Anesth Pain Med.
2021 Jul;16(3):295-298. 10.17085/apm.20096.
Transcutaneous neurostimulatory treatment for peripheral polyneuropathy induced by hypereosinophilic syndrome - A case report -
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2519060
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.20096
Abstract
- Background
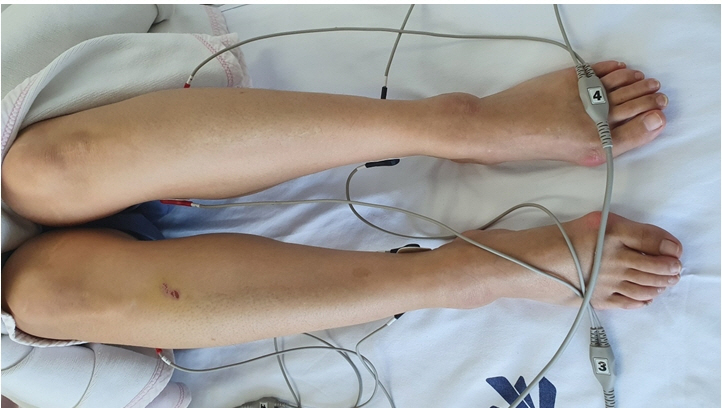
Hypereosinophilic syndrome is a rare disease that increases the number of circulating eosinophils in the body. It has many complications, including peripheral polyneuropathy. Peripheral polyneuropathy often does not respond well to conventional therapies. Transcutaneous neurostimulatory treatment, also known as scrambler therapy, is an alternative modality for the treatment of chronic retractable pain. Case: A 47-year-old woman presented with complaints of bilateral calf pain. She had been under treatment for peripheral polyneuropathy induced by hypereosinophilic syndrome for 7 years. Pharmacologic treatment did not affect the patient’s symptoms.
Conclusions
Transcutaneous neurostimulatory treatment was administered to the patient. It was effective on her symptoms, and the effect of pain alleviation continued for 3 months.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bell D, Mackay IG, Pentland B. Hypereosinophilic syndrome presenting as peripheral neuropathy. Postgrad Med J. 1985; 61:429–32.2. Ogbogu PU, Bochner BS, Butterfield JH, Gleich GJ, Huss-Marp J, Kahn JE, et al. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: a multicenter, retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:1319–25. e3.3. Moore PM, Harley JB, Fauci AS. Neurologic dysfunction in the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985; 102:109–14.4. Marineo G. Untreatable pain resulting from abdominal cancer: new hope from biophysics? JOP. 2003; 4:1–10.5. Pachman DR, Weisbrod BL, Seisler DK, Barton DL, Fee-Schroeder KC, Smith TJ, et al. Pilot evaluation of Scrambler therapy for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Support Care Cancer. 2015; 23:943–51.6. Marineo G, Iorno V, Gandini C, Moschini V, Smith TJ. Scrambler therapy may relieve chronic neuropathic pain more effectively than guideline-based drug management: results of a pilot, randomized, controlled trial. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012; 43:87–95.7. Loprinzi C, Le-Rademacher JG, Majithia N, McMurray RP, O'Neill CR, Bendel MA, et al. Scrambler therapy for chemotherapy neuropathy: a randomized phase II pilot trial. Support Care Cancer. 2020; 28:1183–97.8. Marineo G. Inside the Scrambler therapy, a noninvasive treatment of chronic neuropathic and cancer pain: from the gate control theory to the active principle of information. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019; 18:1534735419845143.9. Curtis C, Ogbogu P. Hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016; 50:240–51.10. Klion AD. How I treat hypereosinophilic syndromes. Blood. 2015; 126:1069–77.11. Crane MM, Chang CM, Kobayashi MG, Weller PF. Incidence of myeloproliferative hypereosinophilic syndrome in the United States and an estimate of all hypereosinophilic syndrome incidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:179–81.12. Dorfman LJ, Ransom BR, Forno LS, Kelts A. Neuropathy in the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1983; 6:291–8.13. Lee YS, Park MK, Park HS, Kim WJ. Scrambler therapy for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98:e15695.14. Park HS, Sin WK, Kim HY, Moon JY, Park SY, Kim YC, et al. Scrambler therapy for patients with cancer pain - case series -. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:65–71.15. Ahuja D, Bharati SJ, Gupta N, Kumar V, Bhatnagar S. Scrambler therapy: a ray of hope for refractory chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Indian J Cancer. 2020; 57:93–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Peripheral Polyneuropathy: A case report
- Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Involving Thoracic Spine
- A Case of Huge Left Ventricular Thrombus Associated with Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
- Peripheral Neuropathy Associated withHypereosinophilic Syndrome
- Concurrence of Acute Cerebral Infarction and Peripheral Neuropathy Associated with Hypereosinophilic Syndrome