J Rhinol.
2021 Nov;28(3):131-140. 10.18787/jr.2021.00382.
Practical Review of Biologics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Republic of Korea
- 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
- 5Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, School of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2522781
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2021.00382
Abstract
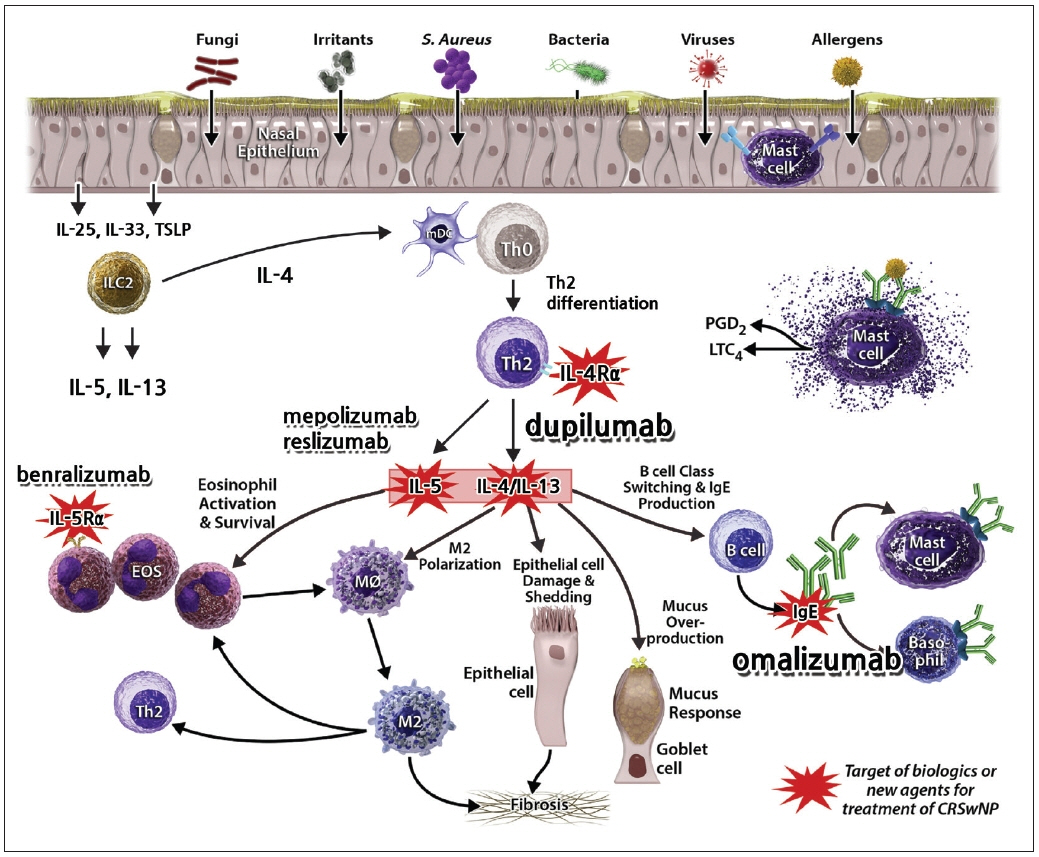
- Well-characterized in chronic rhinosinusitis, type 2 inflammation is frequently associated with nasal polyps, comorbid asthma, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug hypersensitivity. Despite medical and surgical treatment, it recurs in a significant proportion of patients. Thus, severe uncontrolled type 2 chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is the most difficult-to-treat phenotype of chronic rhinosinusitis. Recently, dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody against IL-4 receptor α, and omalizumab, a monoclonal antibody against immunoglobulin E, were approved for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in the United States, Europe, and Korea. Therefore, rhinologists should understand novel biologics and their use. Here, we provide a literature review of several biologics with their indications, effectiveness, and safety.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wang X, Cutting GR. Chronic rhinosinusitis. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011; 70:114–21.2. Chen Y, Dales R, Lin M. The epidemiology of chronic rhinosinusitis in Canadians. Laryngoscope. 2003; 113(7):1199–205.3. Hastan D, Fokkens WJ, Bachert C, Newson RB, Bislimovska J, Bockelbrink A, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Europe--an underestimated disease. A GA²LEN study. Allergy. 2011; 66(9):1216–23.4. Blackwell DL, Lucas JW, Clarke TC. Summary health statistics for U.S. adults: national health interview survey, 2012. Vital Health Stat 10. 2014; 260:1–161.5. Kim YS, Kim NH, Seong SY, Kim KR, Lee GB, Kim KS. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic rhinosinusitis in Korea. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; 25(3):117–21.6. Chung JH, Lee YJ, Kang TW, Kim KR, Jang DP, Kim IY, et al. Altered quality of life and psychological health (SCL-90-R) in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2015; 124(8):663–70.7. Campbell AP, Phillips KM, Hoehle LP, Feng AL, Bergmark RW, Caradonna DS, et al. Depression symptoms and lost productivity in chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017; 118(3):286–9.8. Kim DW, Cho SH. Emerging endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis and its application to precision medicine. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9(4):299–306.9. Khan A, Vandeplas G, Huynh TMT, Joish VN, Mannent L, Tomassen P, et al. The Global Allergy and Asthma European Network (GALEN rhinosinusitis cohort: a large European cross-sectional study of chronic rhinosinusitis patients with and without nasal polyps. Rhinology. 2019; 57(1):32–42.10. Tomassen P, Vandeplas G, Van Zele T, Cardell LO, Arebro J, Olze H, et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137(5):1449–56.e4.11. Zhang Y, Gevaert E, Lou H, Wang X, Zhang L, Bachert C, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Asia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 140(5):1230–9.12. DeConde AS, Mace JC, Levy JM, Rudmik L, Alt JA, Smith TL. Prevalence of polyp recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Laryngoscope. 2017; 127(3):550–5.13. Alobid I, Antón E, Armengot M, Chao J, Colás C, del Cuvillo A, et al. SEAIC-SEORL. Consensus document on nasal polyposis. POLINA project. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011; 21 Suppl 1:1–58.14. Rudmik L, Soler ZM. Medical therapies for adult chronic sinusitis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015; 314(9):926–39.15. Gandhi NA, Pirozzi G, Graham NMH. Commonality of the IL-4/IL13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017; 13(5):425–37.16. Ahern S, Cervin A. Inflammation and endotyping in chronic rhinosinusitis—a paradigm shift. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019; 55(4):95.17. Bachert C, Han JK, Wagenmann M, Hosemann W, Lee SE, Backer V, et al. EUFOREA expert board meeting on uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) and biologics: definitions and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021; 147(1):29–36.18. Wang X, Zhang N, Bo M, Holtappels G, Zheng M, Lou H, et al. Diversity of TH cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 138(5):1344–53.19. Kim SJ, Lee KH, Kim SW, Cho JS, Park YK, Shin SY. Changes in histological features of nasal polyps in a Korean population over a 17- year period. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 149(3):431–7.20. Karin J, Tim D, Gabriele H, Cardell LO, Marit W, Claus B. Type 2 inflammatory shift in chronic rhinosinusitis during 2007-2018 in Belgium. Laryngoscope. 2021; 131(5):E1408–14.21. Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Smith TL, Bleier B, DeConde A, Luong AU, et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: rhinosinusitis 2021. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021; 11(3):213–739.22. Van Zele T, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, Beule A, Wormald PJ, Mayr S, et al. Oral steroids and doxycycline: two different approaches to treat nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125(5):1069–76.e4.23. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology. 2020; 58(Suppl S29):1–464.24. Mauer Y, Taliercio RM. Managing adult asthma: the 2019 GINA guidelines. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020; 87(9):569–75.25. Gan EC, Habib AR, Hathorn I, Javer AR. The efficacy and safety of an office-based polypectomy with a vacuum-powered microdebrider. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013; 3(11):890–5.26. Bachert C, Zhang L, Gevaert P. Current and future treatment options for adult chronic rhinosinusitis: focus on nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 136(6):1431–40.27. Bachert C, Zhang N, Cavaliere C, Weiping W, Gevaert E, Krysko O. Biologics for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020; 145(3):725–39.28. Kaur D, Hollins F, Woodman L, Yang W, Monk P, May R, et al. Mast cells express IL-13R alpha 1: IL-13 promotes human lung mast cell proliferation and Fc epsilon RI expression. Allergy. 2006; 61(9):1047–53.29. Fujieda S, Matsune S, Takeno S, Ohta N, Asako M, Bachert C, et al. Dupilumab efficacy in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps from SINUS-52 is unaffected by eosinophilic status. Allergy. 2021. May. 16. [Epub]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14906.30. Bachert C, Mannent L, Naclerio RM, Mullol J, Ferguson BJ, Gevaert P, et al. Effect of subcutaneous dupilumab on nasal polyp burden in patients with chronic sinusitis and nasal polyposis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016; 315(5):469–79.31. Bachert C, Han JK, Desrosiers M, Hellings PW, Amin N, Lee SE, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2019; 394(10209):1638–50.32. Bachert C, Hellings PW, Mullol J, Hamilos DL, Gevaert P, Naclerio RM, et al. Dupilumab improves health-related quality of life in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Allergy. 2020; 75(1):148–57.33. Bachert C, Hellings PW, Mullol J, Naclerio RM, Chao J, Amin N, et al. Dupilumab improves patient-reported outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and comorbid asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019; 7(7):2447–9.e2.34. Jonstam K, Swanson BN, Mannent LP, Cardell LO, Tian N, Wang Y, et al. Dupilumab reduces local type 2 pro-inflammatory biomarkers in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Allergy. 2019; 74(4):743–52.35. Takabayashi T, Shigeharu F, Bachert C, Cho SH, Swanson BN, Harel S, et al. Dupilumab reduces blood, urine, and nasal biomarkers of type 2 inflammation in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in the phase 3 SINUS-52 trial [Abstract]. Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Rhinologic Society. 2020 Oct 10-11; Tokyo, Japan. In : Japanese Rhinologic Society; 2020.36. Gevaert P, Omachi TA, Corren J, Mullol J, Han J, Lee SE, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in nasal polyposis: 2 randomized phase 3 trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020; 146(3):595–605.37. Pinto JM, Mehta N, DiTineo M, Wang J, Baroody FM, Naclerio RM. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of anti-IgE for chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2010; 48(3):318–24.38. Gevaert P, Calus L, Van Zele T, Blomme K, De Ruyck N, Bauters W, et al. Omalizumab is effective in allergic and nonallergic patients with nasal polyps and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131(1):110–6.e1.39. Bidder T, Sahota J, Rennie C, Lund VJ, Robinson DS, Kariyawasam HH. Omalizumab treats chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and asthma together-a real life study. Rhinology. 2018; 56(1):42–5.40. Mostafa BE, Fadel M, Mohammed MA, Hamdi TAH, Askoura AM. Omalizumab versus intranasal steroids in the post-operative management of patients with allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020; 277(1):121–8.41. Hayashi H, Mitsui C, Nakatani E, Fukutomi Y, Kajiwara K, Watai K, et al. Omalizumab reduces cysteinyl leukotriene and 9α,11β-prostaglandin F2 overproduction in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137(5):1585–7.e4.42. Han JK, Bachert C, Fokkens W, Desrosiers M, Wagenmann M, Lee SE, et al. Mepolizumab for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (SYNAPSE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021; 9:1141–53.43. Gevaert P, Van Bruaene N, Cattaert T, Van Steen K, Van Zele T, Acke F, et al. Mepolizumab, a humanized anti-IL-5 mAb, as a treatment option for severe nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128(5):989–95.e1-8.44. Bachert C, Sousa AR, Lund VJ, Scadding GK, Gevaert P, Nasser S, et al. Reduced need for surgery in severe nasal polyposis with mepolizumab: randomized trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 140(4):1024–31.e14.45. Gevaert P, Lang-Loidolt D, Lackner A, Stammberger H, Staudinger H, Van Zele T, et al. Nasal IL-5 levels determine the response to antiIL-5 treatment in patients with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118(5):1133–41.46. Bachert C, Desrosiers M, Gevaert P, Heffler E, Hopkins C, Tversky JR, et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: results from the phase III OSTRO trial. Proceedings of the EAACI Hybrid Congress 2021. 2021 Jul 10-12; Krakow, Republic of Poland. In : EAACI; 2021.47. Hellings PW, Verhoeven E, Fokkens WJ. State-of-the-art overview on biological treatment for CRSwNP. Rhinology. 2021; 59(2):151–63.48. Peters AT, Han JK, Hellings P, Heffler E, Gevaert P, Bachert C, et al. Indirect treatment comparison of biologics in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021; 9(6):2461–71.e5.49. Kim DW. Can neutrophils be a cellular biomarker in Asian chronic rhinosinusitis? Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; 12(4):325–6.50. Wang H, Pan L, Liu Z. Neutrophils as a protagonist and target in chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; 12(4):337–47.51. Vannella KM, Ramalingam TR, Borthwick LA, Barron L, Hart KM, Thompson RW, et al. Combinatorial targeting of TSLP, IL-25, and IL-33 in type 2 cytokine-driven inflammation and fibrosis. Sci Transl Med. 2016; 8(337):337ra65. ra65.52. Shin HW, Kim DK, Park MH, Eun KM, Lee M, So D, et al. IL-25 as a novel therapeutic target in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135(6):1476–85.e7. e7.53. Nagarkar DR, Poposki JA, Tan BK, Comeau MR, Peters AT, Hulse KE, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin activity is increased in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132(3):593–600.e12.54. Hernandez ML, Mills K, Almond M, Todoric K, Aleman MM, Zhang H, et al. IL-1 receptor antagonist reduces endotoxin-induced airway inflammation in healthy volunteers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135(2):379–85.55. Laidlaw TM, Buchheit KM. Biologics in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020; 124(4):326–32.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical treatment according to phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis
- Update on Biologics in Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyposis
- Biologics for Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps: Current Status and Clinical Considerations in Korea
- Endotypes of Asian chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A narrative review
- Tissue Remodeling in Rhinosinusitis