Korean J Transplant.
2021 Sep;35(3):200-206. 10.4285/kjt.21.0005.
Reusing hepatic grafts in Korea: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Korea Organ Donation Agency, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2520689
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.21.0005
Abstract
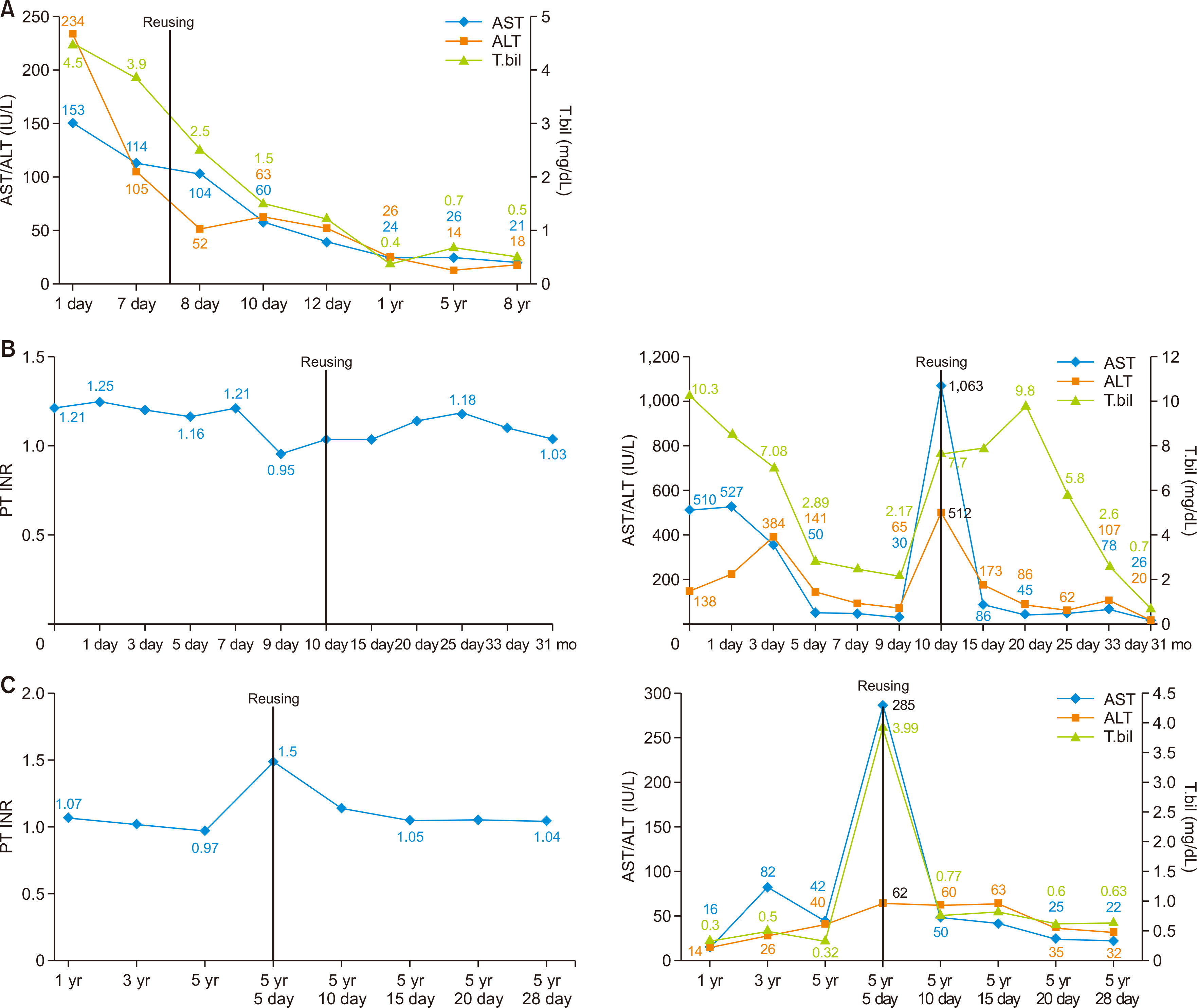
- The shortage of donor organs has compelled transplant centers to use organs from non-standard donors. The Korean Network for Organ Sharing data showed that there were 5,804 potential recipients on the waiting list, and only 1,579 patients underwent liver transplant in 2019. Reuse of a graft that has been transplanted previously to other recipients could be an option in this situation. However, given the susceptibility of hepatic grafts to ischemic damage, their reuse must be considered extremely carefully. In this retrospective, observational study, we investigated the outcomes of six cases of hepatic graft reuse in Korea since the year 2000, from information gathered from patient medical records from ten transplant centers. Only three of the six reused hepatic grafts functioned well. Among the three successful transplants, two had minimal ischemic damage owing to a longer interval between the first and second transplants, and because they were obtained from living donors. Two of the five cadaveric transplants were successful. The outcome of reusing hepatic grafts in Korea has not been ideal. However, in patients with limited choices, it can be carefully considered, provided the graft is thoroughly checked for ischemic damage and the recipient status is ascertained.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). 2020. KONOS waiting list [Internet]. KONOS;Seoul: Available from: https://www.konos.go.kr. cited 2021 Sep 1.2. Rampes S, Ma D. 2019; Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in liver transplant setting: mechanisms and protective strategies. J Biomed Res. 33:221–34.3. Woo EJ, Kim M, Choi YJ, Lee J, Cho WH, Park CI, et al. 2021; Outcomes of reused transplanted kidneys using cases from the Korean Network for Organ Sharing database. Korean J Transplant. 35:112–5. DOI: 10.4285/kjt.21.0003.
Article4. Kim MJ, Hwang S, Jung DH, Park GC, Song GW, Cho HD, et al. 2020; Reuse of liver allograft from a brain-dead recipient: a case report. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 24:192–7. DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.2.192. PMID: 32457266. PMCID: PMC7271115.
Article5. Hu XG, Kim IG, Wang HJ, Kim BW, Hong SY, Kim YB, et al. 2018; Reuse of living-donor liver graft in second recipient with long-term survival. Transplant Proc. 50:3984–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.03.004. PMID: 30577301.
Article6. Ortiz J, Reich DJ, Manzarbeitia C, Humar A. 2005; Successful re-use of liver allografts: three case reports and a review of the UNOS database. Am J Transplant. 5:189–92. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00635.x. PMID: 15636629.
Article7. Rubay R, Wittebolle X, Ciccarelli O, Roggen F, Talpe S, Laterre PF, et al. 2003; Re-use of a liver allograft; an exceptional opportunity to enlarge the organ donor pool. Transpl Int. 16:497–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2003.tb00355.x. PMID: 12712236.
Article8. Tanaka H, McAlister VC, Levstik MA, Ghent CN, Marotta PJ, Quan D, et al. 2014; Reuse of liver grafts following the brain death of the initial recipient. World J Hepatol. 6:443–7. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i6.443. PMID: 25018855. PMCID: PMC4081619.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reusing of Anterior Tibial Artery Used as a Recipient Vessel during the First Surgery for Reconstruction of Foot Burns: A Case Report
- Tailored techniques of graft outflow vein reconstruction in pediatric liver transplantation at Asan Medical Center
- Effect of Microsurgery Training Program for Hepatic Artery Reconstruction in Liver Transplantation
- Human dermis as a new substitute for middle hepatic vein during living donor liver transplantation: early results from ongoing clinical trial
- Outflow vein venoplasty of left lateral section graft for living donor liver transplantation in infant recipients