Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Jul;78(1):59-64. 10.4166/kjg.2021.059.
Prostate Cancer Presenting with Pruritus and Cholestasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 2Departments of Anatomic Pathology, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 3Departments of Urology, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2518756
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.059
Abstract
- Jaundice is a rare symptom of the paraneoplastic syndrome associated with prostate cancer. We report a case of metastatic prostate cancer that presented as jaundice. There was an absence of biliary obstruction and hepatic metastasis; therefore, the paraneoplastic syndrome was suggested as the etiology of cholestasis. Jaundice improved with the treatment of prostate cancer. In the literature, interleukin-6 has been suggested to be associated with paraneoplastic syndrome.
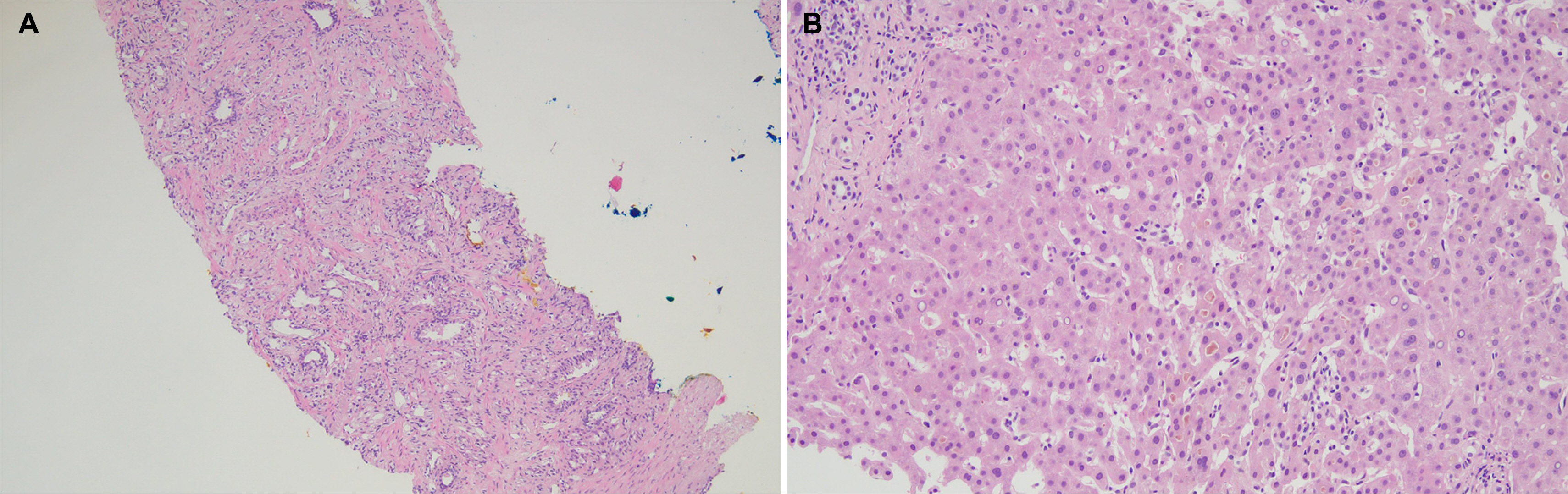
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hinostroza-Yanahuaya J, Mon-Mon C, Ortega-Marcos O, Herrero-Berron JC, Ortiz-Libreros M, Vigil-Medina A. 2013; Stauffer syndrome and prostate carcinoma, two cases in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nefrologia. 33:749–750.2. Sharma N, Darr U, Darr A, Sood G. 2019; Stauffer syndrome: a comprehensive review of the icteric variant of the syndrome. Cureus. 11:e6032. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.6032.
Article3. Reddy AN, Grosberg SJ, Wapnick S. 1977; Intermittent cholestatic jaundice and nonmetastatic prostatic carcinoma. Arch Intern Med. 137:1616–1618. DOI: 10.1001/archinte.1977.03630230088024. PMID: 921451.
Article4. Karakolios A, Kasapis C, Kallinikidis T, Kalpidis P, Grigoriadis N. 2003; Cholestatic jaundice as a paraneoplastic manifestation of prostate adenocarcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1:480–483. DOI: 10.1016/S1542-3565(03)00227-1.
