Blood Res.
2021 Sep;56(3):201-202. 10.5045/br.2021.2020245.
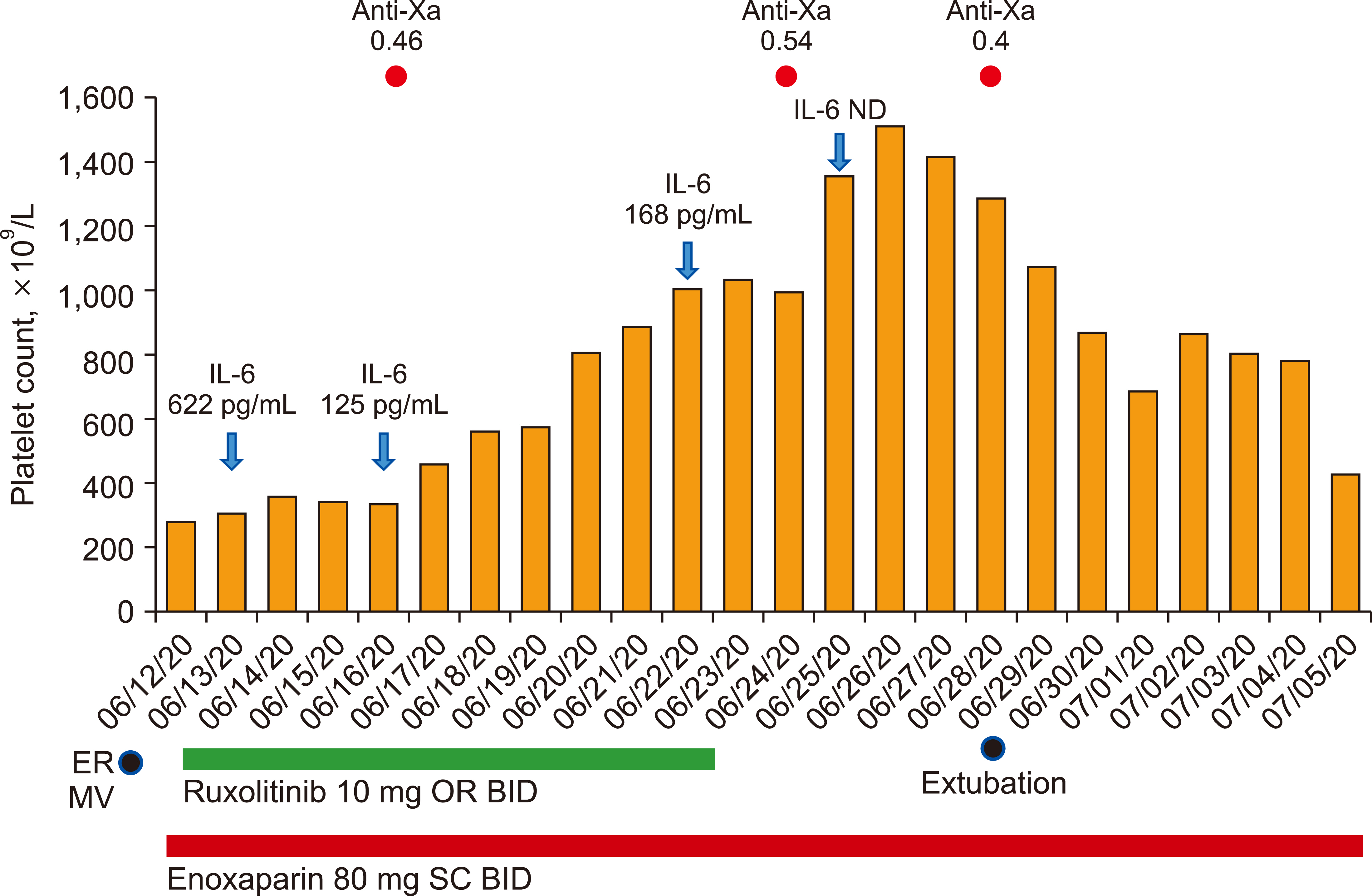
Ruxolitinib-induced extreme thrombocytosis in a COVID-19 patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology, National Institute of Cardiology Ignacio Chávez, Mexico City, Mexico.
- 2Department of Pharmacovigilance, National Institute of Cardiology Ignacio Chávez, Mexico City, Mexico.
- 3Department of Intensive Care Unit, National Institute of Cardiology Ignacio Chávez, Mexico City, Mexico.
- KMID: 2520614
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2021.2020245
Abstract
- No abstract available
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cao Y, Wei J, Zou L, et al. 2020; Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 146:137–46. e3DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.019. PMID: 32470486. PMCID: PMC7250105.2. Giudice V, Pagliano P, Vatrella A, et al. 2020; Combination of ruxolitinib and eculizumab for treatment of severe SARS-CoV-2-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a controlled study. Front Pharmacol. 11:857. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00857. PMID: 32581810. PMCID: PMC7291857.
Article3. Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ, Griesshammer M, et al. 2015; Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med. 372:426–35. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409002. PMID: 25629741. PMCID: PMC4358820.
Article4. Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, et al. 2012; A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 366:799–807. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110557. PMID: 22375971. PMCID: PMC4822164.
Article5. Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, et al. 2012; JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 366:787–98. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110556. PMID: 22375970.
Article6. Zeiser R, von Bubnoff N, Butler J, et al. 2020; Ruxolitinib for glucocorticoid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 382:1800–10. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1917635. PMID: 32320566.
Article7. Polverelli N, Catani L, Vianelli N, Baccarani M, Cavo M, Palandri F. 2015; Ruxolitinib- but not fedratinib-induced extreme thrombocytosis: the combination therapy with hydroxyurea and ruxolitinib is effective in reducing platelet count and splenomegaly/constitutional symptoms. Ann Hematol. 94:1585–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00277-015-2397-9. PMID: 25975976.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prolonged Extreme Thrombocytosis in a Postsplenectomy Patient with Hereditary Spherocytosis
- Contemporary Review of Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19
- Tracheostomy in the Era of COVID-19 Pandemic
- Ruxolitinib and Severe COVID-19
- Ruxolitinib and the Mitigation of Severe COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis