Clin Endosc.
2021 Jul;54(4):542-547. 10.5946/ce.2020.243.
The Outcome of Endoscopic Radiofrequency Anti-Reflux Therapy (STRETTA) for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Previous Gastric Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Upper GI surgery, James Cook University Hospital, South Tees Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Middlesbrough, UK
- KMID: 2518857
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.243
Abstract
- Background/Aims
STRETTA improves the quality of life and reduces the need for anti-reflux medication in select patients, especially those with uncomplicated gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD). We aimed to review the outcomes of STRETTA in patients with medically refractory GERD, who had undergone previous gastric surgery.
Methods
This was a review of a prospective database in a British center. Since 2016, all GERD patients who underwent STRETTA and had a history of previous gastric surgery were studied (n=11). Anti-reflux medication pre- and post-STRETTA was evaluated. The outcomes were assessed objectively by the change in anti-reflux medication and subjectively through a pre- and post-procedure GERD-health-related quality of life (HRQL) questionnaire.
Results
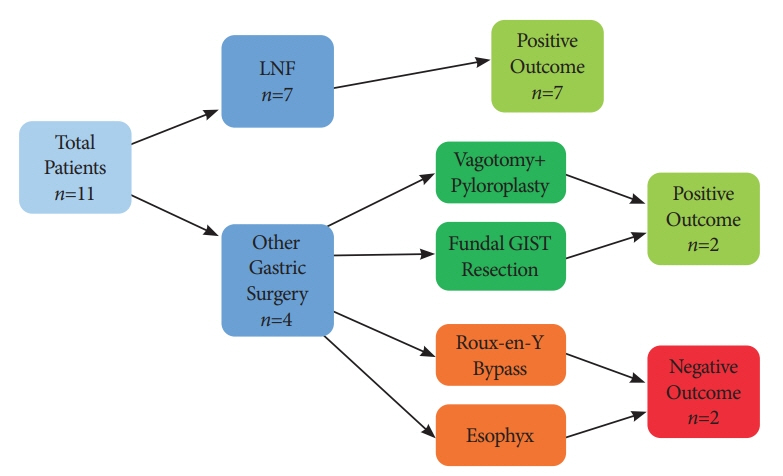
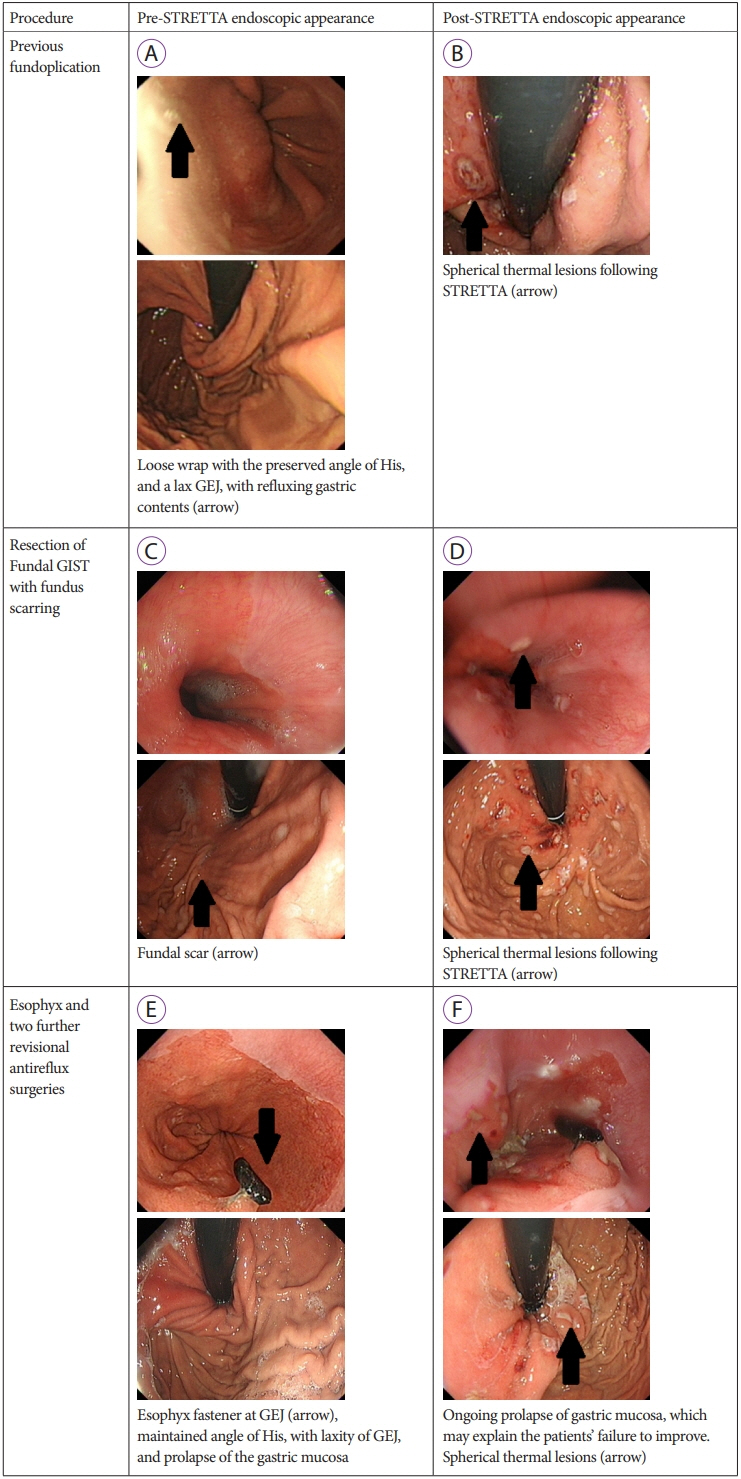
The median length of follow-up was 23 months. Nine patients demonstrated improved GERD-HRQL scores following STRETTA (82%). Of the 7 patients who underwent fundoplication, all reported improved symptoms, with 3 patients discontinuing the medication and 3 patients on a reduced dose of proton pump inhibitor. Four patients underwent surgery other than fundoplication, of which 2 reported improvement and discontinued the proton pump inhibitor. Two patients reported no improvement.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that STRETTA is successful in reducing refractory GERD in patients with previous gastric surgery. The outcomes were comparable to published outcomes in patients with uncomplicated GERD with no previous history of gastric surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
In Which Situation is Endoscopic Radiofrequency Anti-Reflux Therapy (Stretta) Effective for Controlling Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms?
