Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Jul;78(1):53-58. 10.4166/kjg.2021.046.
Two Lethal Cases of Monomorphic Epitheliotropic Intestinal T-cell Lymphoma Deteriorated Rapidly After Emergency Surgery for Intestinal Perforation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2518754
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2021.046
Abstract
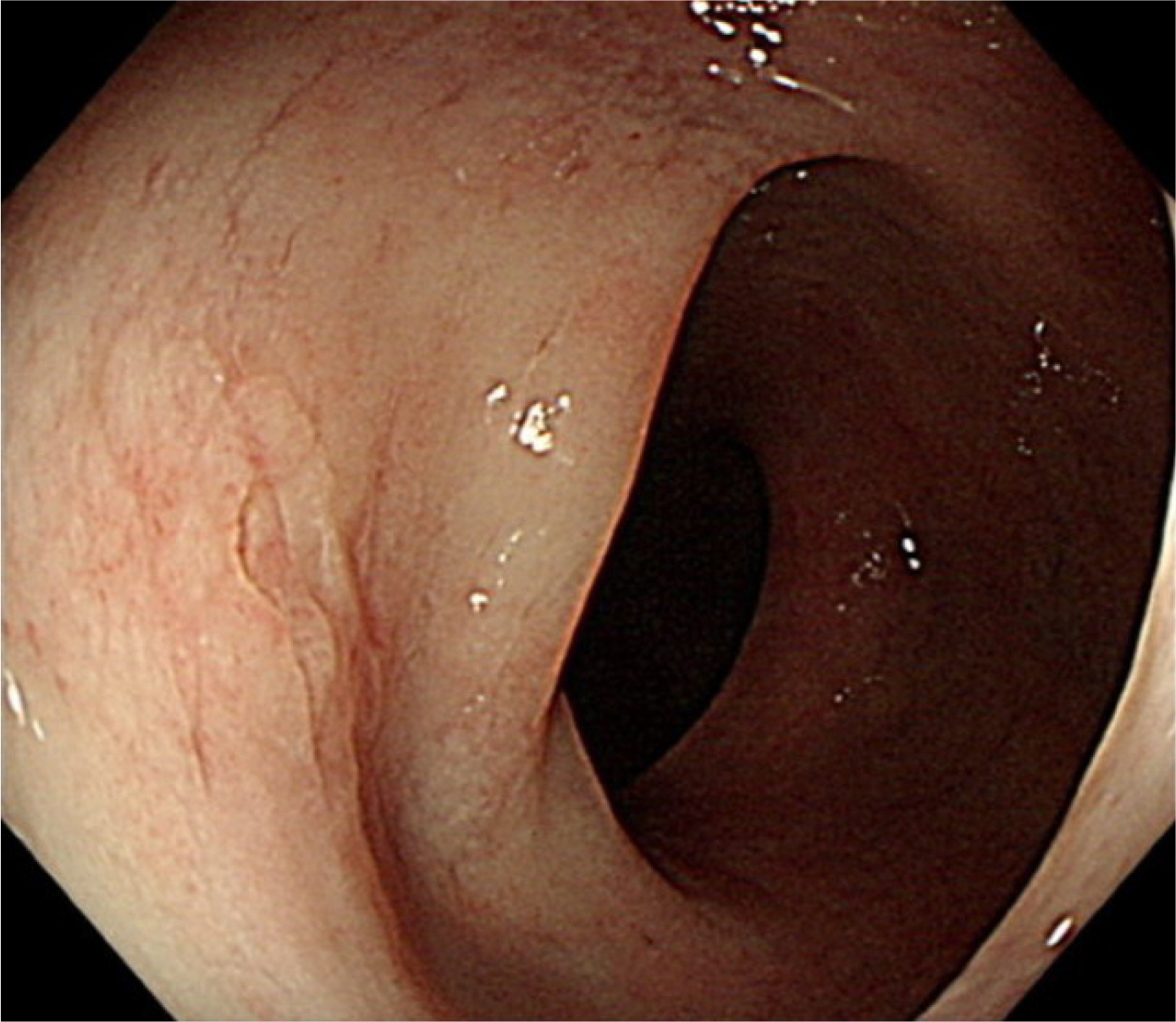
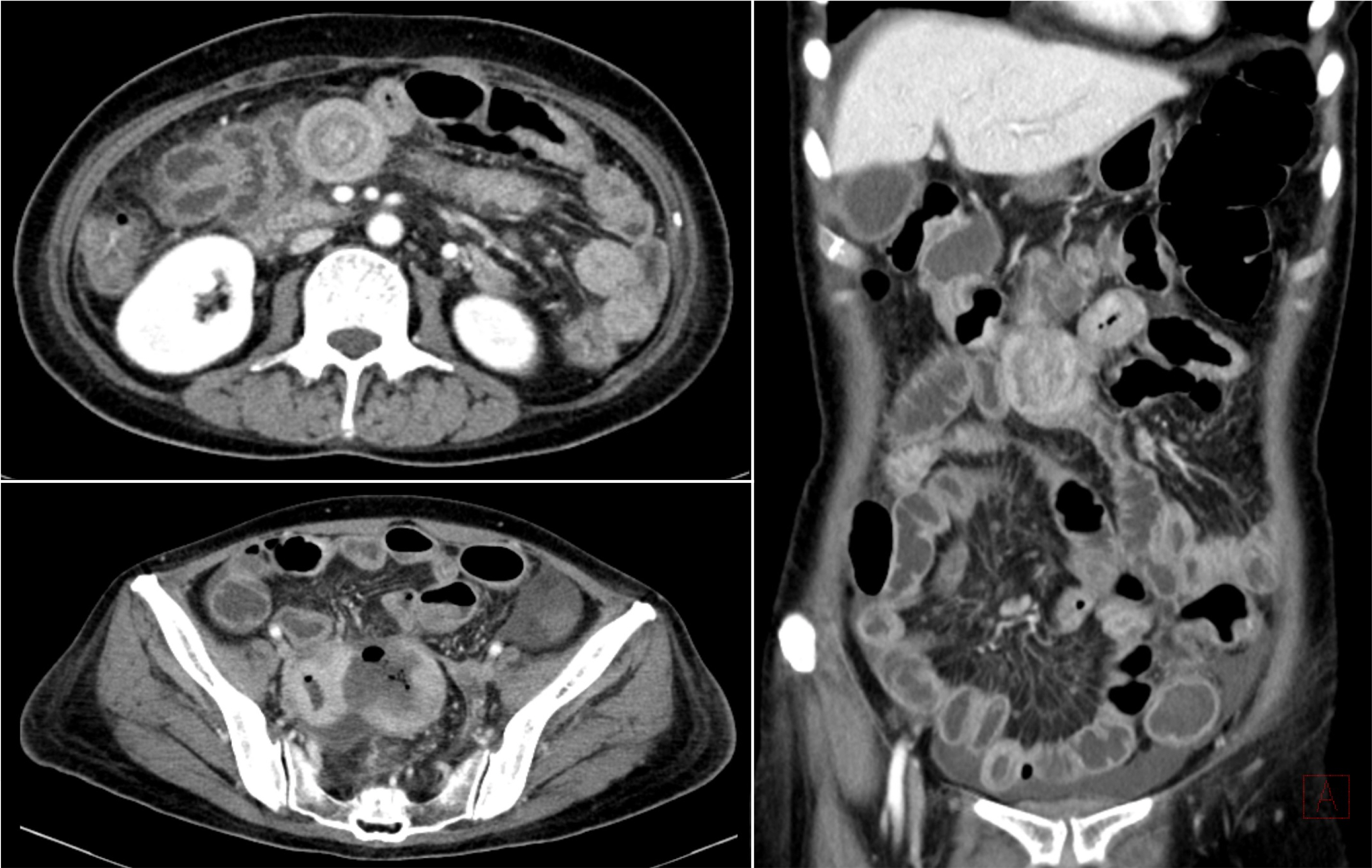
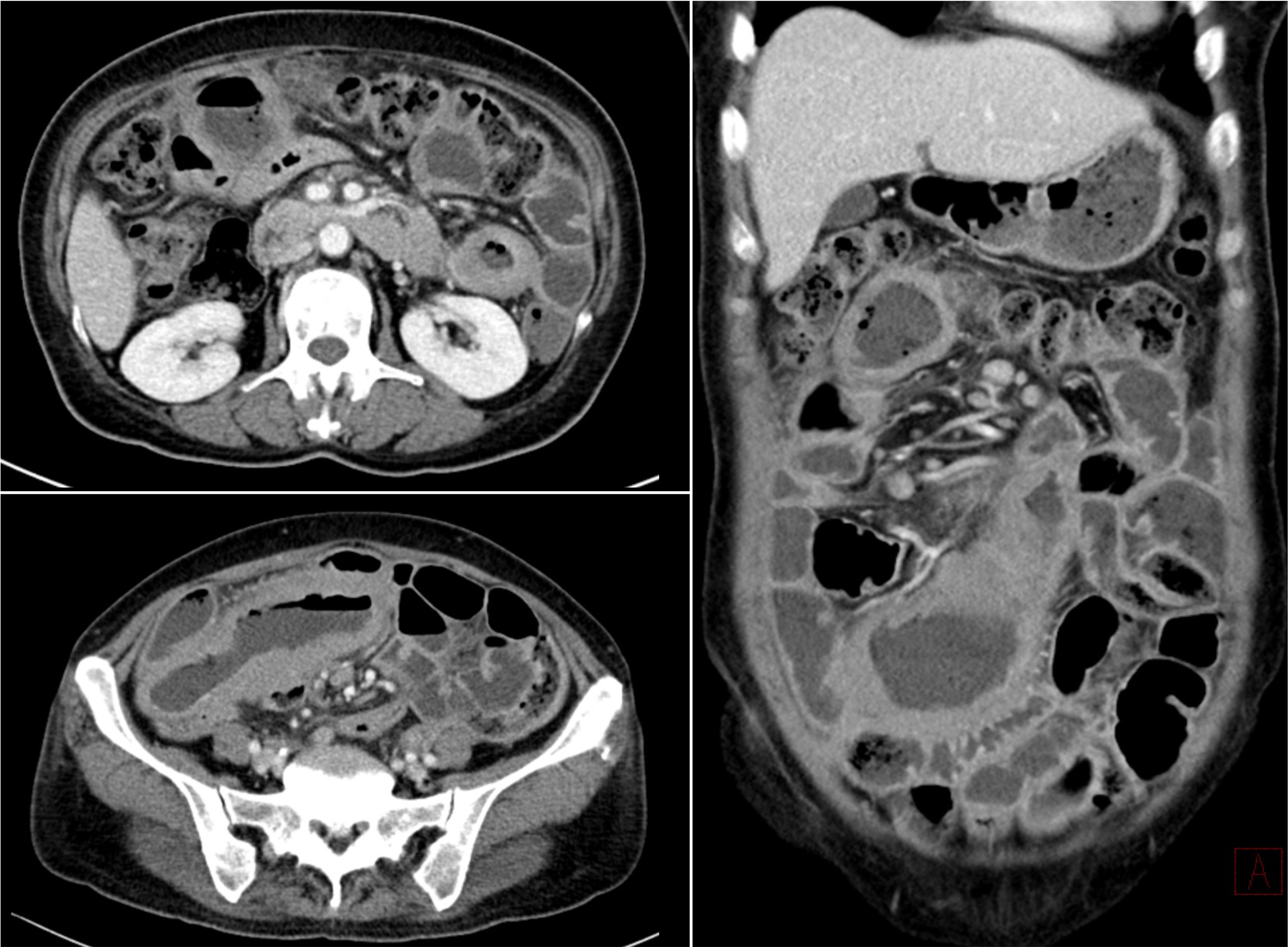
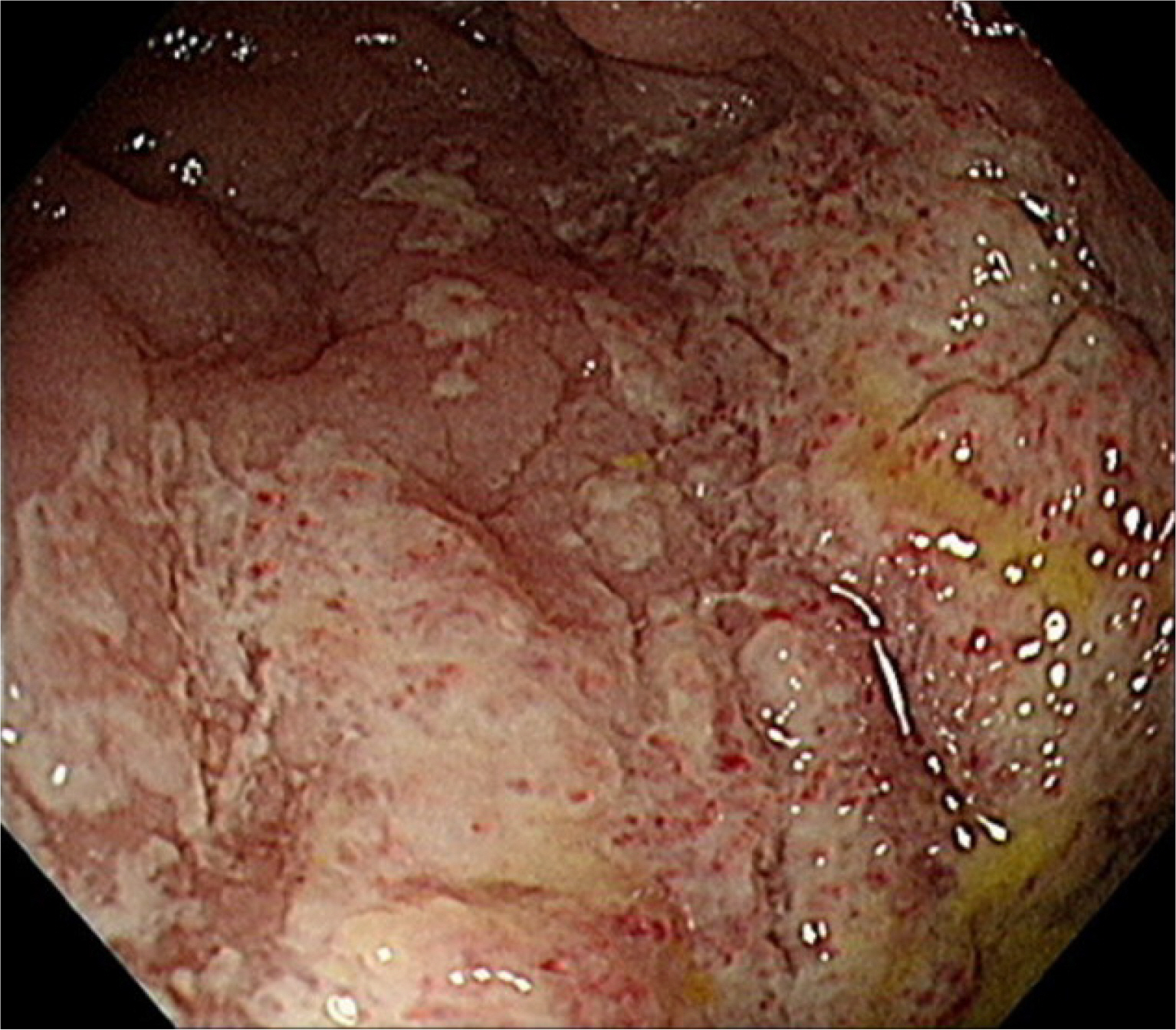
- Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma (MEITL) is a rare and aggressive form of primary gastrointestinal T-cell lymphoma. Symptoms can vary but often include fever, abdominal