Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2021 Oct;23(2):126-129. 10.14253/acn.2021.23.2.126.
Autonomic dysfunction in postoperative primitive neuroectodermal tumor of heart
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, All India Institute of Medical Science, New Delhi, India
- 2Department of Medical Oncology, All India Institute of Medical Science, New Delhi, India
- KMID: 2521891
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2021.23.2.126
Abstract
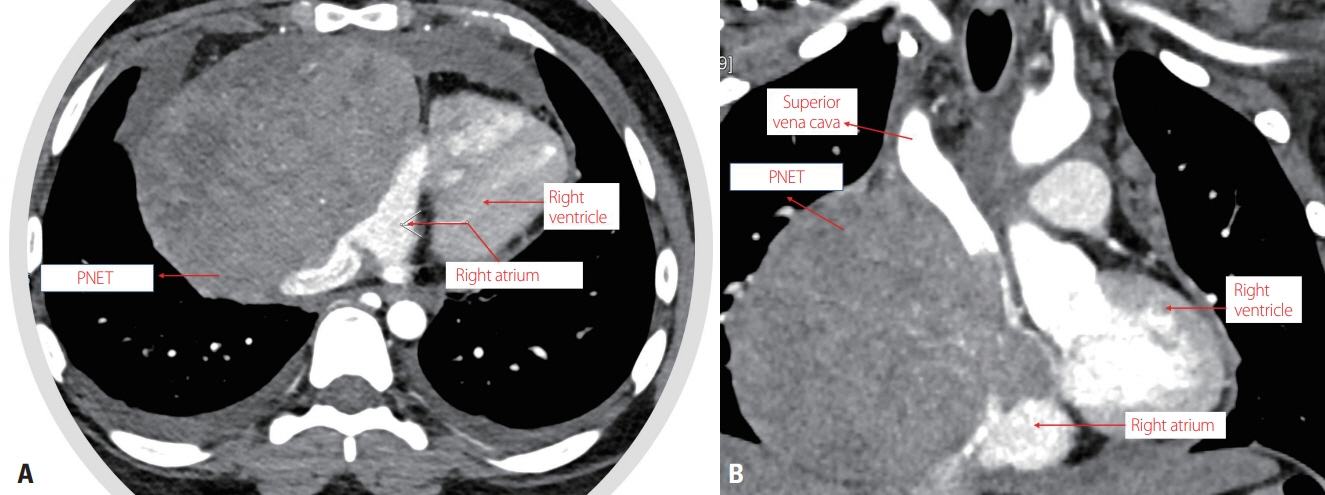
- We present a patient with a primitive neuroectodermal tumor arising from the right atrium who experienced multiple syncope episodes daily, which had first appeared 1 month after surgery. The symptoms continued to worsen over the course of chemotherapy, and the autonomic function test (AFT) was performed after the 14th chemotherapy cycle. The AFT revealed orthostatic hypotension and reduced baroreflex-dependent sympathetic reactivity. Physical counterpressure techniques were applied with a visual biofeedback intervention, and were found to be effective in reducing the syncope episodes.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Beşirli K, Arslan C, Tüzün H, Oz B. The primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the heart. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2000; 18:619–621.
Article2. Ushigusa J, Mukae Y, Takamatsu M, Nogami E, Furutachi A, Itoh M, et al. Adult-onset primary Ewing’s sarcoma of the right atrium: a case report. Surg Case Rep. 2019; 5:171.
Article3. Grier HE, Krailo MD, Tarbell NJ, Link MP, Fryer CJ, Pritchard DJ, et al. Addition of ifosfamide and etoposide to standard chemotherapy for Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor of bone. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:694–701.
Article4. Wieling W, van Dijk N, Thijs RD, de Lange FJ, Krediet CT, Halliwill JR. Physical countermeasures to increase orthostatic tolerance. J Intern Med. 2015; 277:69–82.
Article5. Higgins JC, Katzman PJ, Yeager SB, Dickerman JD, Leavitt BJ, Tischler MD, et al. Extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma of primary cardiac origin. Pediatr Cardiol. 1994; 15:207–208.
Article6. Cai CQ, Zhang QJ, Shen CH, Hu XL. Primary intraspinal primitive neuroectodermal tumor: a case report and review of literature. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2008; 3:154–156.
Article7. Nwaejike N, Rassl D, Ford H, Large SR. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the heart. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012; 93:e27–e29.
Article8. Demir A, Gunluoglu MZ, Dagoglu N, Turna A, Dizdar Y, Kaynak K, et al. Surgical treatment and prognosis of primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the thorax. J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:185–192.
Article9. Macarthur H, Wilken GH, Westfall TC, Kolo LL. Neuronal and non-neuronal modulation of sympathetic neurovascular transmission. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011; 203:37–45.
Article10. Charlton NP, Pellegrino JL, Kule A, Slater TM, Epstein JL, Flores GE, et al. 2019 American Heart Association and American Red Cross Focused Update for First Aid: presyncope: an update to the American Heart Association and American Red Cross Guidelines for First Aid. Circulation. 2019; 140:e931–e938.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of the Kidney with CD99 Positive Staining
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of Mediastinum in an Adult: A Case Report
- A Case of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor in the Nasal Cavity
- Primitive neuroectodermal tumor; CT findings
- A Case of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor in the Maxillary Sinus