Acute Crit Care.
2021 Aug;36(3):215-222. 10.4266/acc.2021.00234.
Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy is associated with higher mortality rates in patients with sepsis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Mount Sinai Beth Israel Hospital, New York, NY, USA
- 2Department of Medicine, Jacobi Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- 3Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
- 4Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Jacobi Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- 5Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
- 6Institute of Critical Care Medicine, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY, USA
- 7Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Beth Israel Lahey Health, Burlington, MA, USA
- 8Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Medical Center, Little Rock, AR, USA
- 9Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Jacobi Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- KMID: 2519448
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2021.00234
Abstract
- Background
Patients with sepsis are at risk for developing sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy (SIC). Previous studies offer inconsistent results regarding the association of SIC and mortality. This study sought to assess whether SIC is linked to mortality in patients with sepsis and to evaluate predictors of the development of SIC.
Methods
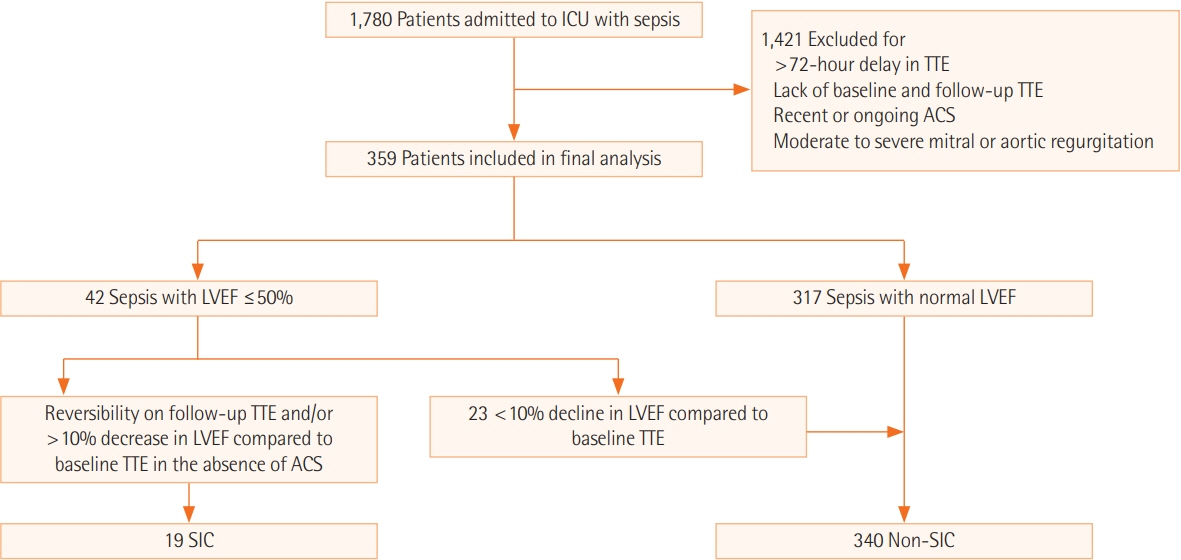
In this retrospective study, patients admitted to the medical intensive care unit with a diagnosis of sepsis in the absence of acute coronary syndrome were included. SIC was identified using transthoracic echo and was defined by a new onset decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤50%, or ≥10% decline in LVEF compared to baseline in patients with a history of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed using the R software program.
Results
Of the 359 patients in the final analysis, 19 (5.3%) had SIC. Eight (42.1%) of the 19 patients in the SIC group and 60 (17.6%) of the 340 patients in the non-SIC group died during hospitalization. SIC was associated with an increased risk for all-cause in-hospital mortality (odds ratio [OR], 4.46; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.15–18.69; P=0.03). Independent predictors for the development of SIC were albumin level (OR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.23–0.93; P=0.03) and culture positivity (OR, 8.47; 95% CI, 2.24–55.61; P=0.006). Concomitant right ventricular hypokinesis was noted in 13 (68.4%) of the 19 SIC patients.
Conclusions
SIC was associated with an increased risk for all-cause in-hospital mortality. Low albumin level and culture positivity were independent predictors of SIC.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315:801–10.
Article2. Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:840–51.
Article3. Parker MM, Shelhamer JH, Bacharach SL, Green MV, Natanson C, Frederick TM, et al. Profound but reversible myocardial depression in patients with septic shock. Ann Intern Med. 1984; 100:483–90.
