J Rheum Dis.
2021 Oct;28(4):183-191. 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.183.
Epidemiologic and Etiological Features of Korean Patients With Behçet’s Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 2Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2520431
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.183
Abstract
- Behçet’s disease (BD) is a multisystem disease in which environmental factors provoke an adverse immune response in patients with genetic susceptibility towards BD, subsequently leading to a cascade of dysregulated inflammation throughout the body. It is particularly prevalent in regions spanning the ancient Silk Road, including Korea, where the first known case of BD was reported in 1961. We summarize the history, epidemiology, and clinical presentation of BD in Korea, highlighting the clinical tendencies that are particularly seen in the Korean BD population as compared to European populations. Analysis of epidemiologic trends over the past three decades in Korea shows a decreasing prevalence of complete BD and a higher prevalence of intestinal BD. We also discuss the ever-evolving understanding of the pathogenesis of BD, noting the complex interplay among genetics, environment, and immunology. The HLA-B51 allele is the most significant known genetic risk factor in developing BD. We also discuss more recently studied associations between BD and immune factors such as IL-10, IL-23R-IL-12RB2, IL-1A-IL-1B, CCR1, ERAP1, and the GIMAP cluster, the last of which has been found to have an association with BD specifically in Korea. Environmental factors such as pollution and microbials are often the inciting event in developing BD, as they trigger an imbalanced immune response in genetically susceptible individuals, one that has been often found to exhibit an aberrant Th1/Th17 response. There would be value to further studying the pathogenesis and clinical characteristics of Korean BD.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Joo CR. 1961; Two cases of Behçet's syndrome. J Cathol Med Coll. 5:393–400.2. Kim D. 1962; Behcet's syndrome: a report of four cases including one with extreme systemic manifestations. J Korean Med Assoc. 5:52–58.3. Bang D, Lee ES, Lee S. 2011. Behçet's disease. Paper presented at: 22nd World Congress of Dermatology. 2011 May 24-29; Seoul, Korea.4. Bang D, Lee ES, Sohn S, Kim DY, Cho S, Choi MJ. 2013. Behçet's disease in Korea. Hanuri Publishing Co.;Seoul:5. International Society for Behçet's Disease. 2000. In : 8-9th Inter-national Conference on Behçet's Disease; 1998 Oct 7-9, 2000 May 27-29; Emilia, Italy, Seoul, Korea. Design Mecca Publishing Co.;Seoul:6. Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet's disease. 1990; International Study Group for Behçet's Disease. Lancet. 335:1078–80. DOI: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92643-V.7. International Team for the Revision of the International Criteria for Behçet's Disease (ITR-ICBD). 2014; The International Criteria for Behçet's Disease (ICBD): a collaborative study of 27 countries on the sensitivity and specificity of the new criteria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 28:338–47. DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12107. PMID: 23441863.8. Kim DY, Choi MJ, Cho S, Kim DW, Bang D. 2014; Changing clinical expression of Behçet disease in Korea during three decades (1983-2012): chronological analysis of 3674 hospital-based patients. Br J Dermatol. 170:458–61. DOI: 10.1111/bjd.12661. PMID: 24117362.9. Bang D, Lee JH, Lee ES, Lee S, Choi JS, Kim YK, et al. 2001; Epidemiologic and clinical survey of Behcet's disease in Korea: the first multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci. 16:615–8. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2001.16.5.615. PMID: 11641532. PMCID: PMC3057606.10. Davatchi F, Sadeghi Abdollahi B, Chams-Davatchi C, Shahram F, Shams H, Nadji A, et al. 2015; The saga of diagnostic/classification criteria in Behcet's disease. Int J Rheum Dis. 18:594–605. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.12520. PMID: 25879654.
Article11. Mizushima Y. 1988; Revised diagnostic criteria for Behçet's disease in 1987. Ryumachi. 28:66–70. Japanese. PMID: 3388149.12. Chang HK, Lee SS, Bai HJ, Lee YW, Yoon BY, Lee CH, et al. 2004; Validation of the classification criteria commonly used in Korea and a modified set of preliminary criteria for Behçet's disease: a multi-center study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 22(4 Suppl 34):S21–6.13. Chang HK, Kim SY. 2003; Survey and validation of the criteria for Behcet's disease recently used in Korea: a suggestion for modification of the International Study Group criteria. J Korean Med Sci. 18:88–92. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2003.18.1.88. PMID: 12589093. PMCID: PMC3054980.
Article14. Kirino Y, Nakajima H. 2019; Clinical and genetic aspects of Behçet's disease in Japan. Intern Med. 58:1199–207. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2035-18. PMID: 30626832. PMCID: PMC6543215.
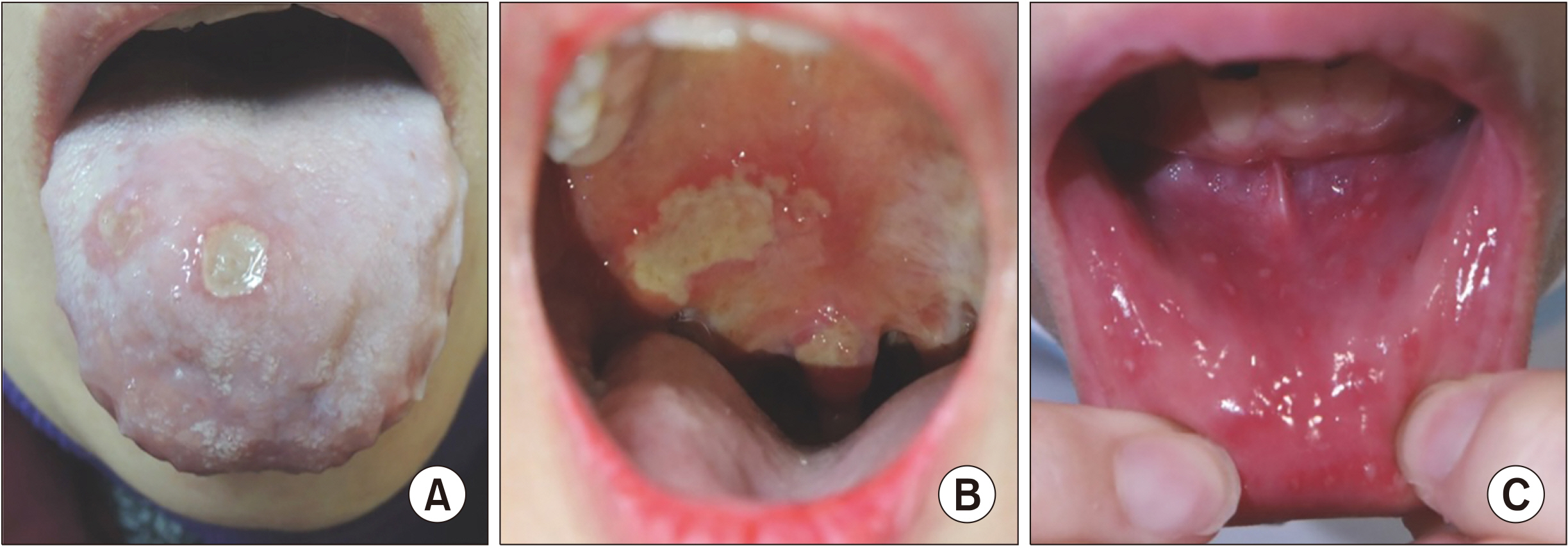
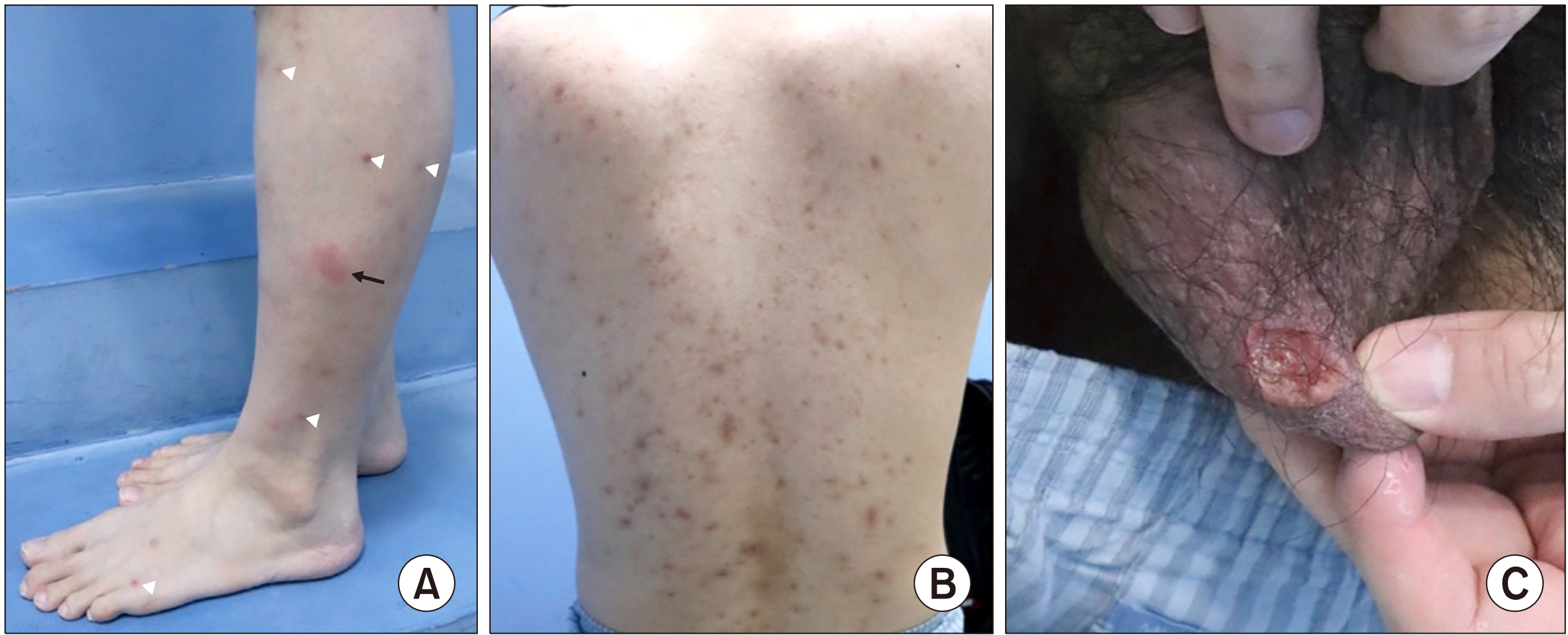
Article15. Lee ES, Bang D, Lee S. 1997; Dermatologic manifestation of Behçet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 38:380–9. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.1997.38.6.380. PMID: 9509907.
Article16. Oh BL, Lee JS, Lee EY, Lee HY, Yu HG. 2020; Apr. 15. Incidence and risk factors for blindness in uveitis: a nationwide cohort study from 2002 to 2013. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. [Epub]. DOI:10.1080/09273948.2020.1746352. DOI: 10.1080/09273948.2020.1746352. PMID: 32293927.
Article17. Lee NH, Bae M, Jin M, Chung SW, Lee CW, Jeon CH. 2020; Characterization of venous involvement in vasculo-Behçet disease. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 53:381–6. DOI: 10.5090/kjtcs.20.027. PMID: 33115969. PMCID: PMC7721530.
Article18. Kim SW, Kim TG, Oh J, Kim DY, Choi YC, Kim SM, et al. 2019; Clinical and radiographic characteristics of neuro-Behçet's disease in South Korea. J Clin Neurol. 15:429–37. DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.429. PMID: 31591829. PMCID: PMC6785476.
