Endocrinol Metab.
2021 Oct;36(5):1131-1141. 10.3803/EnM.2021.1149.
Metabolic Subtyping of Adrenal Tumors: Prospective Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 2Molecular Recognition Research Center, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- 10Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 12Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 13Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea
- 14Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 15Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2521960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1149
Abstract
- Background
Conventional diagnostic approaches for adrenal tumors require multi-step processes, including imaging studies and dynamic hormone tests. Therefore, this study aimed to discriminate adrenal tumors from a single blood sample based on the combination of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and machine learning algorithms in serum profiling of adrenal steroids.
Methods
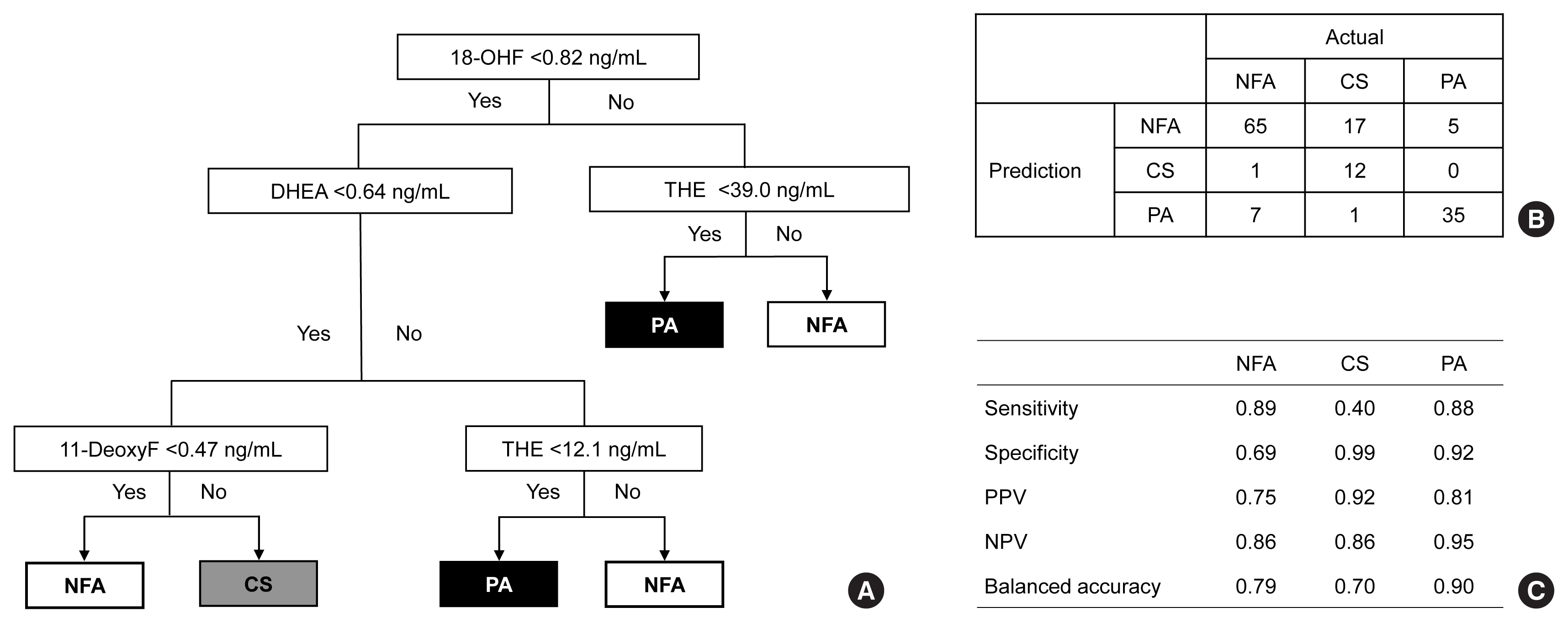
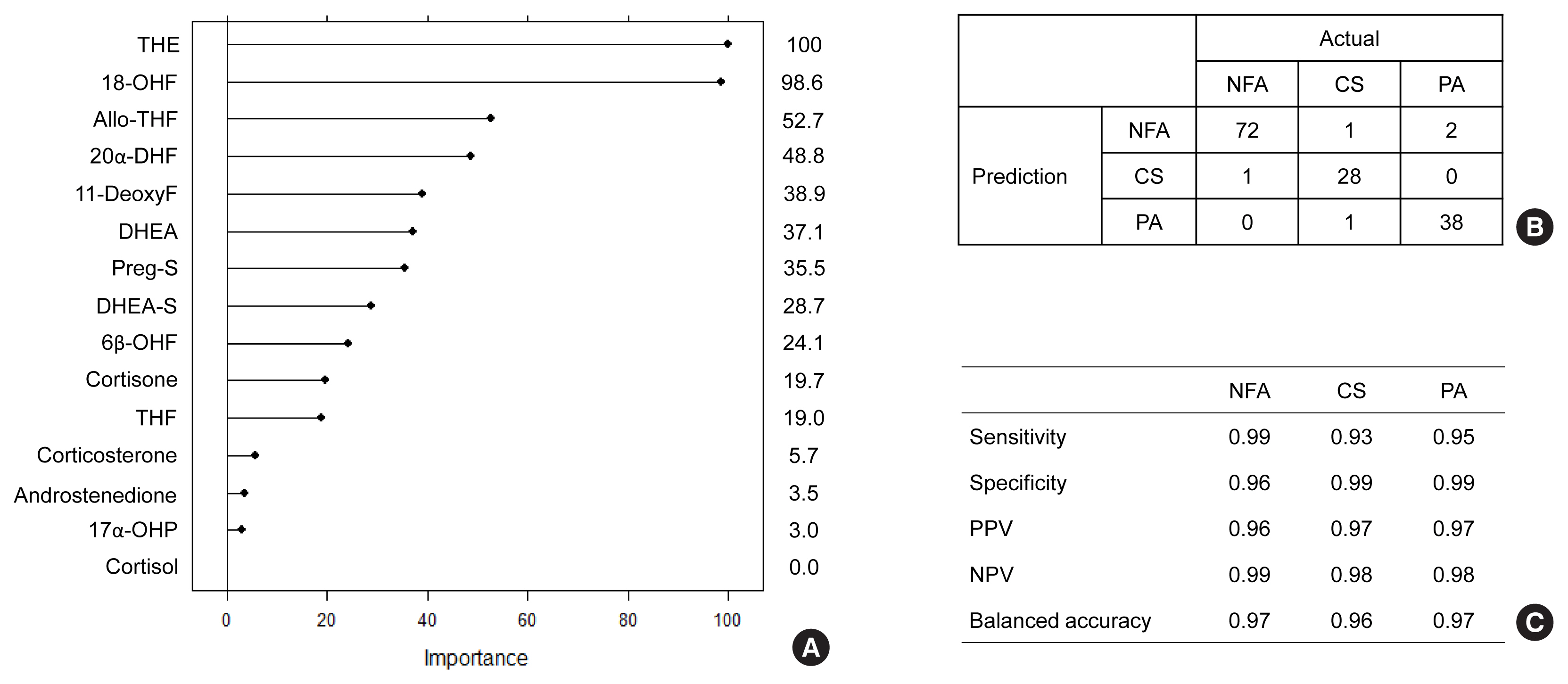
The LC-MS-based steroid profiling was applied to serum samples obtained from patients with nonfunctioning adenoma (NFA, n=73), Cushing’s syndrome (CS, n=30), and primary aldosteronism (PA, n=40) in a prospective multicenter study of adrenal disease. The decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), and extreme gradient boost (XGBoost) were performed to categorize the subtypes of adrenal tumors.
