SungHwan Hwang, Tae Kyung Jin, Hyung Jin Shin, Byung-Kyu Cho
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2023;66(6):703-715. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2023.0071.
Reference
-
References
1. Castellvi AE, Nienke TW, Marulanda GA, Murtagh RD, Santoni BG. Indirect decompression of lumbar stenosis with transpsoas interbody cages and percutaneous posterior instrumentation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 472:1784–1791. 2014.
Article2. Davis TT, Hynes RA, Fung DA, Spann SW, MacMillan M, Kwon B, et al. Retroperitoneal oblique corridor to the L2-S1 intervertebral discs in the lateral position: an anatomic study. J Neurosurg Spine. 21:785–793. 2014.
Article3. Fujibayashi S, Hynes RA, Otsuki B, Kimura H, Takemoto M, Matsuda S. Effect of indirect neural decompression through oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:E175–E182. 2015.
Article4. Jenis LG, An HS. Spine update. Lumbar foraminal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:389–394. 2000.5. Jin C, Jaiswal MS, Jeun SS, Ryu KS, Hur JW, Kim JS. Outcomes of oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease in patients under or over 65 years of age. J Orthop Surg Res. 13:38. 2018.6. Kepler CK, Sharma AK, Huang RC, Meredith DS, Girardi FP, Cammisa FP Jr, et al. Indirect foraminal decompression after lateral transpsoas interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 16:329–333. 2012.
Article7. Kim JS, Choi WG, Lee SH. Minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion followed by percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for isthmic spondylolisthesis: minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine J. 10:404–409. 2010.
Article8. Kim JS, Kang BU, Lee SH, Jung B, Choi YG, Jeon SH, et al. Mini-transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion augmented by percutaneous pedicle screw fixation: a comparison of surgical outcomes in adult low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 22:114–121. 2009.
Article9. Lang G, Perrech M, Navarro-Ramirez R, Hussain I, Pennicooke B, Maryam F, et al. Potential and limitations of neural decompression in extreme lateral interbody fusion-a systematic review. World Neurosurgery. 101:99–113. 2017.
Article10. Lee S, Lee JW, Yeom JS, Kim KJ, Kim HJ, Chung SK, et al. A practical MRI grading system for lumbar foraminal stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 194:1095–1098. 2010.
Article11. Limthongkul W, Tanasansomboon T, Yingsakmongkol W, Tanaviriyachai T, Radcliff K, Singhatanadgige W. Indirect decompression effect to central canal and ligamentum flavum after extreme lateral lumbar interbody fusion and oblique lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 45:E1077–E1084. 2020.
Article12. Lin GX, Rui G, Sharma S, Mahatthanatrakul A, Kim JS. The correlation of intraoperative distraction of intervertebral disc with the postoperative canal and foramen expansion following oblique lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 30:151–163. 2021.
Article13. Mayer HM. A new microsurgical technique for minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:691–699. discussion 700. 1997.
Article14. Mehren C, Mayer HM, Zandanell C, Siepe CJ, Korge A. The oblique anterolateral approach to the lumbar spine provides access to the lumbar spine with few early complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 474:2020–2027. 2016.
Article15. Miscusi M, Ramieri A, Forcato S, Giuffrè M, Trungu S, Cimatti M, et al. Comparison of pure lateral and oblique lateral inter-body fusion for treatment of lumbar degenerative disk disease: a multicentric cohort study. Eur Spine J. 27(Suppl 2):222–228. 2018.
Article16. Mobbs RJ, Phan K, Malham G, Seex K, Rao PJ. Lumbar interbody fusion: techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. J Spine Surg. 1:2–18. 2015.17. Nakashima H, Kanemura T, Satake K, Ishikawa Y, Ouchida J, Segi N, et al. Indirect decompression on MRI chronologically progresses after immediate postlateral lumbar interbody fusion: the results from a minimum of 2 years follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 44:E1411–E1418. 2019.18. Ohtori S, Orita S, Yamauchi K, Eguchi Y, Ochiai N, Kishida S, et al. Miniopen anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for lumbar spinal degeneration disease. Yonsei Med J. 56:1051–1059. 2015.
Article19. Oliveira L, Marchi L, Coutinho E, Pimenta L. A radiographic assessment of the ability of the extreme lateral interbody fusion procedure to indirectly decompress the neural elements. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35(26 Suppl):S331–S337. 2010.
Article20. Ozgur BM, Aryan HE, Pimenta L, Taylor WR. Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF): a novel surgical technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 6:435–443. 2006.
Article21. Park SJ, Lee CS, Chung SS, Kang SS, Park HJ, Kim SH. The ideal cage position for achieving both indirect neural decompression and segmental angle restoration in lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF). Clin Spine Surg. 30:E784–E790. 2017.
Article22. Rao PJ, Maharaj MM, Phan K, Lakshan Abeygunasekara M, Mobbs RJ. Indirect foraminal decompression after anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective radiographic study using a new pedicle-to-pedicle technique. Spine J. 15:817–824. 2015.
Article23. Rauschning W. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the lumbar root canals. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 12:1008–1019. 1987.
Article24. Sato J, Ohtori S, Orita S, Yamauchi K, Eguchi Y, Ochiai N, et al. Radiographic evaluation of indirect decompression of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerated lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 26:671–678. 2017.
Article25. Sembrano JN, Horazdovsky RD, Sharma AK, Yson SC, Santos ERG, Polly DW Jr. Do lordotic cages provide better segmental lordosis versus nonlordotic cages in lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF)? Clin Spine Surg. 30:E338–E343. 2017.
Article26. Silvestre C, Mac-Thiong JM, Hilmi R, Roussouly P. Complications and morbidities of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lumbar interbody fusion in 179 patients. Asian Spine J. 6:89–97. 2012.
Article27. Singh V, Montgomery SR, Aghdasi B, Inoue H, Wang JC, Daubs MD. Factors affecting dynamic foraminal stenosis in the lumbar spine. Spine J. 13:1080–1087. 2013.
Article28. Woods KR, Billys JB, Hynes RA. Technical description of oblique lateral interbody fusion at L1-L5 (OLIF25) and at L5-S1 (OLIF51) and evaluation of complication and fusion rates. Spine J. 17:545–553. 2017.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effectiveness of Indirect Decompression in Severe Degenerative Lumbar Central Canal Stenosis by Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Factors Affecting Cage Obliquity and the Relationship between Cage Obliquity and Radiological Outcomes in Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion at the L4-L5 Level
- Minimally Invasive Strategy for Uniportal Full-Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using a Large Cage Utilized in Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Anterior Cage Migration during Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Successful Criteria for Indirect Decompression With Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion