J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2021 Aug;47(4):249-256. 10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.4.249.
Sagittal split ramus osteotomy, intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy, and lateral corticectomy for asymmetric mandibular prognathism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea
- KMID: 2519822
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.4.249
Abstract
Objectives
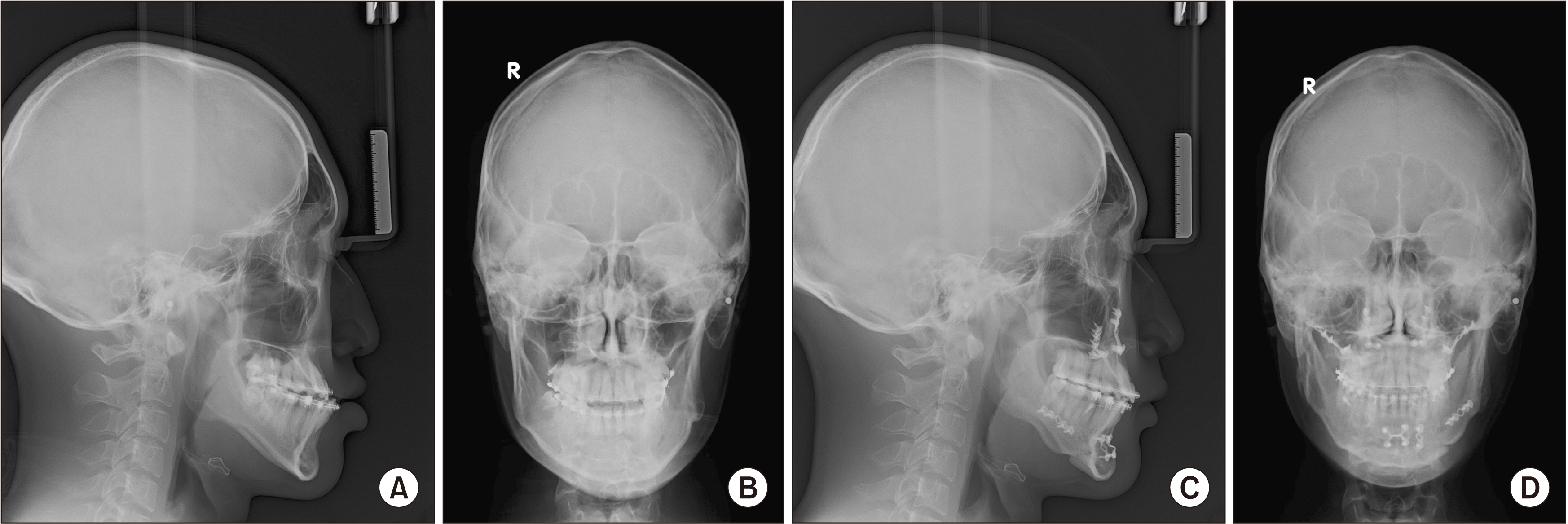
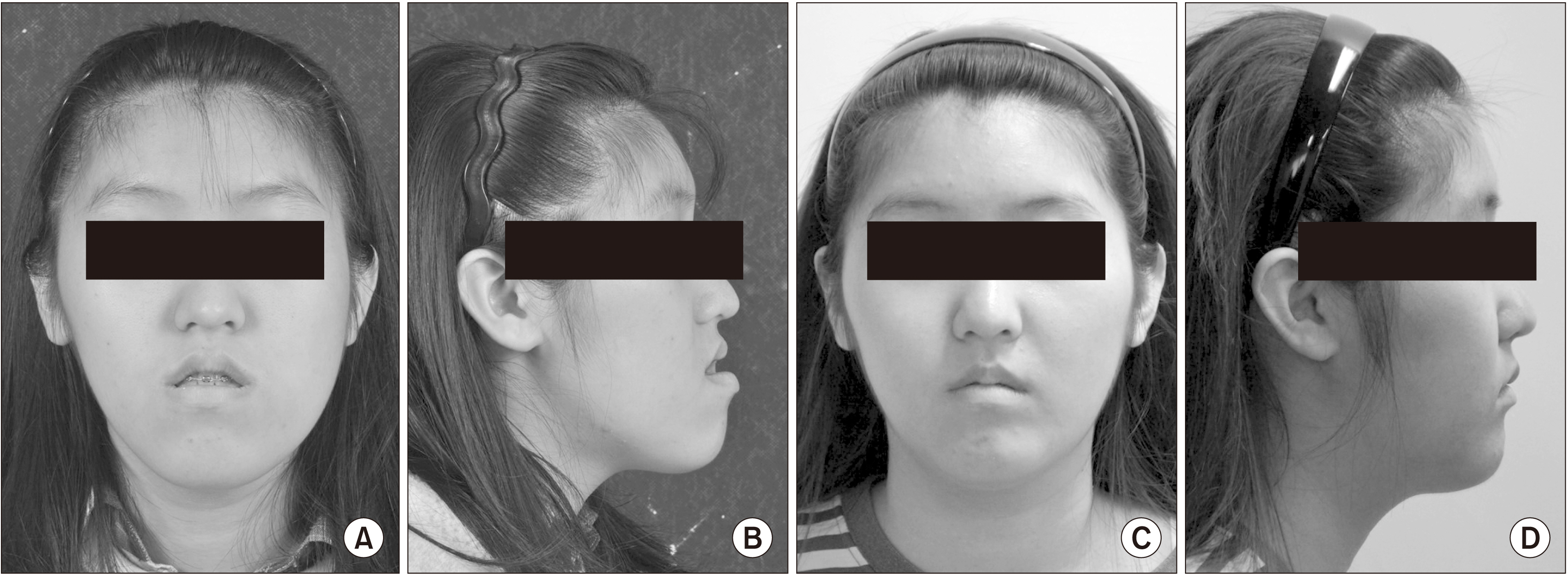
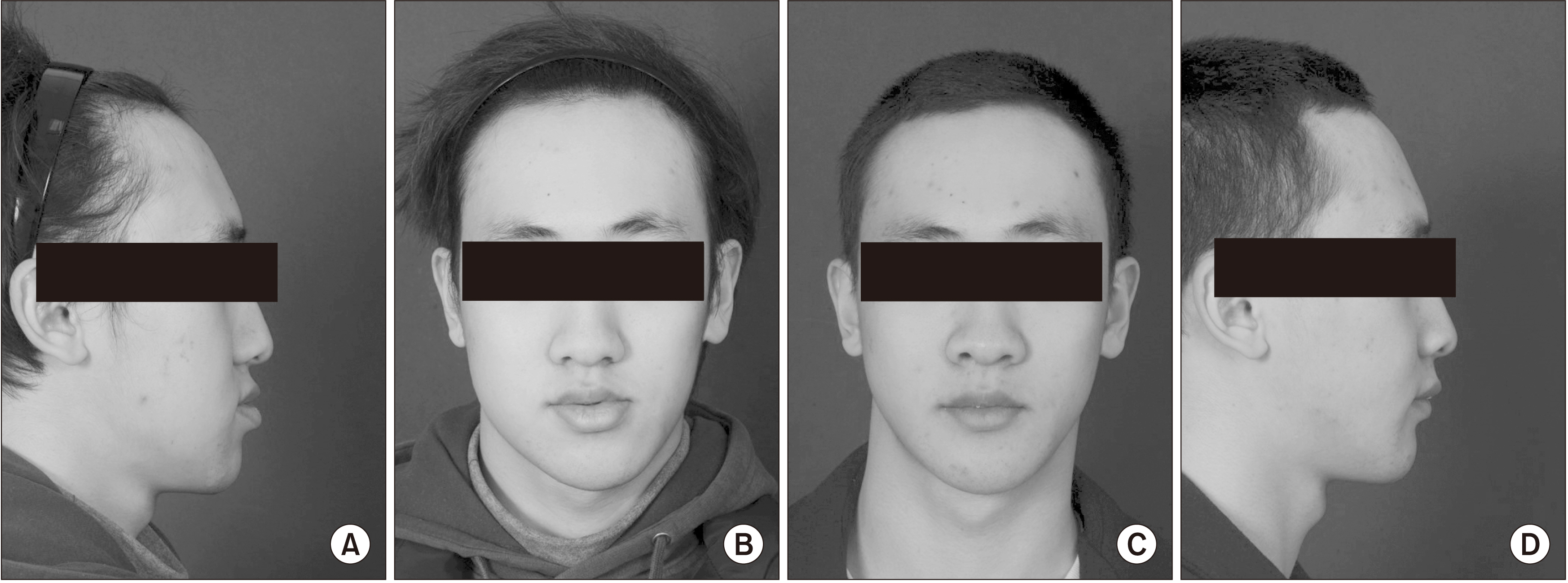
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the postoperative anteroposterior stability and improvements in facial asymmetry after performing LeFort I osteotomy in the maxilla, sagittal split ramus osteotomy (SSRO) and intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy (IVRO) in the mandible, and lateral corticectomy on the IVRO side.