Article4. L’Heureux M, Sternberg M, Brath L, Turlington J, Kashiouris MG. Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: a comprehensive review. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020; 22:35.
Article5. Landesberg G, Gilon D, Meroz Y, Georgieva M, Levin PD, Goodman S, et al. Diastolic dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33:895–903.
Article6. McLean AS, Huang SJ, Hyams S, Poh G, Nalos M, Pandit R, et al. Prognostic values of B-type natriuretic peptide in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2007; 35:1019–26.
Article7. Furian T, Aguiar C, Prado K, Ribeiro RV, Becker L, Martinelli N, et al. Ventricular dysfunction and dilation in severe sepsis and septic shock: relation to endothelial function and mortality. J Crit Care. 2012; 27:319e9–15.
Article8. Sturgess DJ, Marwick TH, Joyce C, Jenkins C, Jones M, Masci P, et al. Prediction of hospital outcome in septic shock: a prospective comparison of tissue Doppler and cardiac biomarkers. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R44.
Article9. Vieillard Baron A, Schmitt JM, Beauchet A, Augarde R, Prin S, Page B, et al. Early preload adaptation in septic shock? A transesophageal echocardiographic study. Anesthesiology. 2001; 94:400–6.10. Sato R, Kuriyama A, Takada T, Nasu M, Luthe SK. Prevalence and risk factors of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e5031.11. Jeong HS, Lee TH, Bang CH, Kim JH, Hong SJ. Risk factors and outcomes of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction and stress-induced cardiomyopathy in sepsis or septic shock: a comparative retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e0263.12. Song MJ, Lee SH, Leem AY, Kim SY, Chung KS, Kim EY, et al. Predictors and outcomes of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy in critically ill patients. Acute Crit Care. 2020; 35:67–76.
Article13. Society of Critical Care Medicine; European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Surviving Sepsis Campaign [Internet]. Prospect (IL): Mount Society of Critical Care Medicine;2012. [cited 2021 Jul 1]. Available from: https://www.sccm.org/SurvivingSepsisCampaign/Guidelines/Adult-Patients.14. Jardin F, Fourme T, Page B, Loubières Y, Vieillard-Baron A, Beauchet A, et al. Persistent preload defect in severe sepsis despite fluid loading: a longitudinal echocardiographic study in patients with septic shock. Chest. 1999; 116:1354–9.15. Vieillard-Baron A, Caille V, Charron C, Belliard G, Page B, Jardin F. Actual incidence of global left ventricular hypokinesia in adult septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2008; 36:1701–6.
Article16. Etchecopar-Chevreuil C, François B, Clavel M, Pichon N, Gastinne H, Vignon P. Cardiac morphological and functional changes during early septic shock: a transesophageal echocardiographic study. Intensive Care Med. 2008; 34:250–6.17. Haddad F, Hunt SA, Rosenthal DN, Murphy DJ. Right ventricular function in cardiovascular disease, part I: anatomy, physiology, aging, and functional assessment of the right ventricle. Circulation. 2008; 117:1436–48.18. Kimchi A, Ellrodt AG, Berman DS, Riedinger MS, Swan HJ, Murata GH. Right ventricular performance in septic shock: a combined radionuclide and hemodynamic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984; 4:945–51.
Article19. Pulido JN, Afessa B, Masaki M, Yuasa T, Gillespie S, Herasevich V, et al. Clinical spectrum, frequency, and significance of myocardial dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012; 87:620–8.
Article20. Qian SZ, Jin D, Chen ZB, Ye YC, Xiang WW, Ye LM, et al. Hypoalbuminemia, a novel prognostic factor for prediction of long-term outcomes in critically ill patients with septic shock. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2019; 12:7401–9.21. Phua J, Ngerng W, See K, Tay C, Kiong T, Lim H, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of culture-negative versus culture-positive severe sepsis. Crit Care. 2013; 17:R202.
Article22. Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Norrby-Teglund A, Mylona V, Savva A, Tsangaris I, Dimopoulou I, et al. Risk assessment in sepsis: a new prognostication rule by APACHE II score and serum soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor. Crit Care. 2012; 16:R149.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mortality difference between early-identified sepsis and late-identified sepsis
- Mortality among adult patients with sepsis and septic shock in Korea: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sepsis Bundle Compliance and Mortality according to Body Temperature of Patients with Sepsis in General Wards Identified Using the Rapid Response System
- Sepsis: Early Recognition and Optimized Treatment
- Effect of D-glucose feeding on mortality induced by sepsis