Diabetes Metab J.
2021 Jul;45(4):606-612. 10.4093/dmj.2020.0047.
A Multicentre, Multinational, Open-Label, 52-Week Extension Study of Gemigliptin (LC15-0444) Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology, Daerim St. Mary’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3M.V. Hospital and Research Centre, Lucknow, India
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Research Health Institute in Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism (RHIDEM), Mumbai, India
- 6Hormone Care and Research Center, Ghaziabad, India
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 9Department of Endocrinology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2518902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0047
Abstract
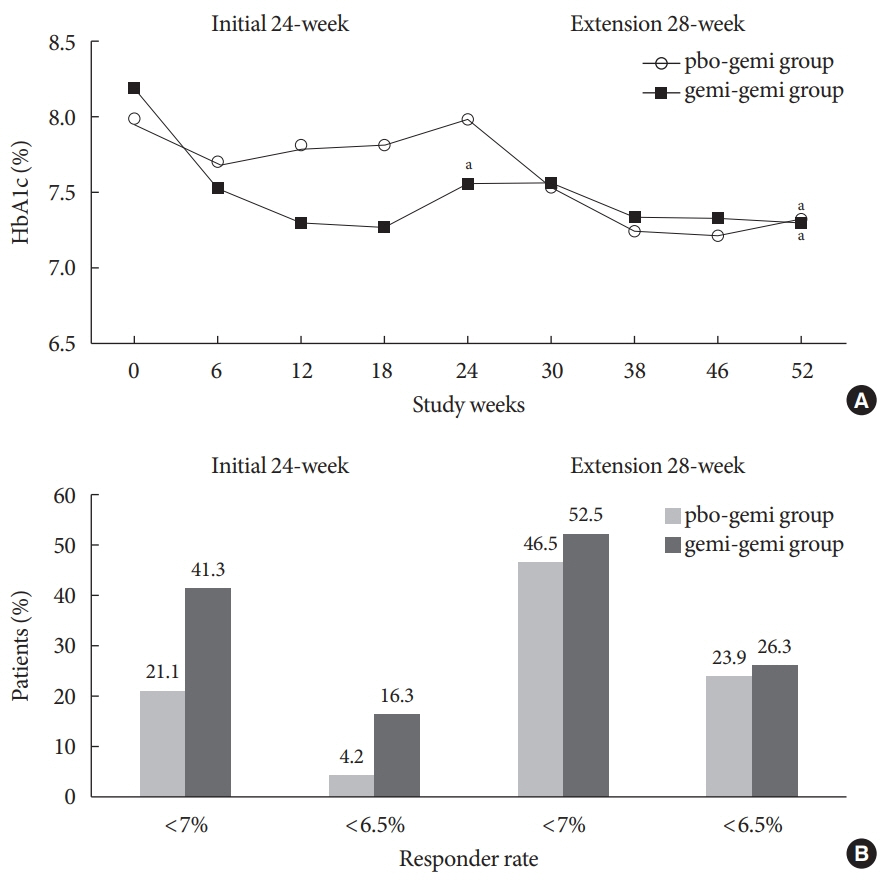
- The purpose of this extension study was to assess the long-term efficacy and safety of gemigliptin 50 mg in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Patients with T2DM who had completed the initial 24-week study comparing gemigliptin monotherapy with placebo were eligible to enrol. In the open-label, 28-week extension study, all enrolled patients received gemigliptin, regardless of the treatment received during the initial 24-week study period. The mean reduction±standard deviation (SD) in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) observed after 24 weeks of treatment (–0.6%±1.1%) was further decreased for the gemi-gemi group and the mean change in HbA1c at week 52 from baseline was –0.9%±1.2% (P<0.0001). For the pbo-gemi group, HbA1c decreased after they were switched to gemigliptin, and the mean change in HbA1c at week 52 from baseline was –0.7%±1.2% (P<0.0001). Furthermore, the overall incidence of adverse events demonstrated that gemigliptin was safe and well tolerated up to 52 weeks.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Scheen AJ. A review of gliptins in 2011. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012; 13:81–99.
Article2. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1364–79.
Article3. Craddy P, Palin HJ, Johnson KI. Comparative effectiveness of dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and mixed treatment comparison. Diabetes Ther. 2014; 5:1–41.
Article4. Ahren B. Clinical results of treating type 2 diabetic patients with sitagliptin, vildagliptin or saxagliptin: diabetes control and potential adverse events. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 23:487–98.5. Nauck MA, Vilsboll T, Gallwitz B, Garber A, Madsbad S. Incretin-based therapies: viewpoints on the way to consensus. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32 Suppl 2:S223–31.
Article6. Yang SJ, Min KW, Gupta SK, Park JY, Shivane VK, Pitale SU, et al. A multicentre, multinational, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gemigliptin (LC15-0444) in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:410–6.7. Monami M, Iacomelli I, Marchionni N, Mannucci E. Dipeptydil peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010; 20:224–35.
Article8. Richard KR, Shelburne JS, Kirk JK. Tolerability of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: a review. Clin Ther. 2011; 33:1609–29.
Article9. Amori RE, Lau J, Pittas AG. Efficacy and safety of incretin therapy in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2007; 298:194–206.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gemigliptin: An Update of Its Clinical Use in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Pharmacokinetic Equivalence of the High Dose Strength Fixed-Dose Combination Tablet of Gemigliptin/Metformin Sustained Release (SR) and Individual Component Gemigliptin and Metformin XR Tablets in Healthy Subjects
- Efficacy of Gemigliptin Add-on to Dapagliflozin and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study (SOLUTION)
- Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a fixed-dose combination of gemigliptin/metformin sustained release 25/500 mg compared to the loose combination in healthy male subjects
- Gemigliptin Inhibits Interleukin-1β–Induced Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Canonical-Bone Morphogenetic Protein Pathway