Results
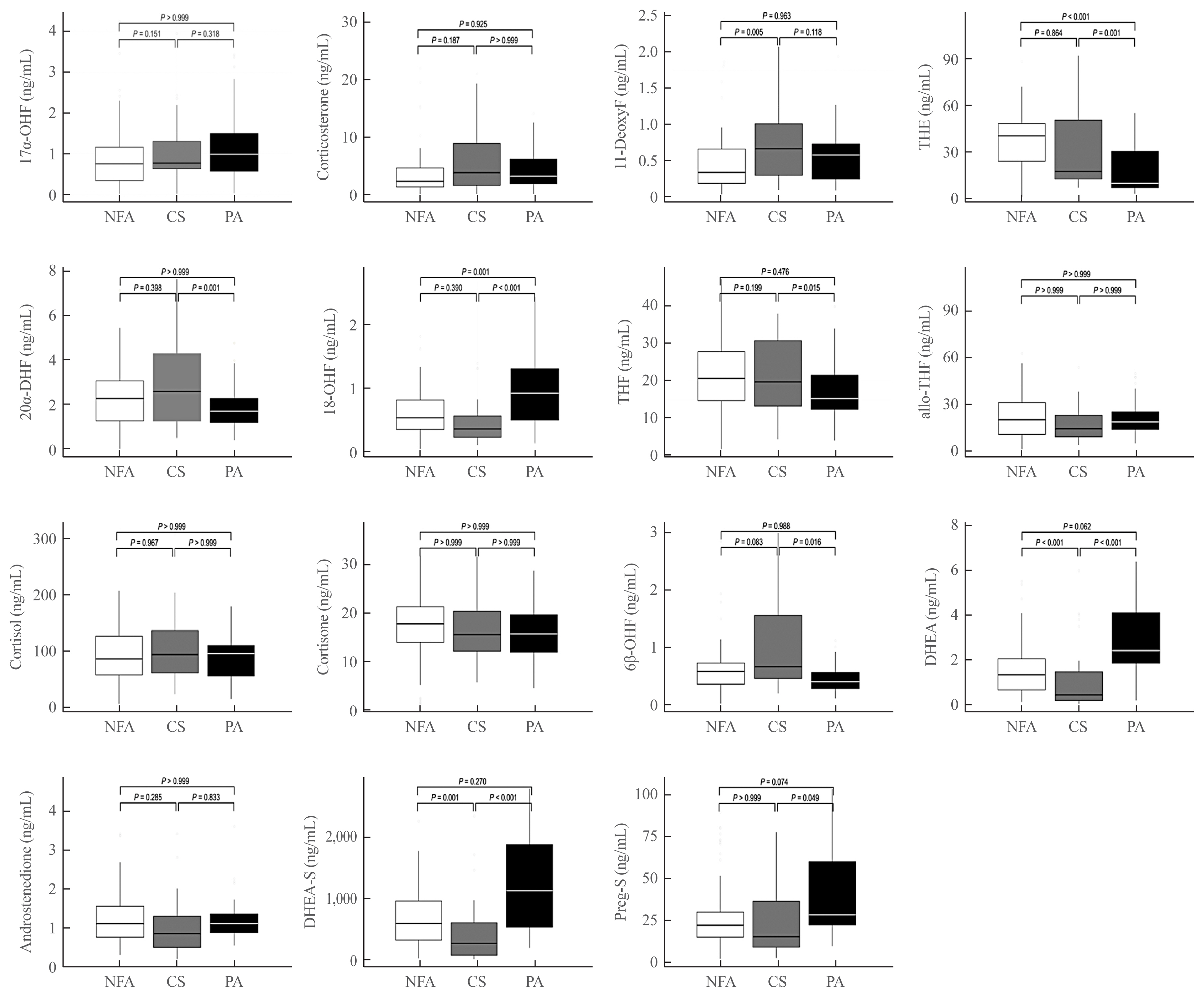
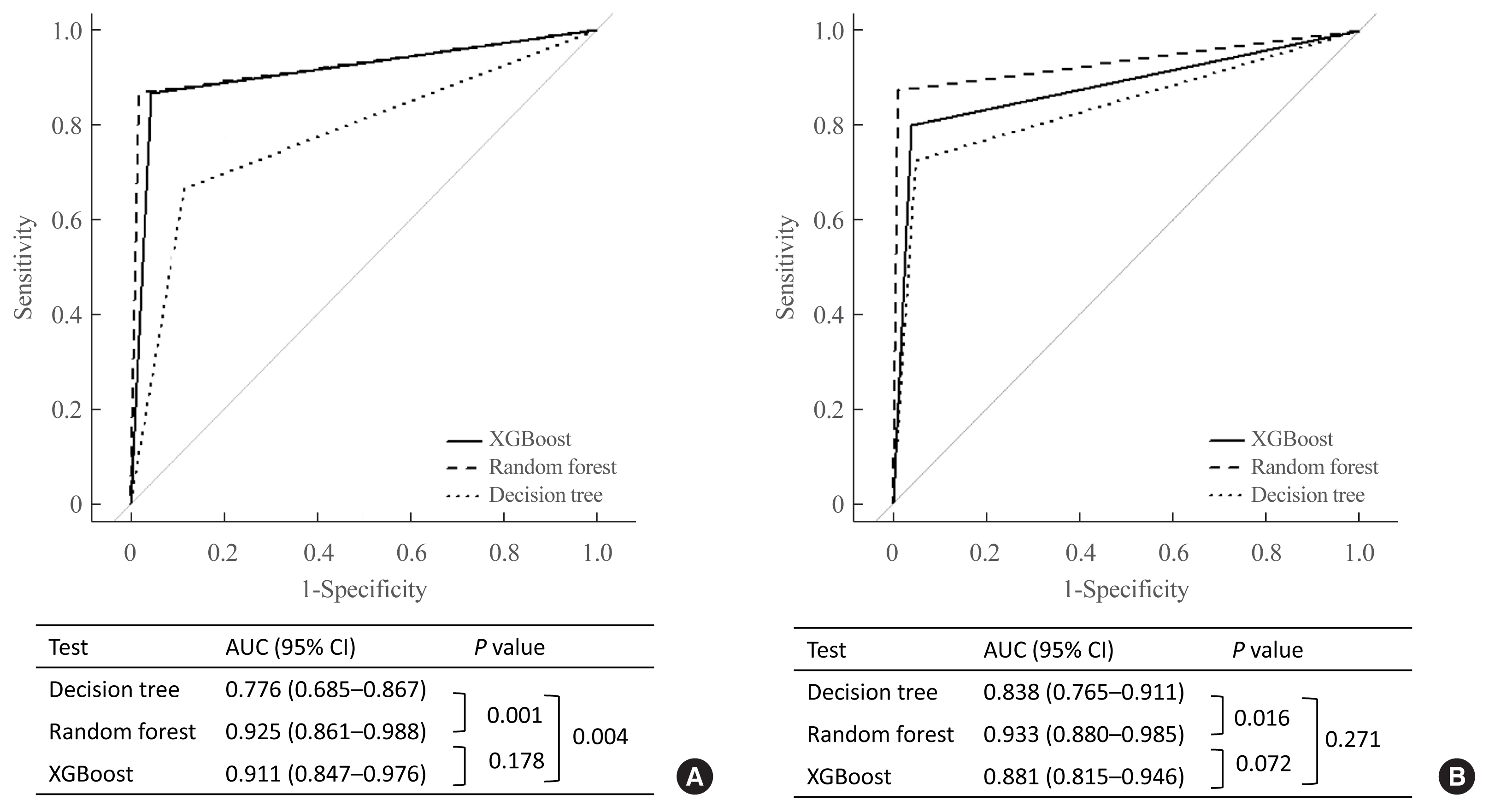
The CS group showed higher serum levels of 11-deoxycortisol than the NFA group, and increased levels of tetrahydrocortisone (THE), 20α-dihydrocortisol, and 6β-hydroxycortisol were found in the PA group. However, the CS group showed lower levels of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulfate derivative (DHEA-S) than both the NFA and PA groups. Patients with PA expressed higher serum 18-hydroxycortisol and DHEA but lower THE than NFA patients. The balanced accuracies of DT, RF, and XGBoost for classifying each type were 78%, 96%, and 97%, respectively. In receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis for CS, XGBoost, and RF showed a significantly greater diagnostic power than the DT. However, in ROC analysis for PA, only RF exhibited better diagnostic performance than DT.
Conclusion
The combination of LC-MS-based steroid profiling with machine learning algorithms could be a promising one-step diagnostic approach for the classification of adrenal tumor subtypes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kloos RT, Gross MD, Francis IR, Korobkin M, Shapiro B. Incidentally discovered adrenal masses. Endocr Rev. 1995; 16:460–84.
Article2. Grossman A, Koren R, Tirosh A, Michowiz R, Shohat Z, Rahamimov R, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of adrenal incidentalomas in potential kidney donors. Endocr Res. 2016; 41:98–102.
Article3. Young WF Jr. Clinical practice. The incidentally discovered adrenal mass. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:601–10.4. Fassnacht M, Arlt W, Bancos I, Dralle H, Newell-Price J, Sahdev A, et al. Management of adrenal incidentalomas: European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016; 175:G1–34.
Article5. Lee JM, Kim MK, Ko SH, Koh JM, Kim BY, Kim SW, et al. Clinical guidelines for the management of adrenal incidentaloma. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2017; 32:200–18.
Article6. Choi MH. Mass spectrometry-based steroid profiling: meeting unmet clinical needs. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2021; 253:171–80.
Article7. Arlt W, Biehl M, Taylor AE, Hahner S, Libe R, Hughes BA, et al. Urine steroid metabolomics as a biomarker tool for detecting malignancy in adrenal tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:3775–84.
Article8. Di Dalmazi G, Fanelli F, Mezzullo M, Casadio E, Rinaldi E, Garelli S, et al. Steroid profiling by LC-MS/MS in nonsecreting and subclinical cortisol-secreting adrenocortical adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:3529–38.
Article9. Lee C, Kim JH, Moon SJ, Shim J, Kim HI, Choi MH. Selective LC-MRM/SIM-MS based profiling of adrenal steroids reveals metabolic signatures of 17α-hydroxylase deficiency. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020; 198:105615.
Article10. Loriaux DL. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:1451–9.
Article11. Peitzsch M, Dekkers T, Haase M, Sweep FC, Quack I, Antoch G, et al. An LC-MS/MS method for steroid profiling during adrenal venous sampling for investigation of primary aldosteronism. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015; 145:75–84.
Article12. El-Maouche D, Arlt W, Merke DP. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet. 2017; 390:2194–210.
Article13. Eisenhofer G, Duran C, Cannistraci CV, Peitzsch M, Williams TA, Riester A, et al. Use of steroid profiling combined with machine learning for identification and subtype classification in primary aldosteronism. JAMA Netw Open. 2020; 3:e2016209.
Article14. Chortis V, Bancos I, Nijman T, Gilligan LC, Taylor AE, Ronchi CL, et al. Urine steroid metabolomics as a novel tool for detection of recurrent adrenocortical carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 105:e307–18.
Article15. Erlic Z, Reel P, Reel S, Amar L, Pecori A, Larsen CK, et al. Targeted metabolomics as a tool in discriminating endocrine from primary hypertension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021; 106:1111–28.
Article16. Ahn CH, Lee C, Shim J, Kong SH, Kim SJ, Kim YH, et al. Metabolic changes in serum steroids for diagnosing and subtyping Cushing’s syndrome. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2021; 210:105856.
Article17. Funder JW, Carey RM, Mantero F, Murad MH, Reincke M, Shibata H, et al. The management of primary aldosteronism: case detection, diagnosis, and treatment: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 101:1889–916.
Article18. Breiman L. Random forests. Mach Learn. 2001; 45:5–32.19. Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. arXiv. 2016. Jun. 10. https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.02754 .20. Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, Stewart PM, et al. The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:1526–40.
Article21. Eisenhofer G, Masjkur J, Peitzsch M, Di Dalmazi G, Bidlingmaier M, Gruber M, et al. Plasma steroid metabolome profiling for diagnosis and subtyping patients with Cushing syndrome. Clin Chem. 2018; 64:586–96.
Article22. Masjkur J, Gruber M, Peitzsch M, Kaden D, Di Dalmazi G, Bidlingmaier M, et al. Plasma steroid profiles in subclinical compared with overt adrenal Cushing syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019; 104:4331–40.
Article23. Katz FH, Lipman MM, Frantz AG, Jailer JW. The physiologic significance of 6beta-hydroxycortisol in human corticoid metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962; 22:71–7.24. Di Dalmazi G, Fanelli F, Zavatta G, Ricci Bitti S, Mezzullo M, Repaci A, et al. The steroid profile of adrenal incidentalomas: subtyping subjects with high cardiovascular risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019; 104:5519–28.
Article25. Melmed S, Williams RH. Williams textbook of endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2019. Chapter 15:The adrenal cortex. p. 480–541.26. Yener S, Yilmaz H, Demir T, Secil M, Comlekci A. DHEAS for the prediction of subclinical Cushing’s syndrome: perplexing or advantageous? Endocrine. 2015; 48:669–76.
Article27. Cunningham SK, McKenna TJ. Dissociation of adrenal androgen and cortisol secretion in Cushing’s syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1994; 41:795–800.
Article28. Pepping J. DHEA: dehydroepiandrosterone. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2000; 57:2048–50.
Article29. Perrini S, Laviola L, Natalicchio A, Giorgino F. Associated hormonal declines in aging: DHEAS. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005; 28(3 Suppl):85–93.30. Ulick S, Chu MD. Hypersecretion of a new corticosteroid, 18-hydroxycortisol in two types of adrenocortical hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1982; 4:1771–7.
Article31. Lenders J, Williams TA, Reincke M, Gomez-Sanchez CE. Diagnosis of endocrine disease: 18-oxocortisol and 18-hydroxycortisol. Is there clinical utility of these steroids? Eur J Endocrinol. 2018; 178:R1–9.
Article32. Mulatero P, di Cella SM, Monticone S, Schiavone D, Manzo M, Mengozzi G, et al. 18-Hydroxycorticosterone, 18-hydroxycortisol, and 18-oxocortisol in the diagnosis of primary aldosteronism and its subtypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:881–9.
Article33. Eisenhofer G, Dekkers T, Peitzsch M, Dietz AS, Bidlingmaier M, Treitl M, et al. Mass spectrometry-based adrenal and peripheral venous steroid profiling for subtyping primary aldosteronism. Clin Chem. 2016; 62:514–24.
Article34. Hong AR, Kim JH, Song YS, Lee KE, Seo SH, Seong MW, et al. Genetics of aldosterone-producing adenoma in Korean patients. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0147590.
Article35. Satoh F, Morimoto R, Ono Y, Iwakura Y, Omata K, Kudo M, et al. Measurement of peripheral plasma 18-oxocortisol can discriminate unilateral adenoma from bilateral diseases in patients with primary aldosteronism. Hypertension. 2015; 65:1096–102.
Article36. Hawkins DM. The problem of overfitting. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 2004; 44:1–12.
Article37. Butler KT, Davies DW, Cartwright H, Isayev O, Walsh A. Machine learning for molecular and materials science. Nature. 2018; 559:547–55.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Experiences of Adrenal Tumors: Studies on the Localization of Adrenal Tumors
- 5 Cases of Primary Adrenal Tumors
- Arteriography of the adrenal tumors
- A Prospective Cohort Study on Predictive Risk Factors Causing Metabolic Syndrome within the First Two Years
- Clinical Experience of Adrenal Tumors Treated by Surgical Management