Materials and Methods
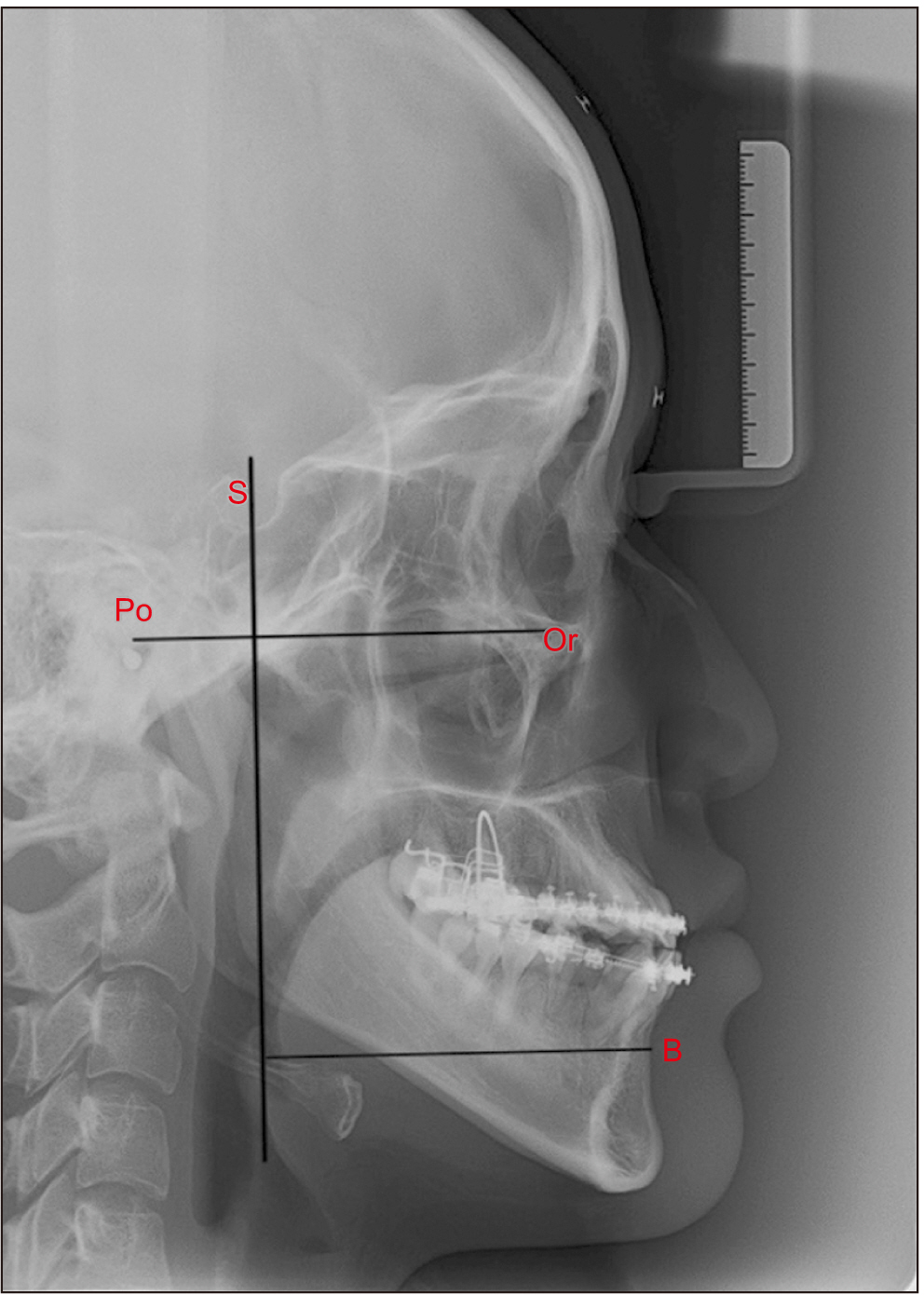
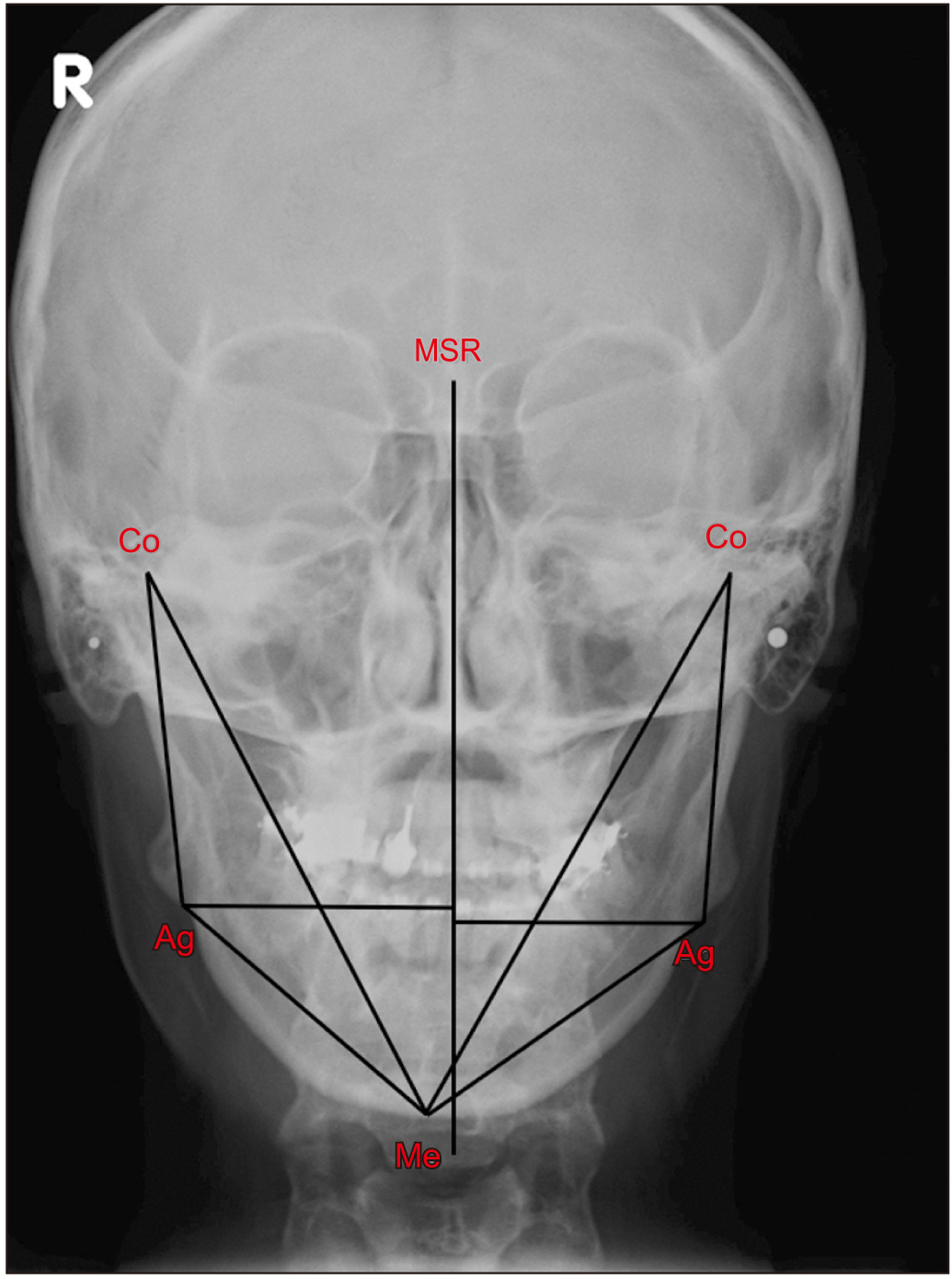
From July 2009 to October 2018, a retrospective analysis was performed on 11 subjects. Lateral cephalometric radiograph was performed preoperatively (T0), postoperatively (T1), and at 12 months of follow-up (T2), and the B point distance was measured. Posteroanterior cephalometric radiograph was performed preoperatively (S0) and at 12 months of follow-up (S1) and was used to measure five indicators (Ag angle, M-Ag, Co-Ag, Co-Me, and Ag-Me) of facial asymmetry.
