Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2021 Aug;14(3):287-294. 10.21053/ceo.2021.00752.
Potential Implications of Slim Modiolar Electrodes for Severely Malformed Cochleae: A Comparison With the Straight Array With Circumferential Electrodes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2519183
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2021.00752
Abstract
Objectives
. Malformations of the inner ear account for approximately 20% of cases of congenital deafness. In current practice, straight arrays with circumferential electrodes (i.e., full-banded electrodes) are widely used in severely malformed cochleae. However, the unpredictability of the location of residual spiral ganglion neurons in such malformations argues against obligatorily using full-banded electrodes in all cases. Here, we present our experience of electrically evoked compound action potential (ECAP) and radiography-based selection of an appropriate electrode for severely malformed cochleae.
Methods
. Three patients with severely malformed cochleae, showing cochlear hypoplasia type II (CH-II), incomplete partition type I (IP-I), and cochlear aplasia with a dilated vestibule (CADV), respectively, were included, and the cochlear nerve deficiency (CND) was evaluated. A full-banded electrode (CI24RE(ST)) and slim modiolar electrode (CI632) were alternately inserted to compare ECAP responses and electrode position.
Results
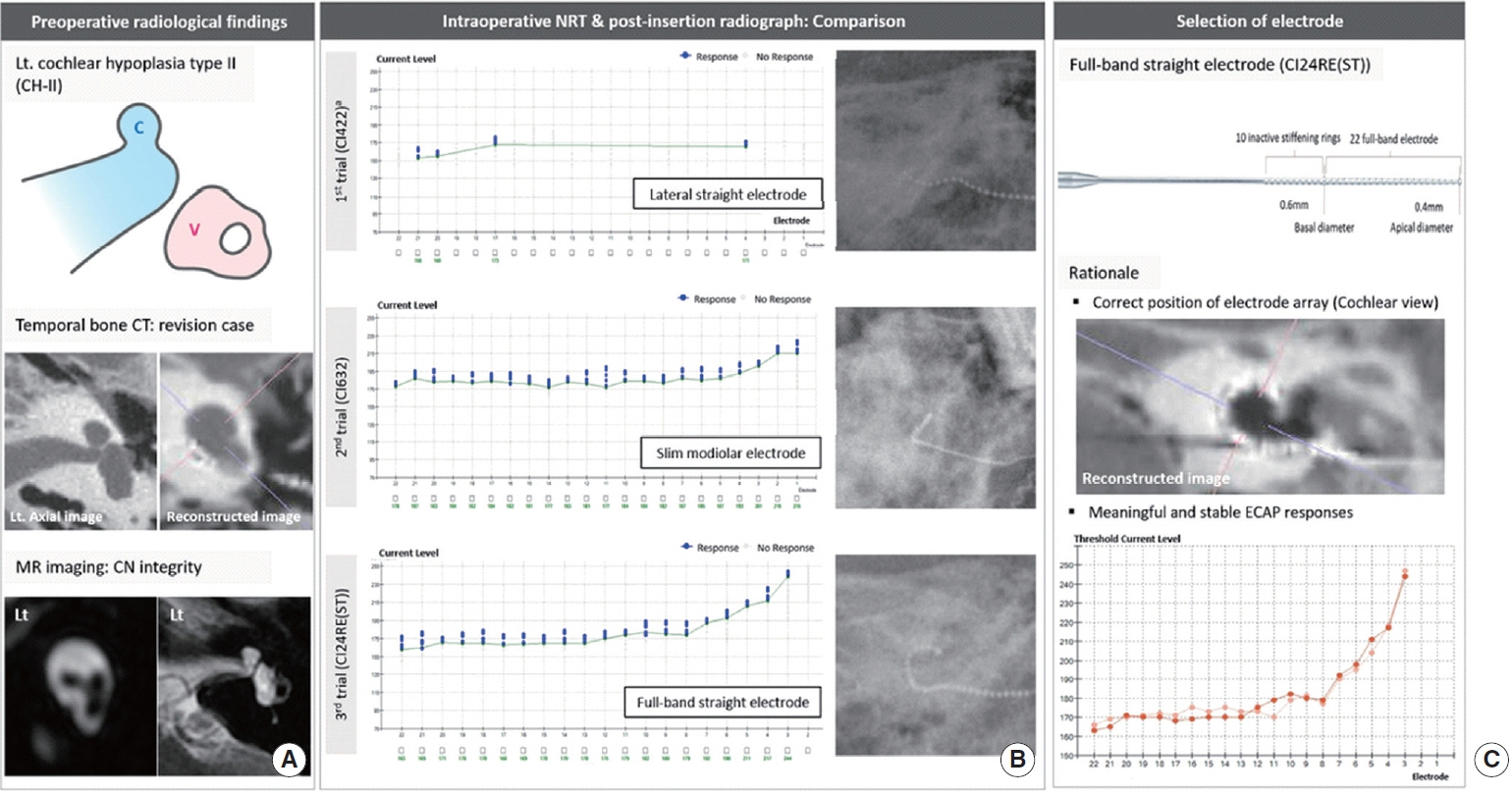
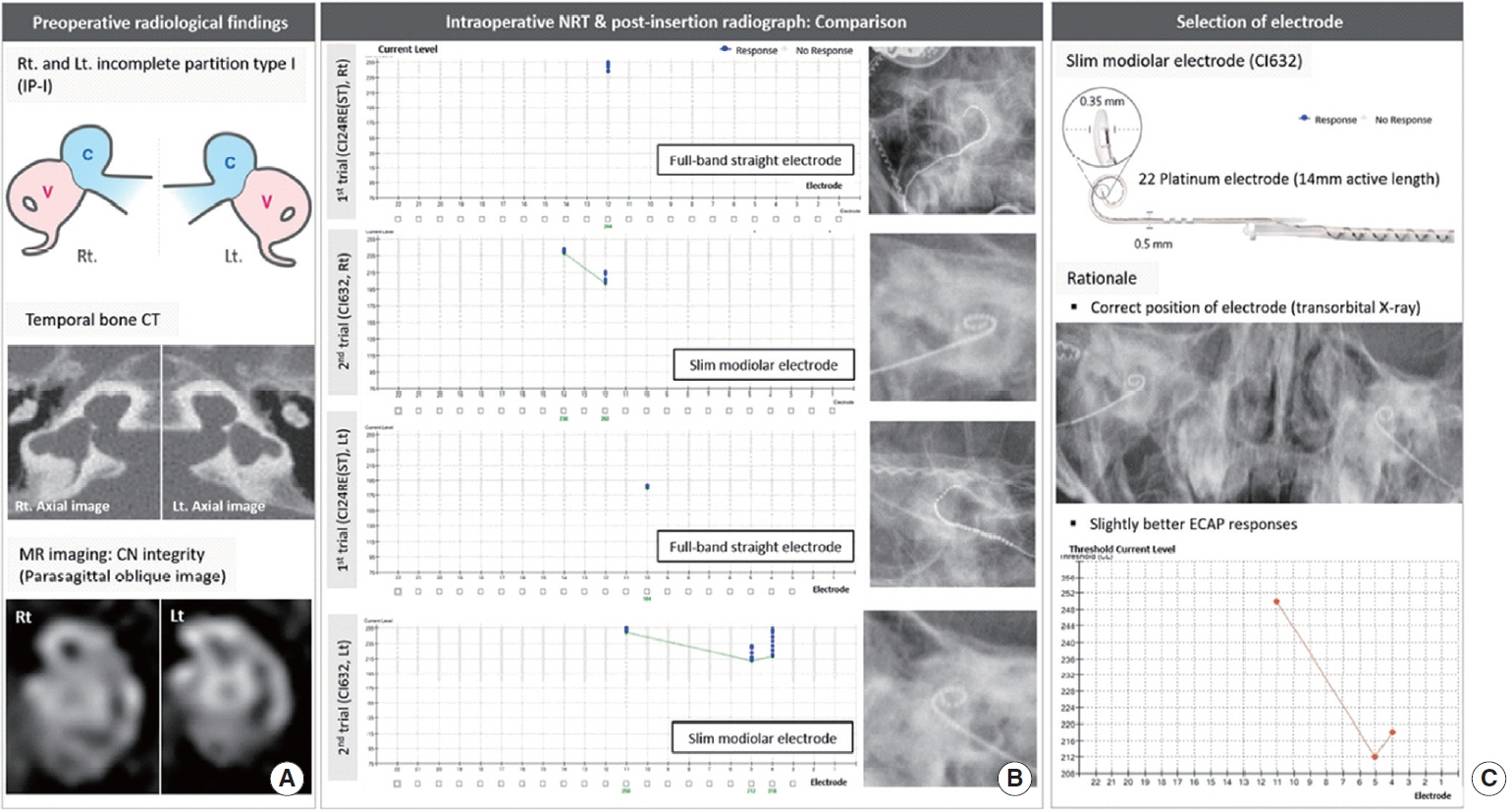
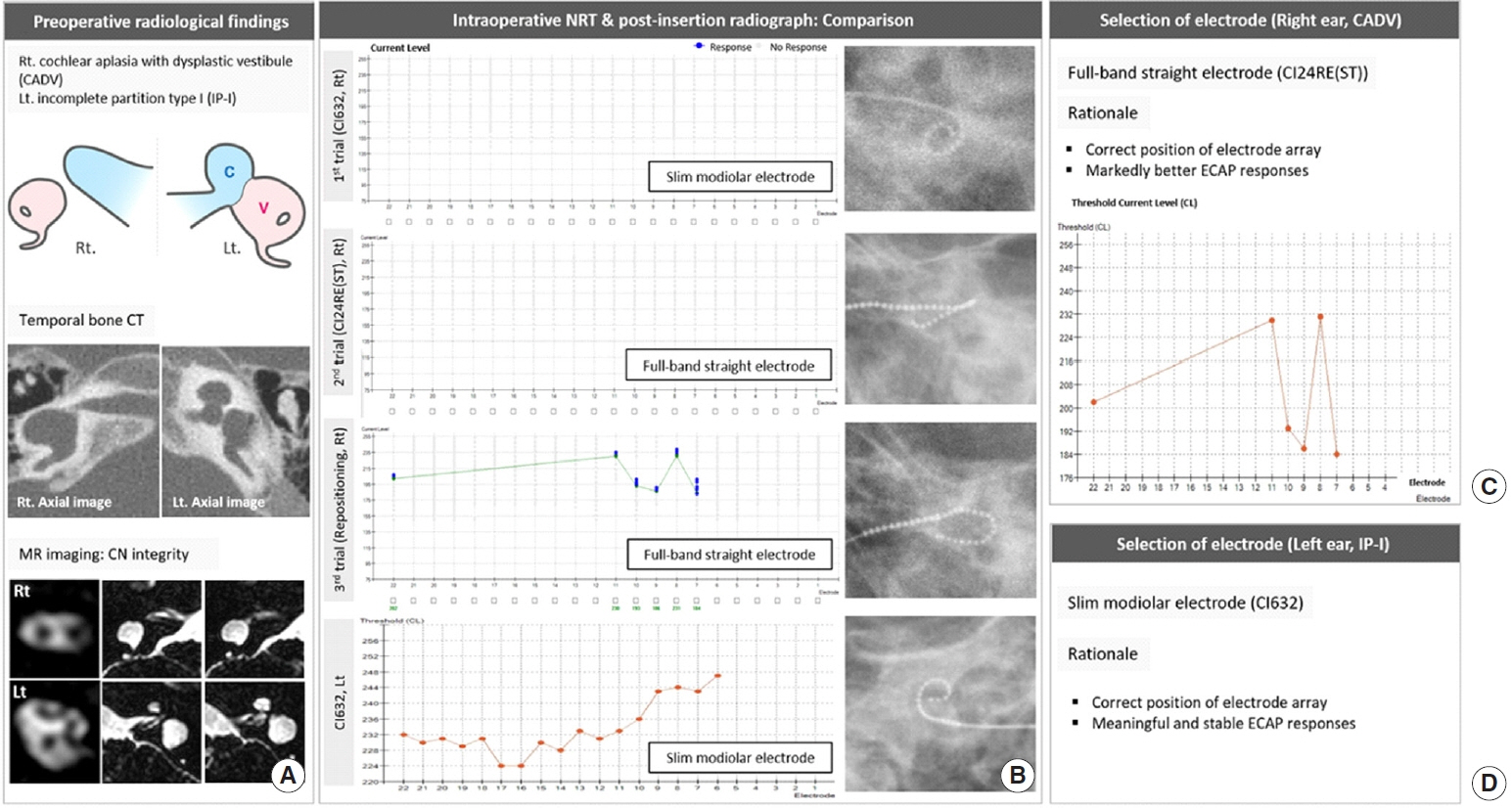
. In patient 1 (CH-II with CND), who had initially undergone cochlear implantation (CI) using a lateral wall electrode (CI422), revision CI was performed due to incomplete insertion of CI422 and resultant unsatisfactory performance by explanting the CI422 and re-inserting the CI24RE(ST) and CI632 sequentially. Although both electrodes elicited reliable ECAP responses with correct positioning, CI24RE(ST) showed overall lower ECAP thresholds compared to CI632; thus, CI24RE(ST) was selected. In patient 2 (IP-I with CND), CI632 elicited superior ECAP responses relative to CI24RE(ST), with correct positioning of the electrode; CI632 was chosen. In patient 3 (CADV), CI632 did not elicit an ECAP response, while meaningful ECAP responses were obtained with the CI24RE(ST) array once correct positioning was achieved. All patients’ auditory performance markedly improved postoperatively.
Conclusion
. The ECAP and radiography-based strategy to identify an appropriate electrode may be useful for severely malformed cochleae, leading to enhanced functional outcomes. The practice of sticking to full-banded straight electrodes may not always be optimal for IP-I and CH-II.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
How to Maximize the Outcomes of Cochlear Implantation in Common Cavity and Cochlear Aplasia With Dilated Vestibule, the Most Severe Inner Ear Anomalies?
Bong Jik Kim, Byung Yoon Choi
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022;15(1):3-4. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2022.00164.Precision Medicine Approach to Cochlear Implantation
Yehree Kim, Byung Yoon Choi
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022;15(4):299-309. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2022.01382.
Reference
-
1. Jensen J. Malformations of the inner ear in deaf children: a tomographic and clinical study. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1968; Suppl 286:3.2. Suk Y, Lee JH, Lee KS. Surgical outcomes after cochlear implantation in children with incomplete partition type I: comparison with deaf children with a normal inner ear structure. Otol Neurotol. 2015; Jan. 36(1):e11–7.3. Eftekharian A, Eftekharian K, Mokari N, Fazel M. Cochlear implantation in 8 incomplete partition type I. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; Oct. 276(10):2763–8.4. Jeong SW, Kim LS. Cochlear implantation in children with cochlear aplasia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012; Sep. 132(9):910–5.
Article5. Schmidt JM. Cochlear neuronal populations in developmental defects of the inner ear: implications for cochlear implantation. Acta Otolaryngol. 1985; Jan-Feb. 99(1-2):14–20.
Article6. Nadol JB Jr. Patterns of neural degeneration in the human cochlea and auditory nerve: implications for cochlear implantation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; Sep. 117(3 Pt 1):220–8.7. Sennaroglu L, Sarac S, Ergin T. Surgical results of cochlear implantation in malformed cochlea. Otol Neurotol. 2006; Aug. 27(5):615–23.
Article8. Berrettini S, Forli F, De Vito A, Bruschini L, Quaranta N. Cochlear implant in incomplete partition type I. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2013; Feb. 33(1):56–62.9. Graham JM, Phelps PD, Michaels L. Congenital malformations of the ear and cochlear implantation in children: review and temporal bone report of common cavity. J Laryngol Otol Suppl. 2000; 25:1–14.
Article10. Eisenman DJ, Ashbaugh C, Zwolan TA, Arts HA, Telian SA. Implantation of the malformed cochlea. Otol Neurotol. 2001; Nov. 22(6):834–41.
Article11. Lee SY, Jung Bae Y, Carandang M, Kim Y, Hee Han J, Huh G, et al. Modiolar proximity of slim modiolar electrodes and cochlear duct length: correlation for potential basis of customized cochlear implantation with perimodiolar electrodes. Ear Hear. 2020; Aug. 42(2):323–33.
Article12. Briaire JJ, Frijns JH. Unraveling the electrically evoked compound action potential. Hear Res. 2005; Jul. 205(1-2):143–56.
Article13. Lee SY, Han JH, Carandang M, Bae YJ, Choi BY. Simpler and effective radiological evaluations for modiolar proximity of a slim modiolar cochlear implant electrode. Sci Rep. 2020; Oct. 10(1):17714.
Article14. Sennaroglu L, Saatci I. A new classification for cochleovestibular malformations. Laryngoscope. 2002; Dec. 112(12):2230–41.
Article15. Sennaroglu L, Bajin MD. Classification and current management of inner ear malformations. Balkan Med J. 2017; Sep. 34(5):397–411.
Article16. Archbold S, Lutman ME, Marshall DH. Categories of auditory performance. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1995; Sep. 166:312–4.17. Yoon MS. Validity and reliability of the IT-MAIS Korean version in children with normal hearing. Commun Sci Disord. 2011; 16(4):494–502.18. Dhanasingh A, Jolly C. An overview of cochlear implant electrode array designs. Hear Res. 2017; Dec. 356:93–103.
Article19. Sennaroglu L. Histopathology of inner ear malformations: do we have enough evidence to explain pathophysiology. Cochlear Implants Int. 2016; 17(1):3–20.
Article20. Kim SY, Kim MB, Chung WH, Cho YS, Hong SH, Moon IJ. Evaluating reasons for revision surgery and device failure rates in patients who underwent cochlear implantation surgery. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020; May. 146(5):414–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Short-Term Experience in Cochlear Implantation with Slim Modiolar Electrode Array (CI532): Comparison to Previous Devices
- Comparison of Cheek Electrode with Sphenoidal Electrodes for Identification of Ictal Onset Activity
- Comparison of Sensory Nerve Action Potential Parameters Using Different Recording Electrodes
- A Comparison of the Size and Shape of Radiofrequency Lesions Produced by Different Temperatures Using Straight and Curved Electrodes
- Efficacy of Non-standard Surface Electrodes for Detecting Epileptiform DLwharges in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsies