J Stroke.
2021 Sep;23(3):401-410. 10.5853/jos.2021.00962.
Effectiveness of Thrombectomy in Stroke According to Baseline Prognostic Factors: Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting Analysis of a Population-Based Registry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Comprehensive Stroke Center, Department of Neuroscience, Hospital Clínic of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
- 2Clinical and Experimental Neuroscience: Cerebrovascular Diseases, August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS), Barcelona, Spain
- 3Medical Statistics Core Facility, August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS) and Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain
- 4Biostatistics Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Autonomous University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
- 5Stroke Unit, Department of Neuroscience, Germans Trias Hospital, Badalona, Spain
- 6Department of Neurology, Moisès-Broggi Hospital, Sant Joan Despí, Spain
- 7Department of Neurology, Althaia Foundation Hospital, Manresa, Spain
- 8Stroke Unit, Department of Neurology, University Hospital Arnau of Vilanova, Lleida, Spain
- 9Stroke Unit, Department of Neurology, Josep Trueta University Hospital, Girona, Spain
- 10Stroke Unit, Department of Neurology, Santa Creu i Sant Pau, Barcelona, Spain
- 11Stroke Unit, Department of Neurology, Bellvitge University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain
- 12Stroke Unit, Department of Neurology, Vall d'Hebron University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain
- 13Stroke Unit, Department of Neurology, Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, Spain
- 14Department of Neurology, Parc Taulí Hospital, Sabadell, Spain
- 15Department of Neurology, Mutua de Terrassa University Hospital, Terrassa, Spain
- 16Stroke Unit, Department of Neurology, Joan XXIII University Hospital, Terragona, Spain
- 17Department of Radiology, Hospital Clínic of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
- 18Department of Health, Pla Director Malaltia Vascular Cerebral (Catalan Stroke Program), Barcelona, Spain
- 19Emergency Medical Services of Catalonia, Barcelona, Spain
- 20Department of Neurology, Hospital of Mataró, Mataró, Spain
- 21Department of Neurology, Consorci Sanitari Garraf Hospital, Sant Pere de Ribes, Spain
- 22Department of Emergency, Hospital of Igualada, Igualada, Spain
- 23Department of Emergency, Hospital of Granollers, Granollers, Spain
- 24Department of Emergency, Verge de la Cinta Hospital, Tortosa, Spain
- 25Department of Emergency, Vic University Hospital, Vic, Spain
- 26Department of Emergency, Hospital of Campdevànol, Campdevànol, Spain
- 27Department of Emergency, Hospital of Figueres, Figueres, Spain
- 28Department of Emergency, Hospital of Palamós, Palamós, Spain
- 29Department of Emergency, Hospital of Olot, Olot, Spain
- 30Department of Emergency, Cerdanya Hospital, Puigcerdá, Spain
- 31Department of Emergency, Hospital of Móra d’Ebre, Móra d’Ebre, Spain
- 32Department of Emergency, Seu d’Urgell Hospital, Seu d’Urgell, Spain
- 33Department of Emergency, Hospital of Tremp, Tremp, Spain
- 34University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
- KMID: 2520917
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2021.00962
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
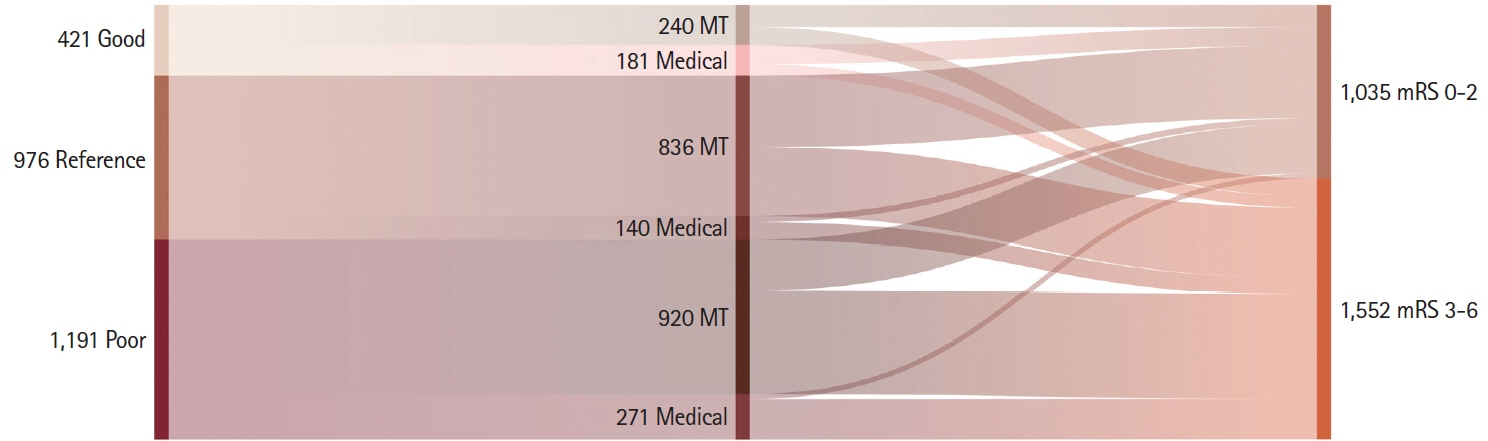
In real-world practice, the benefit of mechanical thrombectomy (MT) is uncertain in stroke patients with very favorable or poor prognostic profiles at baseline. We studied the effectiveness of MT versus medical treatment stratifying by different baseline prognostic factors. Methods Retrospective analysis of 2,588 patients with an ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion nested in the population-based registry of stroke code activations in Catalonia from January 2017 to June 2019. The effect of MT on good functional outcome (modified Rankin Score ≤2) and survival at 3 months was studied using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis in three pre-defined baseline prognostic groups: poor (if pre-stroke disability, age >85 years, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale [NIHSS] >25, time from onset >6 hours, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score <6, proximal vertebrobasilar occlusion, supratherapeutic international normalized ratio >3), good (if NIHSS <6 or distal occlusion, in the absence of poor prognostic factors), or reference (not meeting other groups’ criteria).
Results
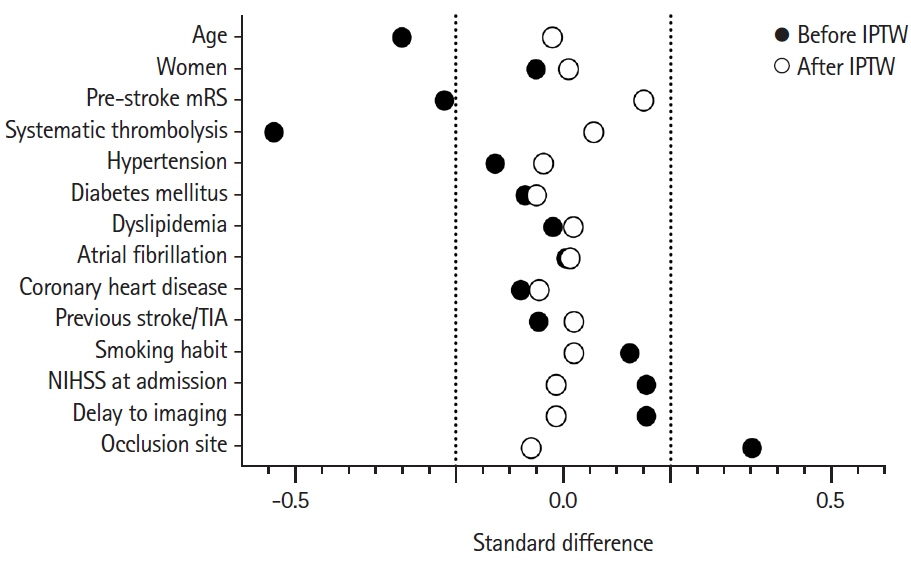
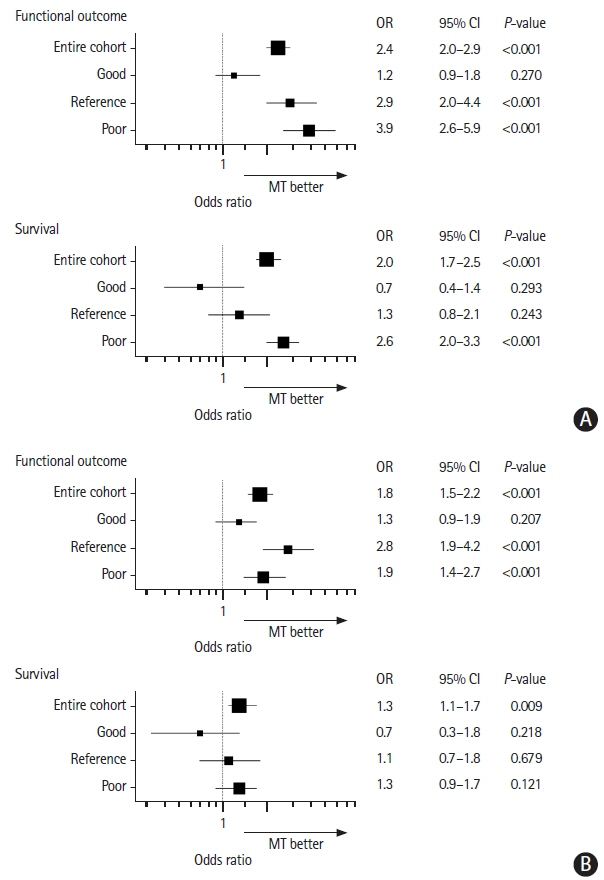
Patients receiving MT (n=1,996, 77%) were younger, had less pre-stroke disability, and received systemic thrombolysis less frequently. These differences were balanced after the IPTW stratified by prognosis. MT was associated with good functional outcome in the reference (odds ratio [OR], 2.9; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.0 to 4.4), and especially in the poor baseline prognostic stratum (OR, 3.9; 95% CI, 2.6 to 5.9), but not in the good prognostic stratum. MT was associated with survival only in the poor prognostic stratum (OR, 2.6; 95% CI, 2.0 to 3.3).