Article5. Koruk M, Büyükberber M, Savaş C, Kadayifçi A. 2004; Paraneoplastic cholestasis associated with prostate carcinoma. Turk J Gastroenterol. 15:53–55.6. Shah SH. 2006; Paraneoplastic liver dysfunction in prostate cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage. 32:511–513. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.03.015. PMID: 17157749.
Article7. Nguyen V, Gurney H, van der Poorten D. 2011; Paraneoplastic hepatic dysfunction in metastatic prostate cancer: the role of cytokine dysregulation. J Clin Oncol. 29:e21–e23. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.6522. PMID: 20940196.
Article8. Kuramoto T, Senzaki H, Koike H, et al. 2013; Cholestatic jaundice as a paraneoplastic manifestation of prostate cancer. Case Rep Urol. 2013:303727. DOI: 10.1155/2013/303727. PMID: 24191227. PMCID: PMC3804369.
Article9. Okano A, Ohana M, Kusumi F. 2014; Idiopathic cholestatic jaundice may be a paraneoplastic manifestation of underlying malignancy: a case of prostate cancer. Clin J Gastroenterol. 7:278–282. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-014-0484-4. PMID: 26183750.
Article10. Kato D, Okwara C, Moreland C, Parker A. 2014; Hepatic dysfunction as a paraneoplastic manifestation of metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2:2324709614539927. DOI: 10.1177/2324709614539927. PMID: 26425613. PMCID: PMC4528893.
Article11. Walter H, Backus N, Aragon G. 2015; Intrahepatic cholestasis in the setting of recurrent prostate cancer: a paraneoplastic syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 110:S394. DOI: 10.14309/00000434-201510001-00913.
Article12. Vieira AC, Alvarenga MJ, Santos JC, Silva AM. 2017; Paraneoplastic jaundice and prostate cancer. BMJ Case Rep. 2017:bcr2016218001. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-218001. PMID: 28433972. PMCID: PMC5534789.
Article13. Bhangoo MS, Cheng B, Botta GP, Thorson P, Kosty MP. 2018; Reversible intrahepatic cholestasis in metastatic prostate cancer: an uncommon paraneoplastic syndrome. Mol Clin Oncol. 8:609–612. DOI: 10.3892/mco.2018.1564. PMID: 29541472. PMCID: PMC5838296.
Article14. Ravindranathan D, Hitron EE, Russler GA, Xue Y, Bilen MA. 2018; Metastatic prostate cancer manifesting as cholestatic jaundice: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2018:1809432. DOI: 10.1155/2018/1809432. PMID: 29780650. PMCID: PMC5892301.
Article15. Kang MK, Park JG, Lee HJ. 2018; Cholestatic jaundice as a paraneoplastic manifestation of prostate cancer aggravated by steroid therapy. Med Princ Pract. 27:197–200. DOI: 10.1159/000486717. PMID: 29320775. PMCID: PMC5968241.
Article16. Romašovs A, Puķītis A, Mokricka V, Frolova E. 2019; Stauffer's syndrome in patient with metastatic prostate cancer. Case Rep Urol. 2019:9745301. DOI: 10.1155/2019/9745301. PMID: 31179152. PMCID: PMC6501217.
Article17. Liu J, Agyapong G, Misra D, Taylor CD, Hirsh DA. 2019; A rare case of idiopathic cholestasis: Clinical conundrums complicating enzalutamide therapy in metastatic prostate cancer. Clin Case Rep. 7:2068–2073. DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.2427. PMID: 31788253. PMCID: PMC6878062.
Article18. Gökçen P, Gökçen K, Çakmak E, Gökçe G. 2018; Paraneoplastic hyperbilirubinemia in metastatic prostate cancer and review of the current literature. Turk J Urol. 45:70–72. DOI: 10.5152/tud.2018.52059. PMID: 30668309. PMCID: PMC6342570.19. Blay JY, Rossi JF, Wijdenes J, et al. 1997; Role of interleukin-6 in the paraneoplastic inflammatory syndrome associated with renal-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 72:424–430. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19970729)72:3<424::AID-IJC9>3.0.CO;2-R.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bleeding due to Vitamin K Deficiency as Presenting Symptom of Cholestasis
- Cholestasis beyond the Neonatal and Infancy Periods
- Dermatoses of Pregnancy: Clues to Diagnosis, Fetal Risk and Therapy
- A Case of Nonfamilial Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis
- Atrophy of the Tongue as the Presenting Feature of Metastatic Prostate Cancer