pain, weight loss, diarrhea, obstruction, and perforation. Disease-specific symptoms rarely present before patients reach an advanced stage, which contributes to delayed diagnosis and poor survival outcomes. Approximately half of the patients with MEITL undergo emergency surgery for acute intestinal obstruction or perforation, leading to peritonitis, septic shock, and multiple organ failure. These factors contribute to treatment delays, which are associated with a worse prognosis, particularly in the case of chemotherapy. This paper reports two fatal cases of patients with MEITL who deteriorated rapidly after emergency surgery for intestinal perforation. Patient 1 complained of persistent diarrhea, but a delayed diagnosis led to bowel perforation, and the subsequent chemotherapy treatment was canceled. Patient 2 was diagnosed relatively early, but treatment was delayed due to intestinal perforation. Despite its rarity, MEITL should be considered through a “high index of suspicion” approach when a patient complains of unexplained abdominal pain and diarrhea. This is expected to improve early diagnosis and ultimately patient prognosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi SM, O'Malley DP. 2018; Diagnostically relevant updates to the 2017 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Ann Diagn Pathol. 37:67–74. DOI: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2018.09.011. PMID: 30308438.
Article2. Jaffe ES. 2009; The 2008 WHO classification of lymphomas: implications for clinical practice and translational research. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 523–31. DOI: 10.1182/asheducation.V2009.1.523.0010523.
Article3. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. 2016; The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 127:2375–2390. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569. PMID: 26980727. PMCID: PMC4874220.
Article4. Tian S, Xiao SY, Chen Q, Liu H, Ping J. 2019; Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma may mimic intestinal inflammatory disorders. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 33:2058738419829387. DOI: 10.1177/2058738419829387. PMID: 30757928. PMCID: PMC6376542.
Article5. Ondrejka S, Jagadeesh D. 2016; Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 11:504–513. DOI: 10.1007/s11899-016-0357-7. PMID: 27900603.
Article6. Soardo G, Castaldo V, Donnini D, Uzzau A, Pizzolitto S, Sechi LA. 2020; Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T cell lymphoma of the appendix: a case report and review of literature. J Gastrointest Cancer. 51:688–694. DOI: 10.1007/s12029-020-00363-6. PMID: 31970655.
Article7. Kasinathan G. 2020; Jun. 6. Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma of the duodenum: an aggressive disease. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1016/j.htct.2020.04.005. PMID: 32536535.
Article8. Tse E, Gill H, Loong F, et al. 2012; Type II enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma: a multicenter analysis from the Asia Lymphoma Study Group. Am J Hematol. 87:663–668. DOI: 10.1002/ajh.23213. PMID: 22641357.
Article9. Fontaine Kent L, Rodgers DL, McGhee JA, Patel VG. 2021; Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma (MEITL) within a Meckel's diverticulum. Am Surg. 87:101–102. DOI: 10.1177/0003134820943563. PMID: 32830541.
Article10. Suzuki Y, Minemura H, Tomita H, et al. 2020; Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma involving the lung and brain: a rare case study. Intern Med. 59:2559–2563. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4710-20. PMID: 32641648. PMCID: PMC7662048.
Article11. Olmos-Alpiste F, Vázquez I, Gallardo F, Sánchez-Gonzalez B, Colomo L, Pujol RM. 2021; Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma with secondary cutaneous involvement: a diagnostic challenge. Am J Dermatopathol. 43:300–304. DOI: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000001855. PMID: 33264131.
Article12. Akiyama T, Okino T, Konishi H, et al. 2008; CD8+, CD56+ (natural killer-like) T-cell lymphoma involving the small intestine with no evidence of enteropathy: clinicopathology and molecular study of five Japanese patients. Pathol Int. 58:626–634. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02281.x. PMID: 18801082.
Article13. Gopalakrishna H, Al-Abdouh A, Nair G, Bekele A. 2020; Incidental diagnosis of monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma: a case report. Cureus. 12:e10084. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10084.
Article14. Sieniawski M, Angamuthu N, Boyd K, et al. 2010; Evaluation of enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma comparing standard therapies with a novel regimen including autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood. 115:3664–3670. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-231324. PMID: 20197551.
Article15. Chin CK, Tsang E, Mediwake H, et al. 2019; Frequency of bowel perforation and impact of bowel rest in aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma with gastrointestinal involvement. Br J Haematol. 184:826–828. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.15173. PMID: 29676487.
Article16. Halphen M, Najjar T, Jaafoura H, Cammoun M, Tufrali G. 1986; Diagnostic value of upper intestinal fiber endoscopy in primary small intestinal lymphoma. A prospective study by the Tunisian-French Intestinal Lymphoma Group. Cancer. 58:2140–2145. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861101)58:9<2140::AID-CNCR2820580930>3.0.CO;2-P.
Article17. van de Water JM, Cillessen SA, Visser OJ, Verbeek WH, Meijer CJ, Mulder CJ. 2010; Enteropathy associated T-cell lymphoma and its precursor lesions. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 24:43–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2009.11.002. PMID: 20206108.
Article18. de Baaij LR, Berkhof J, van de Water JM, et al. 2015; A new and validated clinical prognostic model (EPI) for enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3013–3019. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2195. PMID: 25779949.
Article19. Mutzbauer G, Maurus K, Buszello C, et al. 2018; SYK expression in monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol. 31:505–516. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.145. PMID: 29052597.
Article20. Tomita S, Kikuti YY, Carreras J, et al. 2020; Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma in Asia frequently shows SETD2 alterations. Cancers (Basel). 12:3539. DOI: 10.3390/cancers12123539. PMID: 33260897. PMCID: PMC7759862.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Rare Case of Intestinal T-cell Lymphoma with Multiple Complications
- A Case of Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Presenting with Small Bowel Perforation
- Jejunal Perforation Caused by Primary Jejunal Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
- Intestinal Perforation in a Case of Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma after Initiation of Chemotherapy
- Spontaneous Perforation of Small Bowel Lymphoma Causing Massive Pneumoperitoneum: A case Report