Conclusions
Despite their worse overall outcomes, the impact of thrombectomy over medical management was more substantial in patients with poorer baseline prognostic factors than patients with good prognostic factors.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Broderick JP, Palesch YY, Demchuk AM, Yeatts SD, Khatri P, Hill MD, et al. Endovascular therapy after intravenous t-PA versus t-PA alone for stroke. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:893–903.
Article2. Chimowitz MI. Endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke—still unproven. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:952–955.3. Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after largevessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 2016; 387:1723–1731.
Article4. Urra X, Abilleira S, Dorado L, Ribó M, Cardona P, Millán M, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in and outside the REVASCAT trial: insights from a concurrent population-based stroke registry. Stroke. 2015; 46:3437–3442.5. Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, Bonafe A, Budzik RF, Bhuva P, et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:11–21.6. Albers GW, Marks MP, Kemp S, Christensen S, Tsai JP, OrtegaGutierrez S, et al. Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:708–718.
Article7. Sarraj A, Hassan AE, Savitz S, Sitton C, Grotta J, Chen P, et al. Outcomes of endovascular thrombectomy vs medical management alone in patients with large ischemic cores: a secondary analysis of the optimizing patient's selection for endovascular treatment in acute ischemic stroke (SELECT) study. JAMA Neurol. 2019; 76:1147–1156.8. Renú A, Laredo C, Montejo C, Zhao Y, Rudilosso S, Macias N, et al. Greater infarct growth limiting effect of mechanical thrombectomy in stroke patients with poor collaterals. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019; 11:989–993.
Article9. Renú Jornet A, Urra X, Laredo C, Montejo C, Rudilosso S, Llull L, et al. Benefit from mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke with fast and slow progression. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020; 12:132–135.
Article10. Román LS, Menon BK, Blasco J, Hernández-Pérez M, Dávalos A, Majoie CBLM, et al. Imaging features and safety and efficacy of endovascular stroke treatment: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data. Lancet Neurol. 2018; 17:895–904.11. Kaesmacher J, Chaloulos-Iakovidis P, Panos L, Mordasini P, Michel P, Hajdu SD, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in ischemic stroke patients with alberta stroke program early computed tomography score 0-5. Stroke. 2019; 50:880–888.
Article12. Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet. 1998; 352:1245–1251.13. Khatri P, Hill MD, Palesch YY, Spilker J, Jauch EC, Carrozzella JA, et al. Methodology of the interventional management of stroke III trial. Int J Stroke. 2008; 3:130–137.
Article14. Austin PC, Stuart EA. Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat Med. 2015; 34:3661–3679.
Article15. Austin PC. Using the standardized difference to compare the prevalence of a binary variable between two groups in observational research. Commun Stat Simul Comput. 2009; 38:1228–1234.
Article16. Austin PC. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat Med. 2009; 28:3083–3107.
Article17. Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc Series B Methodol. 1977; 39:1–22.18. Bender R, Blettner M. Calculating the "number needed to be exposed" with adjustment for confounding variables in epidemiological studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2002; 55:525–530.
Article19. Bender R, Kuss O, Hildebrandt M, Gehrmann U. Estimating adjusted NNT measures in logistic regression analysis. Stat Med. 2007; 26:5586–5595.
Article20. Sarraj A, Hassan A, Savitz SI, Grotta JC, Cai C, Parsha KN, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy for mild strokes: how low should we go? Stroke. 2018; 49:2398–2405.
Article21. Urra X, San Román L, Gil F, Millán M, Cánovas D, Roquer J, et al. Medical and endovascular treatment of patients with large vessel occlusion presenting with mild symptoms: an observational multicenter study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014; 38:418–424.
Article22. Goyal N, Tsivgoulis G, Malhotra K, Ishfaq MF, Pandhi A, Frohler MT, et al. Medical management vs mechanical thrombectomy for mild strokes: an international multicenter study and systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2020; 77:16–24.23. Groot AE, Treurniet KM, Jansen IGH, Lingsma HF, Hinsenveld W, van de Graaf RA, et al. Endovascular treatment in older adults with acute ischemic stroke in the MR CLEAN Registry. Neurology. 2020; 95:e131–e139.
Article24. Ospel JM, Goyal M. Cherry-picking the wrong patients has to be avoided at all cost! Clin Neuroradiol. 2020; 30:43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Impact of Left Atrial or Left Atrial Appendage Thrombus on Stroke Outcome: A Matched Control Analysis
- Differences in Effectiveness among Devices for Endovascular Thrombectomy in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Epidemiology and Registry Studies of Stroke in Japan
- Intravenous Thrombolysis and Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke with Minor Symptom
- Comparison between Nivolumab and Regorafenib as Second-line Systemic Therapies after Sorafenib Failure in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma