Ann Dermatol.
2008 Sep;20(3):149-152. 10.5021/ad.2008.20.3.149.
Peripheral Neuropathy Associated withHypereosinophilic Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. cjpark777@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2156383
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2008.20.3.149
Abstract
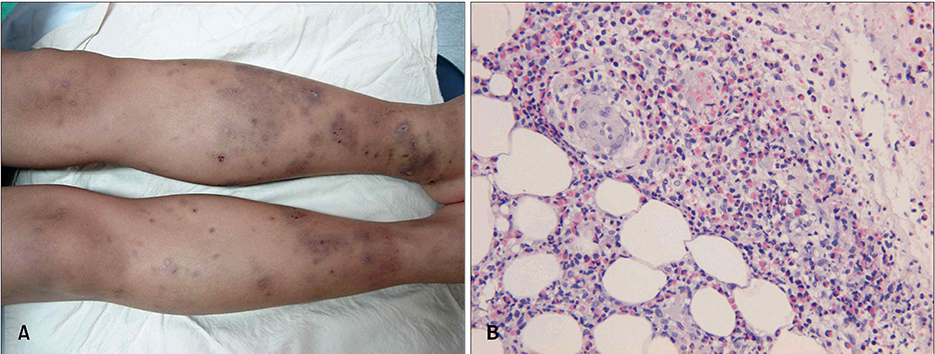
- The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) represents a leukoproliferative disorder, characterized by unexplained prolonged eosinophilia (>6 months) and evidence of specific organ damage. So far, the peripheral neuropathy associated with skin manifestations of HES has not been reported in the dermatologic literature although the incidence of peripheral neuropathy after HES ranges from 6~52%. Herein, we report the peripheral neuropathy associated with HES, documented by clinical, histopathological, and electrodiagnostic criteria.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weller PF. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1996; 132:583–585.
Article2. Werner RA, Wolf LL. Peripheral neuropathy associated with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1990; 71:433–435.3. Lee GH, Lee KW, Chi JG. Peripheral neuropathy as a hypereosinophilic syndrome and anti-GM1 antibodies. J Korean Med Sci. 1993; 8:225–229.
Article4. Prick JJ, Gabreels-Festen AA, Korten JJ, van der Wiel TW. Neurological manifestations of the hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES). Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1988; 90:269–273.
Article5. Leiferman KM, Gleich GJ. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: case presentation and update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:50–58.6. Mcnutt NS, Moreno A, Contreras F. Inflammatory disease of the subcutaneous fat. In : Elder DE, Elenitsas R, Johnson BL, Murphy GF, editors. Lever's histopathology of the skin. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2005. p. 525–526.7. Leiferman KM, Peters MS, Gleich GJ. Eosinophils in cutaneous diseases. In : Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, editors. Dermatology in general medicine. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2003. p. 959–966.8. Barna M, Kemeny L, Dobozy A. Skin lesions as the only manifestation of the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1997; 136:646–647.
Article9. Stetson C. Eosinophilic dermatoses. In : Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, editors. Dermatology. 1st ed. London: Mosby;2003. p. 403–410.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Peripheral Neuropathy in Metabolic Syndrome
- Clinical Scales for Peripheral Neuropathy - Revision 2021
- One Case of Subacute Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy Associated with Primary Sj gren's Syndrome: A case report
- Peripheral neuropathy as a hypereosinophilic syndrome and anti-GM1 antibodies
- Treatment of peripheral neuropathy: a multidisciplinary approach is necessary