Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2021 Nov;14(4):414-423. 10.21053/ceo.2020.02061.
Feasibility of Surgical Treatment for Laryngomalacia Using the Spontaneous Respiration Technique
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2522433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2020.02061
Abstract
Objectives
. In this study, we review our institutional experience with pediatric laryngomalacia (LM) and report our experiences of patients undergoing supraglottoplasty using the spontaneous respiration using intravenous anesthesia and high-flow nasal oxygen (STRIVE Hi) technique.
Methods
. The medical records of 29 children with LM who visited Seoul National University Hospital between January 2017 and March 2019 were retrospectively reviewed. Surgical management was performed using the STRIVE Hi technique. Intraoperative findings and postoperative surgical outcomes, including complications and changes in symptoms and weight, were analyzed.
Results
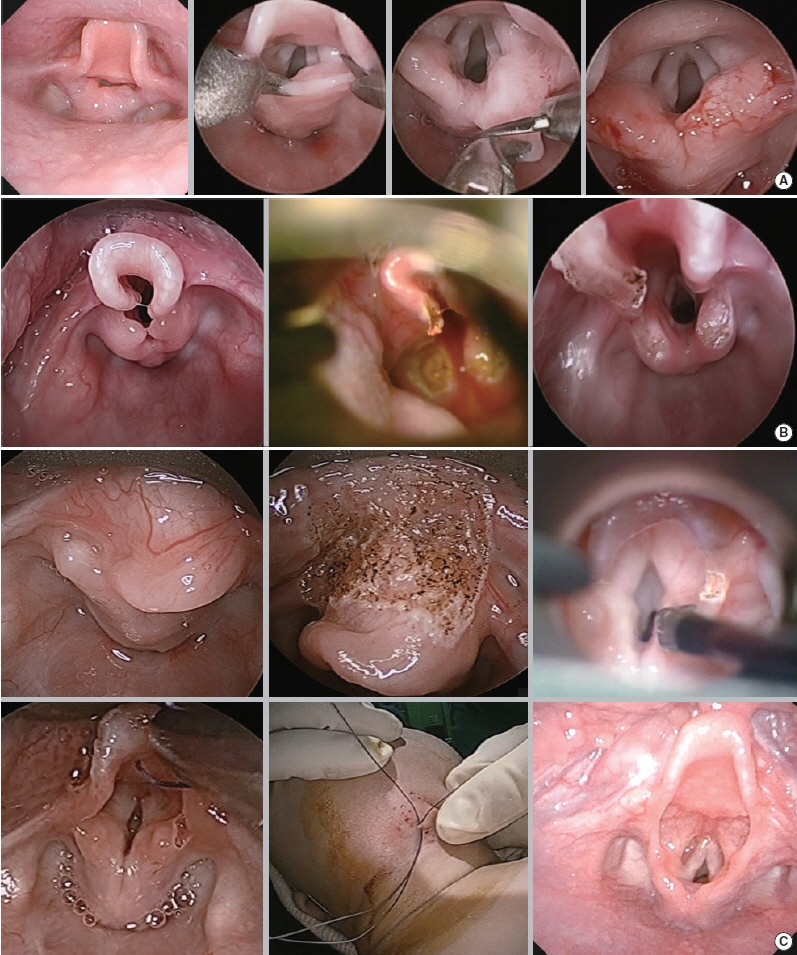
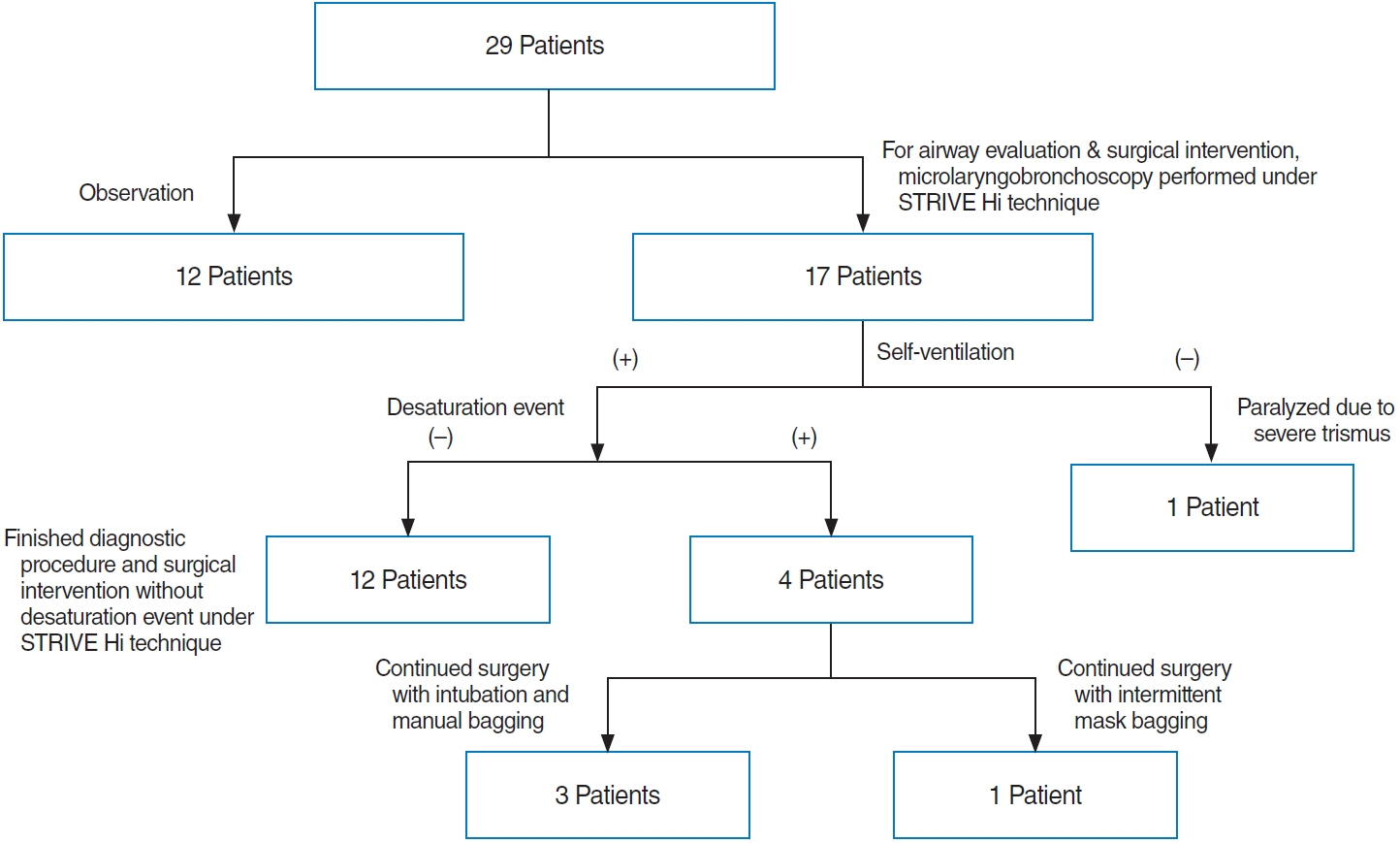
. Of the total study population of 29 subjects, 20 (68.9%) were female. The patients were divided according to the Onley classification as follows: type I (n=13, 44.8%), II (n=10, 34.5%), and III (n=6, 20.7%). Twenty-five patients (86.2%) had comorbidities. Seventeen patients (58.6%) underwent microlaryngobronchoscopy under STRIVE Hi anesthesia. Four patients with several desaturation events required rescue oxygenation by intermittent intubation and mask bagging during the STRIVE Hi technique. However, the procedure was completed in all patients without any severe adverse effects. Overall, 15 children (51.7%) underwent supraglottoplasty, of whom 14 (93.3%) showed symptom improvement, and their postoperative weight percentile significantly increased (P=0.026). One patient required tracheostomy immediately after supraglottoplasty due to associated neurological disease.
Conclusion
. The STRIVE Hi technique is feasible for supraglottoplasty in LM patients, while type III LM patients with micrognathia or glossoptosis may have a higher risk of requiring rescue oxygenation during the STRIVE Hi technique.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Clinical Features and Risk Factors of Subglottic Cysts in Children: A Clinical Experience Using the Spontaneous Respiration Technique
Seung Hoon Han, Minju Kim, Jeong-Yeon Ji, Seong Keun Kwon
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023;16(2):177-183. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2023.00031.
Reference
-
1. Olney DR, Greinwald JH Jr, Smith RJ, Bauman NM. Laryngomalacia and itstreatment. Laryngoscope. 1999; Nov. 109(11):1770–5.2. Bedwell J, Zalzal G. Laryngomalacia. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2016; Jun. 25(3):119–22.
Article3. Kusak B, Cichocka-Jarosz E, Jedynak-Wasowicz U, Lis G. Types of laryngomalacia in children: interrelationship between clinical course and comorbid conditions. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017; Mar. 274(3):1577–83.
Article4. Thompson DM. Abnormal sensorimotor integrative function of the larynx in congenital laryngomalacia: a new theory of etiology. Laryngoscope. 2007; Jun. 117(6 Pt 2 Suppl 114):1–33.
Article5. Ji JY, Kim EH, Lee JH, Jang YE, Kim HS, Kwon SK. Pediatric airway surgery under spontaneous respiration using high-flow nasal oxygen. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020; Jul. 134:110042.
Article6. Jaquet Y, Monnier P, Van Melle G, Ravussin P, Spahn DR, CholletRivier M. Complications of different ventilation strategies in endoscopic laryngeal surgery: a 10-year review. Anesthesiology. 2006; Jan. 104(1):52–9.7. Craft TM, Chambers PH, Ward ME, Goat VA. Two cases of barotrauma associated with transtracheal jet ventilation. Br J Anaesth. 1990; Apr. 64(4):524–7.8. Booth AW, Vidhani K, Lee PK, Thomsett CM. SponTaneous Respiration using IntraVEnous anaesthesia and Hi-flow nasal oxygen (STRIVE Hi) maintains oxygenation and airway patency during management of the obstructed airway: an observational study. Br J Anaesth. 2017; Mar. 118(3):444–51.
Article9. Riva T, Seiler S, Stucki F, Greif R, Theiler L. High-flow nasal cannula therapy and apnea time in laryngeal surgery. Paediatr Anaesth. 2016; Dec. 26(12):1206–8.
Article10. Ayari S, Aubertin G, Girschig H, Van Den Abbeele T, Mondain M. Pathophysiology and diagnostic approach to laryngomalacia in infants. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2012; Oct. 129(5):257–63.
Article11. Krashin E, Ben-Ari J, Springer C, Derowe A, Avital A, Sivan Y. Synchronous airway lesions in laryngomalacia. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008; Apr. 72(4):501–7.
Article12. Roger G, Denoyelle F, Triglia JM, Garabedian EN. Severe laryngomalacia: surgical indications and results in 115 patients. Laryngoscope. 1995; Oct. 105(10):1111–7.
Article13. Hoff SR, Schroeder JW Jr, Rastatter JC, Holinger LD. Supraglottoplasty outcomes in relation to age and comorbid conditions. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; Mar. 74(3):245–9.
Article14. Thompson DM. Laryngomalacia: factors that influence disease severity and outcomes of management. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; Dec. 18(6):564–70.
Article15. Dickson JM, Richter GT, Meinzen-Derr J, Rutter MJ, Thompson DM. Secondary airway lesions in infants with laryngomalacia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009; Jan. 118(1):37–43.
Article16. Schroeder JW Jr, Bhandarkar ND, Holinger LD. Synchronous airway lesions and outcomes in infants with severe laryngomalacia requiring supraglottoplasty. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009; Jul. 135(7):647–51.
Article17. Yuen HW, Tan HK, Balakrishnan A. Synchronous airway lesions and associated anomalies in children with laryngomalacia evaluated with rigid endoscopy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; Oct. 70(10):1779–84.
Article18. Escher A, Probst R, Gysin C. Management of laryngomalacia in children with congenital syndrome: the role of supraglottoplasty. J Pediatr Surg. 2015; Apr. 50(4):519–23.
Article19. Bradley J, Lee GS, Peyton J. Anesthesia for shared airway surgery in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2020; Mar. 30(3):288–95.
Article20. Weisberger EC, Emhardt JD. Apneic anesthesia with intermittent ventilation for microsurgery of the upper airway. Laryngoscope. 1996; Sep. 106(9 Pt 1):1099–102.
Article21. Gleason JM, Christian BR, Barton ED. Nasal cannula apneic oxygenation prevents desaturation during endotracheal intubation: an integrative literature review. West J Emerg Med. 2018; Mar. 19(2):403–11.
Article22. Grubler MR, Wigger O, Berger D, Blochlinger S. Basic concepts of heart-lung interactions during mechanical ventilation. Swiss Med Wkly. 2017; Sep. 147:w14491.
Article23. Gustafsson IM, Lodenius A, Tunelli J, Ullman J, Jonsson Fagerlund M. Apnoeic oxygenation in adults under general anaesthesia using Transnasal Humidified Rapid-Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): a physiological study. Br J Anaesth. 2017; Apr. 118(4):610–7.24. Humphreys S, Rosen D, Housden T, Taylor J, Schibler A. Nasal highflow oxygen delivery in children with abnormal airways. Paediatr Anaesth. 2017; Jun. 27(6):616–20.
Article25. Scheeren TW, Belda FJ, Perel A. The oxygen reserve index (ORI): a new tool to monitor oxygen therapy. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018; Jun. 32(3):379–89.
Article26. Renda T, Corrado A, Iskandar G, Pelaia G, Abdalla K, Navalesi P. High-flow nasal oxygen therapy in intensive care and anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2018; Jan. 120(1):18–27.
Article27. Walczynska A, Sobczyk L. The underestimated role of temperatureoxygen relationship in large-scale studies on size-to-temperature response. Ecol Evol. 2017; Aug. 7(18):7434–41.
Article28. Kilgour E, Rankin N, Ryan S, Pack R. Mucociliary function deteriorates in the clinical range of inspired air temperature and humidity. Intensive Care Med. 2004; Jul. 30(7):1491–4.
Article29. Sivan Y, Ben-Ari J, Soferman R, DeRowe A. Diagnosis of laryngomalacia by fiberoptic endoscopy: awake compared with anesthesia-aided technique. Chest. 2006; Nov. 130(5):1412–8.30. Ramprasad VH, Ryan MA, Farjat AE, Eapen RJ, Raynor EM. Practice patterns in supraglottoplasty and perioperative care. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016; Jul. 86:118–23.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Classification and Management in Patients with Laryngomalacia
- Supraglottoplasty in Congenital Laryngomalacia Patient Without Tracheostomy
- A Case of Acquired Transient Laryngomalacia Associated with Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- A Case of Aryepiglottoplasty with Apnea Technique in Laryngomalacia Patient
- One Case of Laser Microsurgery Management in Severe Laryngomalacia