Hwoon-Yong Jung
Clin Endosc. 2021;54(4):451-452. doi: 10.5946/ce.2021.190.
Reference
-
1. He S, Xu F, Xiong X, et al. Stretta procedure versus proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of nonerosive reflux disease: a 6-month follow-up. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99:e18610.2. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stretta system for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease [Internet]. London: NICE;c2016. [updated 2016 Jul 26]. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/advice/mib74.3. Viswanath Y, Maguire N, Obuobi RB, Dhar A, Punnoose S. Endoscopic day case antireflux radiofrequency (Stretta) therapy improves quality of life and reduce proton pump inhibitor (PPI) dependency in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a prospective study from a UK tertiary centre. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2019; 10:113–119.
Article4. Viswanath YKS. Endoscopic prudence to assess gastro-esophageal junction (GEJ); a necessity rather a prerequisite prior to endoscopic anti-reflux treatment in gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) patients. Acta Scientific Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2020; 3:29–31.5. Funk LM, Zhang JY, Drosdeck JM, Melvin WS, Walker JP, Perry KA. Long-term cost-effectiveness of medical, endoscopic and surgical management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surgery. 2015; 157:126–136.
Article6. Mattar SG, Qureshi F, Taylor D, Schauer PR. Treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease with radiofrequency energy (Stretta) in patients after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc. 2006; 20:850–854.
Article7. Noar M, Squires P, Khan S. Radiofrequency energy delivery to the lower esophageal sphincter improves gastroesophageal reflux patient-reported outcomes in failed laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication cohort. Surg Endosc. 2017; 31:2854–2862.
Article8. McClusky DA, Khaitan L, Swafford VA, Smith CD. Radiofrequency energy delivery to the lower esophageal sphincter (Stretta procedure) in patients with recurrent reflux after antireflux surgery: can surgery be avoided? Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:1207–1211.9. Velanovich V. The development of the GERD-HRQL symptom severity instrument. Dis Esophagus. 2007; 20:130–134.
Article10. Coron E, Sebille V, Cadiot G, et al. Clinical trial: radiofrequency energy delivery in proton pump inhibitor-dependent gastro-oesophageal reflux disease patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 28:1147–1158.
Article11. Kelly JJ, Watson DI, Chin KF, Devitt PG, Game PA, Jamieson GG. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: clinical outcomes at 10 years. J Am Coll Surg. 2007; 205:570–575.
Article12. Shah NH, LePendu P, Bauer-Mehren A, et al. Proton pump inhibitor usage and the risk of myocardial infarction in the general population. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0124653.
Article13. Gregory D, Scotti DJ, Buck D, Triadafilopoulos G. Budget impact analysis to estimate the cost dynamics of treating refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease with radiofrequency energy: a payer perspective. Manag Care. 2016; 25:42–50.14. Testoni PA, Testoni S, Mazzoleni G, Vailati C, Passaretti S. Long-term efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication with Esophyx (Tif 2.0) and factors affecting outcomes in GERD patients followed for up to 6 years: a prospective single-center study. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:2770–2780.15. Testoni PA, Mazzoleni G, Testoni SG. Transoral incisionless fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: Techniques and outcomes. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016; 7:179–189.
Article16. Vaezi MF. Use of symptom indices in the management of GERD. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2012; 8:185–187.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In Which Situation is Endoscopic Radiofrequency Anti-Reflux Therapy (Stretta) Effective for Controlling Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms?
- Endoscopic radiofrequency Stretta therapy reduces proton pump inhibitor dependency and the need for anti-reflux surgery for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Endoscopic Treatment of Refractory Gastroesohageal Reflux Disease
- Long-term efficacy of endoscopic radiofrequency Stretta therapy for patients with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Endoscopic Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Revisited