Results
The B point distances for T0 and T1 were significantly different (P=0.007), whereas those for T1 and T2 were not significantly different (P=0.1). In addition, there was a significant difference between the B point distances of T2 and T0 (P=0.026). Comparison of the facial asymmetry indicators before and after surgery showed a significant difference for all indicators between S0 and S1: the P-values of Ag angle, M-Ag, Co-Ag, Co-Me, and Ag-Me were 0.003, 0.003, 0.008, 0.006, and 0.004, respectively. The Z value was based on negative ranks.
Conclusion
There was no significant difference in the B point distances from postoperation to the 12-month follow-up. However, there were significant differences in all five indicators related to facial asymmetry before and after surgery. The values for the five indicators of facial asymmetry all increased postoperatively.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yun HJ. 2020; Effect of social pressure related to appearance and body image dissatisfaction on mental health in adolescents. J Korean Acad Soc Home Health Care Nurs. 27:92–101. https://doi.org/10.22705/jkashcn.2020.27.1.92 .
Article2. Rhodes G, Proffitt F, Grady JM, Sumich A. 1998; Facial symmetry and the perception of beauty. Psychon Bull Rev. 5:659–69. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03208842 .
Article3. Beyer JW, Lindauer SJ. 1998; Evaluation of dental midline position. Semin Orthod. 4:146–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1073-8746(98)80016-9 . DOI: 10.1016/s1073-8746(98)80016-9. PMID: 9807151.
Article4. Lee GH, Cho HK, Hwang HS, Kim JC. 1998; Studies of relationship between P-A cephalometric measurements and vidual facial asymmetry. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 11:41–8. https://doi.org/10.11637/kjpa.1998.11.1.41 .
Article5. Masuoka N, Momoi Y, Ariji Y, Nawa H, Muramatsu A, Goto S, et al. 2005; Can cephalometric indices and subjective evaluation be consistent for facial asymmetry? Angle Orthod. 75:651–5. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2005)75[651:CCIASE]2.0.CO;2 . DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2005)75[651:CCIASE]2.0.CO;2. PMID: 16097236.
Article6. Rajpara Y, Shyagali TR, Trivedi K, Kambalyal P, Sha T, Jain V. 2014; Evaluation of facial asymmetry in esthetically pleasing faces. J Orthod Res. 2:79–84. https://doi.org/10.4103/2321-3825.131118 .
Article7. Vig PS, Hewitt AB. 1975; Asymmetry of the human facial skeleton. Angle Orthod. 45:125–9. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(1975)045<0125:AOTHFS>2.0.CO;2 . DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1975)045<0125:AOTHFS>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 1054939.
Article8. Al-Gunaid T, Yamada K, Takagi R, Saito C, Saito I. 2008; Postoperative stability of bimaxillary surgery in Class III patients with mandibular protrusion and mandibular deviation: a frontal cephalometric study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 37:992–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2008.05.018 . DOI: 10.1016/j.ijom.2008.05.018. PMID: 18621507.
Article9. Lai W, Yamada K, Hanada K, Ali IM, Takagi R, Kobayashi T, et al. 2002; Postoperative mandibular stability after orthognathic surgery in patients with mandibular protrusion and mandibular deviation. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 17:13–22. PMID: 11934051.10. Lee JH, Park TJ, Jeon JH. 2015; Unilateral intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy and sagittal split ramus osteotomy for the treatment of asymmetric mandibles. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 41:102–8. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.2.102 . DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.2.102. PMID: 25922823. PMCID: PMC4411725.
Article11. Lee SH, Chung DH, Cha KS, Lee JW, Lee SM. 2019; Orthognathic treatment using combination surgery (unilateral sagittal ramus osteotomy and unilateral intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy) for skeletal class III malocclusion patient with facial asymmetry. Clin J Korean Assoc Orthod. 9:178–88. https://doi.org/10.33777/cjkao.2019.9.3.178 .
Article12. Proffit WR, Phillips C, Prewitt JW, Turvey TA. 1991; Stability after surgical-orthodontic correction of skeletal class III malocclusion. 2. Maxillary advancement. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 6:71–80. PMID: 1811032.13. Jakobsone G, Stenvik A, Sandvik L, Espeland L. 2011; Three-year follow-up of bimaxillary surgery to correct skeletal class III malocclusion: stability and risk factors for relapse. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 139:80–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2009.03.050 . DOI: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2009.03.050. PMID: 21195281.
Article14. Al-Gunaid T, Yamaki M, Takagi R, Saito I. 2012; Soft and hard tissue changes after bimaxillary surgery in Japanese class III asymmetric patients. J Orthod Sci. 1:69–76. https://doi.org/10.4103/2278-0203.103865 . DOI: 10.4103/2278-0203.103865. PMID: 24987630. PMCID: PMC4072358.
Article15. Ricketts RM, Bench RW, Hilgers JJ, Schulhof R. 1972; An overview of computerized cephalometrics. Am J Orthod. 61:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9416(72)90172-8 . DOI: 10.1016/0002-9416(72)90172-8. PMID: 4550123.
Article16. Grummons DC, Kappeyne van de Coppello MA. 1987; A frontal asymmetry analysis. J Clin Orthod. 21:448–65. PMID: 3476493.17. Hwang HS, Lee JJ, Hwang CH, Choi HH, Lim HJ. 2008; Prediction of frontal soft tissue changes after mandibular surgery in facial asymmetry individuals. Korean J Orthod. 38:252–64. https://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2008.38.4.252 .
Article18. Major PW, Johnson DE, Hesse KL, Glover KE. 1994; Landmark identification error in posterior anterior cephalometrics. Angle Orthod. 64:447–54. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(1994)064<0447:LIEIPA>2.0.CO;2 . DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1994)064<0447:LIEIPA>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 7864466.
Article19. Baek SM, Kim SS, Bindiger A. 1989; The prominent mandibular angle: preoperative management, operative technique, and results in 42 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 83:272–80. PMID: 2911627.20. Deguchi M, Iio Y, Kobayashi K, Shirakabe T. 1997; Angle-splitting ostectomy for reducing the width of the lower face. Plast Reconstr Surg. 99:1831–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199706000-00005 . DOI: 10.1097/00006534-199706000-00005. PMID: 9180706.
Article21. Jin H, Kim BG. 2004; Mandibular angle reduction versus mandible reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 114:1263–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000135904.40986.f8 . DOI: 10.1097/01.prs.0000135904.40986.f8. PMID: 15457047.
Article22. Han K, Kim J. 2001; Reduction mandibuloplasty: ostectomy of the lateral cortex around the mandibular angle. J Craniofac Surg. 12:314–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001665-200107000-00004 . DOI: 10.1097/00001665-200107000-00004. PMID: 11482616.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical correction of maxillofacial deformity with fibrous-osseous lesion of mandible using the intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy
- Skeletal relapse pattern after sagittal split ramus osteotomy of mandibular prognathic patient
- Unilateral intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy and sagittal split ramus osteotomy for the treatment of asymmetric mandibles
- Stability after Surgical Correction of Mandibular Prognathism Using Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy with Rigid Fixation
- A STUDY ON THE CHANGE THE UPPER LIP AFTER SAGITTAL SPLIT RAMUS OSTEOTOMY