Article19. Yoon DL, Kim YJ, Koo BS, Kim YG, Lee CK, Yoo B. 2014; Neuro-behçet's disease in South Korea: clinical characteristics and treatment response. Int J Rheum Dis. 17:453–8. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.12265. PMID: 24506839.
Article20. Cheon JH, Kim ES, Shin SJ, Kim TI, Lee KM, Kim SW, et al. 2009; Development and validation of novel diagnostic criteria for intestinal Behçet's disease in Korean patients with ileocolonic ulcers. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:2492–9. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2009.331. PMID: 19532129.
Article21. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Park SJ, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. 2013; Clinical course of intestinal Behcet's disease during the first five years. Dig Dis Sci. 58:496–503. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-012-2351-9. PMID: 22899244.
Article22. Jung YS, Yoon JY, Lee JH, Jeon SM, Hong SP, Kim TI, et al. 2011; Prognostic factors and long-term clinical outcomes for surgical patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:1594–602. DOI: 10.1002/ibd.21517. PMID: 21674717.
Article23. Chung YR, Lee ES, Kim MH, Lew HM, Song JH. 2015; Changes in ocular manifestations of Behçet disease in Korean patients over time: a single-center experience in the 1990s and 2000s. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 23:157–61. DOI: 10.3109/09273948.2014.918154. PMID: 24867632.
Article24. Kirino Y, Ideguchi H, Takeno M, Suda A, Higashitani K, Kunishita Y, et al. 2016; Continuous evolution of clinical phenotype in 578 Japanese patients with Behçet's disease: a retrospective observational study. Arthritis Res Ther. 18:217. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-1115-x. PMID: 27716399. PMCID: PMC5048408.
Article25. Kim JN, Kwak SG, Choe JY, Kim SK. 2017; The prevalence of Behçet's disease in Korea: data from Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service from 2011 to 2015. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 35 Suppl 108(6):38–42. PMID: 28134076.26. Lee YB, Lee SY, Choi JY, Lee JH, Chae HS, Kim JW, et al. 2018; Incidence, prevalence, and mortality of Adamantiades-Behçet's disease in Korea: a nationwide, population-based study (2006-2015). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 32:999–1003. DOI: 10.1111/jdv.14601. PMID: 28940547.
Article27. Jun JB, Kim HJ, Kazmi SZ, Kang T, Kim KB, Kang MJ, et al. 2020; Aug. 8. Significant decline in the incidence of Behcet's disease in South Korea: a nationwide population-based study (2004-2017). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). [Epub]. DOI:10.1002/acr.24408. DOI: 10.1002/acr.24408. PMID: 32770715.
Article28. Cho SB, Cho S, Bang D. 2012; New insights in the clinical understanding of Behçet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 53:35–42. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.35. PMID: 22187230. PMCID: PMC3250322.
Article29. de Menthon M, Lavalley MP, Maldini C, Guillevin L, Mahr A. 2009; HLA-B51/B5 and the risk of Behçet's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control genetic association studies. Arthritis Rheum. 61:1287–96. DOI: 10.1002/art.24642. PMID: 19790126. PMCID: PMC3867978.30. Kirino Y, Bertsias G, Ishigatsubo Y, Mizuki N, Tugal-Tutkun I, Seyahi E, et al. 2013; Genome-wide association analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for Behçet's disease and epistasis between HLA-B*51 and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 45:202–7. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2520. PMID: 23291587. PMCID: PMC3810947.
Article31. McGonagle D, Aydin SZ, Gül A, Mahr A, Direskeneli H. 2015; 'MHC-I-opathy'-unified concept for spondyloarthritis and Behçet disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 11:731–40. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.147. PMID: 26526644.
Article32. Ryu HJ, Seo MR, Choi HJ, Baek HJ. 2018; Clinical phenotypes of Korean patients with Behcet disease according to gender, age at onset, and HLA-B51. Korean J Intern Med. 33:1025–31. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2016.202. PMID: 28073242. PMCID: PMC6129630.
Article33. Chang HK, Kim JU, Cheon KS, Chung HR, Lee KW, Lee IH. 2001; HLA-B51 and its allelic types in association with Behçet's disease and recurrent aphthous stomatitis in Korea. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 19(5 Suppl 24):S31–5. PMID: 11760395.34. Mizuki Y, Horita N, Horie Y, Takeuchi M, Ishido T, Mizuki R, et al. 2020; The influence of HLA-B51 on clinical manifestations among Japanese patients with Behçet's disease: a nationwide survey. Mod Rheumatol. 30:708–14. DOI: 10.1080/14397595.2019.1649103. PMID: 31386589.
Article35. Han M, Jung YS, Kim WH, Cheon JH, Park S. 2017; Incidence and clinical outcomes of intestinal Behçet's disease in Korea, 2011-2014: a nationwide population-based study. J Gastro-enterol. 52:920–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-016-1300-3. PMID: 28028610.
Article36. Kim SW, Jung YS, Ahn JB, Shin ES, Jang HW, Lee HJ, et al. 2017; Identification of genetic susceptibility loci for intestinal Behçet's disease. Sci Rep. 7:39850. DOI: 10.1038/srep39850. PMID: 28045058. PMCID: PMC5206652.
Article37. Remmers EF, Cosan F, Kirino Y, Ombrello MJ, Abaci N, Satorius C, et al. 2010; Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MHC class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behçet's disease. Nat Genet. 42:698–702. DOI: 10.1038/ng.625. PMID: 20622878. PMCID: PMC2923807.
Article38. Mizuki N, Meguro A, Ota M, Ohno S, Shiota T, Kawagoe T, et al. 2010; Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R-IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behçet's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 42:703–6. DOI: 10.1038/ng.624. PMID: 20622879.
Article39. Kang EH, Kim S, Park MY, Choi JY, Choi IA, Kim MJ, et al. 2017; Behçet's disease risk association fine-mapped on the IL23R-IL12RB2 intergenic region in Koreans. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:227. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1435-5. PMID: 29017598. PMCID: PMC5633897.
Article40. Kang EH, Choi JY, Lee YJ, Lee EY, Lee EB, Song YW. 2014; Single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL-10-mediated signalling pathways in Korean patients with Behçet's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 32(4 Suppl 84):S27–32. PMID: 24428981.41. Ortiz-Fernández L, Conde-Jaldón M, García-Lozano JR, Montes-Cano MA, Ortego-Centeno N, Castillo-Palma MJ, et al. 2014; GIMAP and Behçet disease: no association in the European population. Ann Rheum Dis. 73:1433–4. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205156. PMID: 24625627.42. Kim ES, Kim SW, Moon CM, Park JJ, Kim TI, Kim WH, et al. 2012; Interactions between IL17A, IL23R, and STAT4 polymorphisms confer susceptibility to intestinal Behcet's disease in Korean population. Life Sci. 90:740–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.03.017. PMID: 22483685.
Article43. Kang EH, Kim JY, Takeuchi F, Kim JW, Shin K, Lee EY, et al. 2011; Associations between the HLA-A polymorphism and the clinical manifestations of Behcet's disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 13:R49. DOI: 10.1186/ar3292. PMID: 21429233. PMCID: PMC3132038.
Article44. Nakamura J, Meguro A, Ishii G, Mihara T, Takeuchi M, Mizuki Y, et al. 2019; The association analysis between HLA-A*26 and Behçet's disease. Sci Rep. 9:4426. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-40824-y. PMID: 30872678. PMCID: PMC6418292.
Article45. Kwon M, Yoo SJ, Yoo IS, Kim J, Kang SW, Choi IA, et al. 2019; Associations of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid polymorphisms with Behçet's disease in the Korean population. Arch Rheumatol. 34:211–9. DOI: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2019.7113. PMID: 31497768. PMCID: PMC6719587.
Article46. Lee YJ, Horie Y, Wallace GR, Choi YS, Park JA, Choi JY, et al. 2013; Genome-wide association study identifies GIMAP as a novel susceptibility locus for Behcet's disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 72:1510–6. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200288. PMID: 23041938.47. Park KS, Baek JA, Do JE, Bang D, Lee ES. 2009; CTLA4 gene polymorphisms and soluble CTLA4 protein in Behcet's disease. Tissue Antigens. 74:222–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2009.01303.x. PMID: 19563524.48. Kim SK, Jang WC, Park SB, Park DY, Bang KT, Lee SS, et al. 2006; SLC11A1 gene polymorphisms in Korean patients with Behçet's disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 35:398–401. DOI: 10.1080/03009740600704221. PMID: 17062442.
Article49. Park SH, Park KS, Seo YI, Min DJ, Kim WU, Kim TG, et al. 2002; Association of MICA polymorphism with HLA-B51 and disease severity in Korean patients with Behcet's disease. J Korean Med Sci. 17:366–70. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2002.17.3.366. PMID: 12068141. PMCID: PMC3054872.
Article50. Karacayli U, Mumcu G, Simsek I, Pay S, Kose O, Erdem H, et al. 2009; The close association between dental and periodontal treatments and oral ulcer course in behcet's disease: a prospective clinical study. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:410–5. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2009.00765.x. PMID: 19320802.
Article51. Kaneko F, Oyama N, Yanagihori H, Isogai E, Yokota K, Oguma K. 2008; The role of streptococcal hypersensitivity in the pathogenesis of Behçet's disease. Eur J Dermatol. 18:489–98. DOI: 10.1684/ejd.2008.0484. PMID: 18693149.52. Cho SB, Zheng Z, Ahn KJ, Choi MJ, Cho S, Kim DY, et al. 2013; Serum IgA reactivity against GroEL of Streptococcus sanguinis and human heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 in patients with Behçet disease. Br J Dermatol. 168:977–83. DOI: 10.1111/bjd.12128. PMID: 23137016.53. Kim DY, Cho S, Choi MJ, Sohn S, Lee ES, Bang D. 2013; Immunopathogenic role of herpes simplex virus in Behçet's disease. Genet Res Int. 2013:638273. DOI: 10.1155/2013/638273. PMID: 24349789. PMCID: PMC3857840.
Article54. Lee S, Bang D, Cho YH, Lee ES, Sohn S. 1996; Polymerase chain reaction reveals herpes simplex virus DNA in saliva of patients with Behçet's disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 288:179–83. DOI: 10.1007/BF02505221. PMID: 8967789.
Article55. Sohn S, Lee ES, Bang D. 2012; Learning from HSV-infected mice as a model of Behçet's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 30(3 Suppl 72):S96–103. PMID: 22766172.56. Sohn S, Lee ES, Bang D, Lee S. 1998; Behçet's disease-like symptoms induced by the Herpes simplex virus in ICR mice. Eur J Dermatol. 8:21–3.57. Islam SMS, Ryu HM, Sayeed HM, Sohn S. 2021; Interrelationship of stress, environment, and herpes simplex virus type-1 on Behçet's disease: using a mouse model. Front Immunol. 12:607768. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.607768. PMID: 33868228. PMCID: PMC8044423.
Article58. Bai YC, Wang CY, Lin CL, Lai JN, Wei JC. 2021; Association between air pollution and the risk of uveitis: a nationwide, population-based cohort study. Front Immunol. 12:613893. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.613893. PMID: 33815370. PMCID: PMC8013994.
Article59. Lee YB, Lee JH, Lee SY, Lee JH, Yu DS, Han KD, et al. 2019; Association between smoking and Behçet's disease: a nationwide population-based study in Korea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 33:2114–22. DOI: 10.1111/jdv.15708. PMID: 31121063.
Article60. Tong B, Liu X, Xiao J, Su G. 2019; Immunopathogenesis of Behcet's disease. Front Immunol. 10:665. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00665. PMID: 30984205. PMCID: PMC6449449.
Article61. Yamaguchi Y, Takahashi H, Satoh T, Okazaki Y, Mizuki N, Takahashi K, et al. 2010; Natural killer cells control a T-helper 1 response in patients with Behçet's disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 12:R80. DOI: 10.1186/ar3005. PMID: 20459787. PMCID: PMC2911862.
Article62. Emmi G, Becatti M, Bettiol A, Hatemi G, Prisco D, Fiorillo C. 2019; Behçet's syndrome as a model of thrombo-inflammation: the role of neutrophils. Front Immunol. 10:1085. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01085. PMID: 31139195. PMCID: PMC6527740.
Article63. Li L, Yu X, Liu J, Wang Z, Li C, Shi J, et al. 2021; Neutrophil extracellular traps promote aberrant macrophages activation in Behçet's disease. Front Immunol. 11:590622. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.590622. PMID: 33633724. PMCID: PMC7901995.
Article64. Nakano H, Kirino Y, Takeno M, Higashitani K, Nagai H, Yoshimi R, et al. 2018; GWAS-identified CCR1 and IL10 loci contribute to M1 macrophage-predominant inflammation in Behçet's disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 20:124. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-018-1613-0. PMID: 29895319. PMCID: PMC5998575.
Article65. Islam SMS, Sohn S. 2018; HSV-induced systemic inflammation as an animal model for Behçet's disease and therapeutic applications. Viruses. 10:511. DOI: 10.3390/v10090511. PMID: 30235840. PMCID: PMC6163530.
Article66. Kirino Y, Zhou Q, Ishigatsubo Y, Mizuki N, Tugal-Tutkun I, Seyahi E, et al. 2013; Targeted resequencing implicates the familial Mediterranean fever gene MEFV and the toll-like receptor 4 gene TLR4 in Behçet disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110:8134–9. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1306352110. PMID: 23633568. PMCID: PMC3657824.67. Ahn Y, Hwang JH, Zheng Z, Bang D, Kim DY. 2017; Enhancement of Th1/Th17 inflammation by TRIM21 in Behçet's disease. Sci Rep. 7:3018. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03251-5. PMID: 28592884. PMCID: PMC5462739.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiological and clinical features of Behcet's disease in Korea
- Etiopathology of Behcet's disease: herpes simplex virus infection and animal model
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- Diagnostic criteria of Behcet's disease: problems and suggestions
- A Case of Pyoderma Gangrenosum Occurring in Behcet's Disease