J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2021 Jun;47(3):153-174. 10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.3.153.
Bone loss-related factors in tissue and bone level dental implants: a systematic review of clinical trials
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 2Member of Iranian Association of Periodontology, Private Practice, Tehran, Iran
- 3Student Research Committee, School of Dentistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 4Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Islamic Azad University, Isfahan (Khorasgan) Branch, Isfahan, Iran
- KMID: 2517266
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.3.153
Abstract
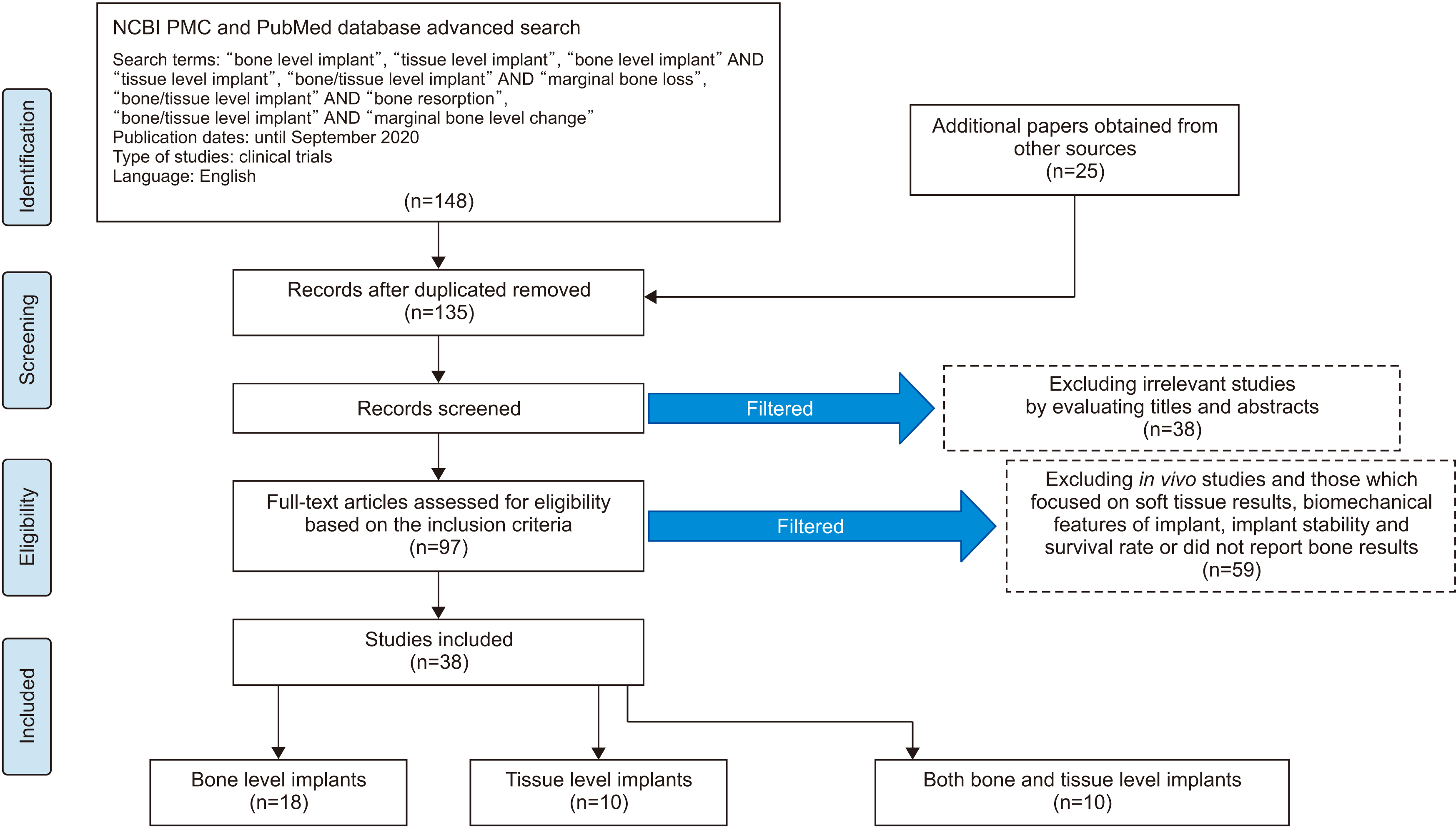
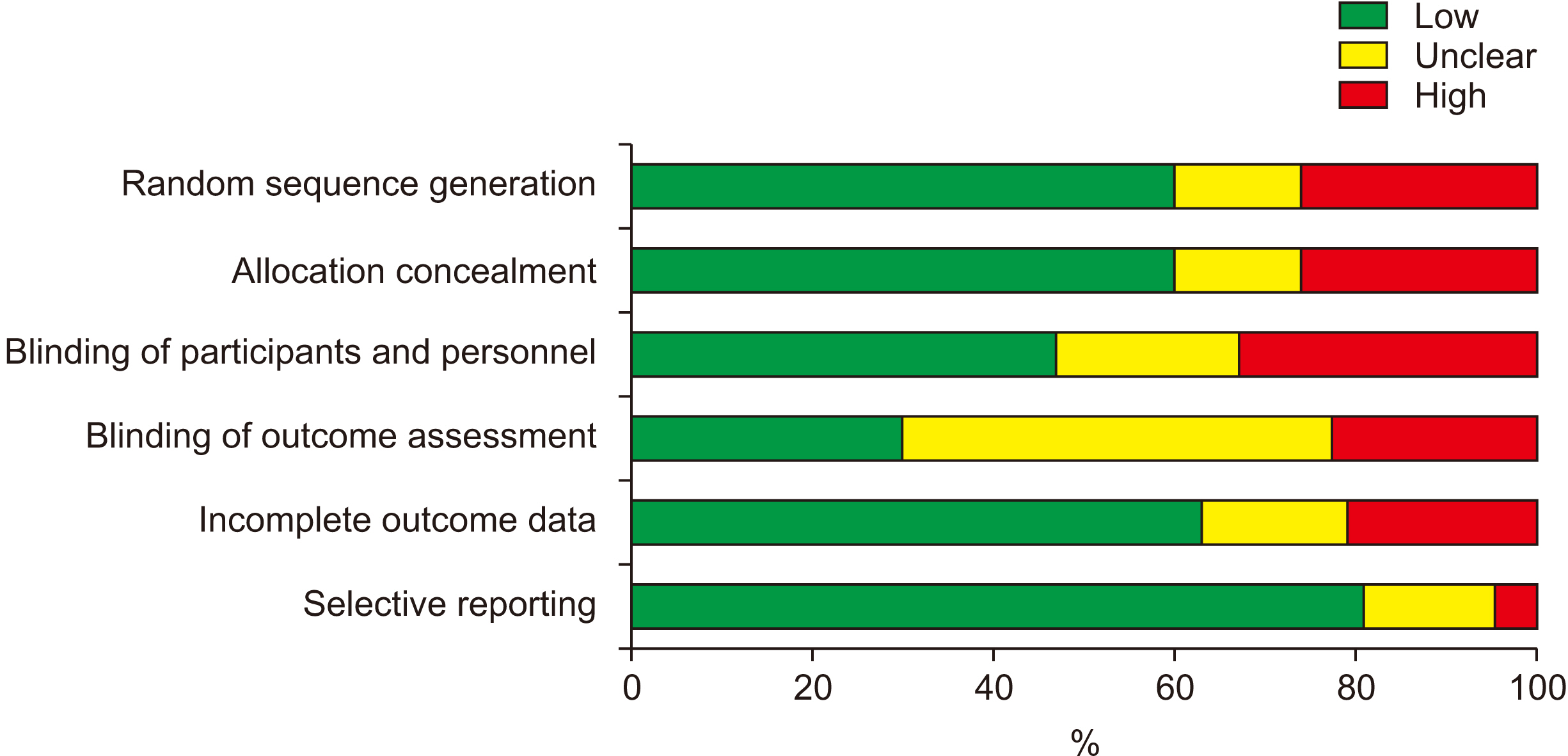
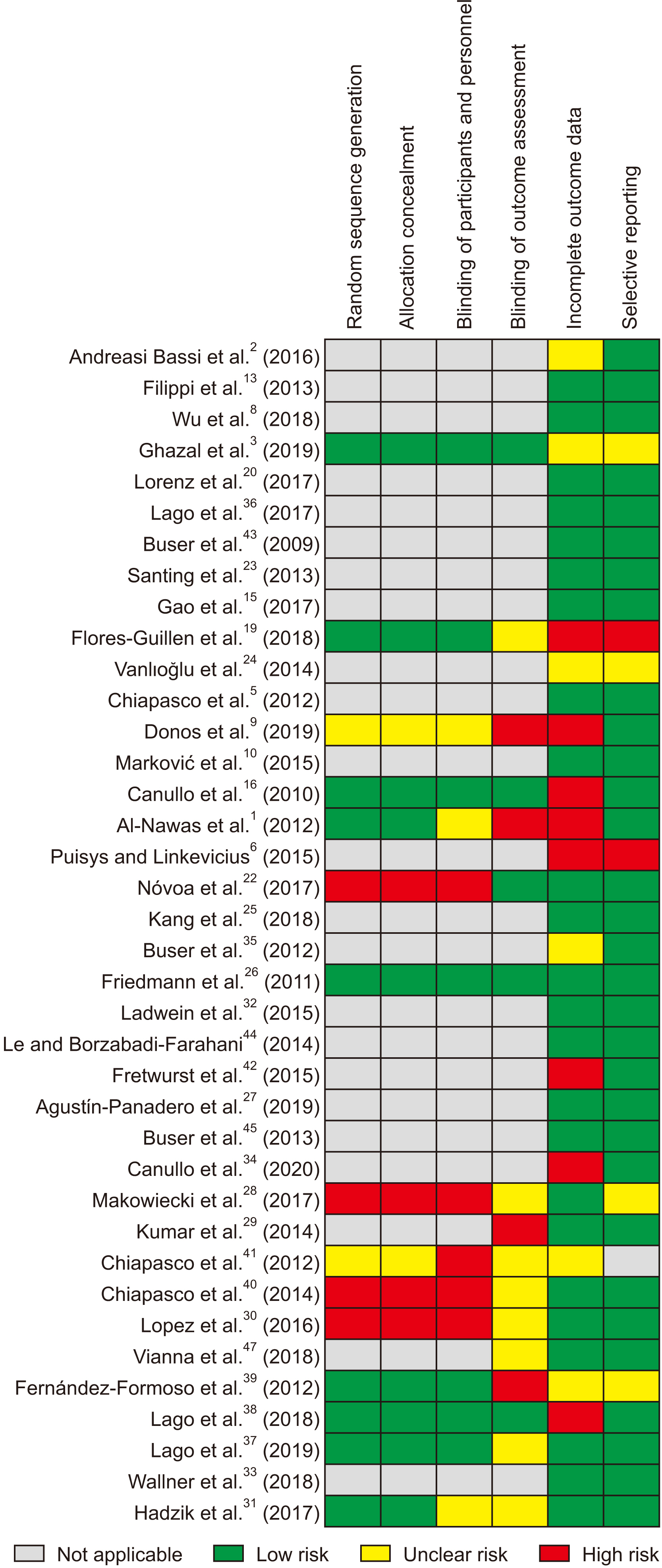
- Dental implants are popular for dental rehabilitation after tooth loss. The goal of this systematic review was to assess bone changes around bone-level and tissue-level implants and the possible causes. Electronic searches of PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science, and a hand search limited to English language clinical trials were performed according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis) guidelines up to September 2020. Studies that stated the type of implants used, and that reported bone-level changes after insertion met the inclusion criteria. The risk of bias was also evaluated. A total of 38 studies were included. Eighteen studies only used bone-level implants, 10 utilized tissuelevel designs and 10 observed bone-level changes in both types of implants. Based on bias assessments, evaluating the risk of bias was not applicable in most studies. There are vast differences in methodologies, follow-ups, and multifactorial characteristics of bone loss around implants, which makes direct comparison impossible. Therefore, further well-structured studies are needed.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Al-Nawas B, Brägger U, Meijer HJ, Naert I, Persson R, Perucchi A, et al. 2012; A double-blind randomized controlled trial (RCT) of Titanium-13Zirconium versus Titanium Grade IV small-diameter bone level implants in edentulous mandibles--results from a 1-year observation period. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 14:896–904. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00324.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00324.x. PMID: 21414131.
Article2. Andreasi Bassi M, Lopez MA, Confalone L, Gaudio RM, Lombardo L, Lauritano D. 2016; Clinical outcome of a two-piece implant system with an internal hexagonal connection: a prospective study. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 30(2 Suppl 1):7–12. PMID: 27469542.3. Ghazal SS, Huynh-Ba G, Aghaloo T, Dibart S, Froum S, O'Neal R, et al. 2019; A randomized, controlled, multicenter clinical study evaluating the crestal bone level change of SLActive Bone Level Ø 3.3 mm implants compared to SLActive Bone Level Ø 4.1 mm implants for single-tooth replacement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 34:708–18. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.6927 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.6927. PMID: 30934041.
Article4. Alharbi HM, Babay N, Alzoman H, Basudan S, Anil S, Jansen JA. 2015; Bone morphology changes around two types of bone-level implants installed in fresh extraction sockets--a histomorphometric study in Beagle dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 26:1106–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12388 . DOI: 10.1111/clr.12388. PMID: 24690000.
Article5. Chiapasco M, Casentini P, Zaniboni M, Corsi E. 2012; Evaluation of peri-implant bone resorption around Straumann Bone Level implants placed in areas reconstructed with autogenous vertical onlay bone grafts. Clin Oral Implants Res. 23:1012–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02262.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02262.x. PMID: 22092480.
Article6. Puisys A, Linkevicius T. 2015; The influence of mucosal tissue thickening on crestal bone stability around bone-level implants. A prospective controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 26:123–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12301 . DOI: 10.1111/clr.12301. PMID: 24313250.
Article7. Güven SŞ, Cabbar F, Güler N. 2020; Local and systemic factors associated with marginal bone loss around dental implants: a retrospective clinical study. Quintessence Int. 51:128–41. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.qi.a42950 . DOI: 10.3290/j.qi.a42950. PMID: 31942574.
Article8. Wu S, Wu X, Shrestha R, Lin J, Feng Z, Liu Y, et al. 2018; Clinical and radiologic outcomes of submerged and nonsubmerged bone-level implants with internal hexagonal connections in immediate implantation: a 5-year retrospective study. J Prosthodont. 27:101–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.12647 . DOI: 10.1111/jopr.12647. PMID: 29143389.
Article9. Donos N, Horvath A, Calciolari E, Mardas N. 2019; Immediate provisionalization of bone level implants with a hydrophilic surface. A five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 30:139–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13400 . DOI: 10.1111/clr.13400. PMID: 30584682.
Article10. Marković A, Čolić S, Šćepanović M, Mišić T, Ðinić A, Bhusal DS. 2015; A 1-year prospective clinical and radiographic study of early-loaded bone level implants in the posterior maxilla. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 17:1004–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12201 . DOI: 10.1111/cid.12201. PMID: 24461229.
Article11. Schwarz F, Sager M, Kadelka I, Ferrari D, Becker J. 2010; Influence of titanium implant surface characteristics on bone regeneration in dehiscence-type defects: an experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 37:466–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01533.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01533.x. PMID: 20507369.
Article12. Cochran DL, Bosshardt DD, Grize L, Higginbottom FL, Jones AA, Jung RE, et al. 2009; Bone response to loaded implants with non-matching implant-abutment diameters in the canine mandible. J Periodontol. 80:609–17. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.080323 . DOI: 10.1902/jop.2009.080323. PMID: 19335081.
Article13. Filippi A, Higginbottom FL, Lambrecht T, Levin BP, Meier JL, Rosen PS, et al. 2013; A prospective noninterventional study to document implant success and survival of the Straumann Bone Level SLActive dental implant in daily dental practice. Quintessence Int. 44:499–512. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.qi.a29611 . DOI: 10.3290/j.qi.a29611. PMID: 23616977.
Article14. Elian N, Bloom M, Trushkowsky RD, Dard MM, Tarnow D. 2014; Effect of 3- and 4-mm interimplant distances on the height of interimplant bone crest: a histomorphometric evaluation measured on bone level dental implants in minipig. Implant Dent. 23:522–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0000000000000153 . DOI: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000153. PMID: 25192165.
Article15. Gao E, Hei WH, Park JC, Pang K, Kim SK, Kim B, et al. 2017; Bone-level implants placed in the anterior maxilla: an open-label, single-arm observational study. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 47:312–27. https://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2017.47.5.312 . DOI: 10.5051/jpis.2017.47.5.312. PMID: 29093988. PMCID: PMC5663668.
Article16. Canullo L, Fedele GR, Iannello G, Jepsen S. 2010; Platform switching and marginal bone-level alterations: the results of a randomized-controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 21:115–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01867.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01867.x. PMID: 20070752.
Article17. Koutouzis T, Mesia R, Calderon N, Wong F, Wallet S. 2014; The effect of dynamic loading on bacterial colonization of the dental implant fixture-abutment interface: an in vitro study. J Oral Implantol. 40:432–7. https://doi.org/10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-11-00207 . DOI: 10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-11-00207. PMID: 25106007.
Article18. Lauritano D, Moreo G, Lucchese A, Viganoni C, Limongelli L, Carinci F. 2020; The impact of implant-abutment connection on clinical outcomes and microbial colonization: a narrative review. Materials (Basel). 13:1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051131 . DOI: 10.3390/ma13051131. PMID: 32138368. PMCID: PMC7085009.
Article19. Flores-Guillen J, Álvarez-Novoa C, Barbieri G, Martín C, Sanz M. 2018; Five-year outcomes of a randomized clinical trial comparing bone-level implants with either submerged or transmucosal healing. J Clin Periodontol. 45:125–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12832 . DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12832. PMID: 29032574.
Article20. Lorenz J, Lerner H, Sader RA, Ghanaati S. 2017; Investigation of peri-implant tissue conditions and peri-implant tissue stability in implants placed with simultaneous augmentation procedure: a 3-year retrospective follow-up analysis of a newly developed bone level implant system. Int J Implant Dent. 3:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-017-0104-4 . DOI: 10.1186/s40729-017-0104-4. PMID: 28875278. PMCID: PMC5585115.
Article21. Tesmer M, Wallet S, Koutouzis T, Lundgren T. 2009; Bacterial colonization of the dental implant fixture-abutment interface: an in vitro study. J Periodontol. 80:1991–7. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.090178 . DOI: 10.1902/jop.2009.090178. PMID: 19961382.
Article22. Nóvoa L, Batalla P, Caneiro L, Pico A, Liñares A, Blanco J. 2017; Influence of abutment height on maintenance of peri-implant crestal bone at bone-level implants: a 3-year follow-up study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 37:721–7. https://doi.org/10.11607/prd.2762 . DOI: 10.11607/prd.2762. PMID: 28817138.
Article23. Santing HJ, Raghoebar GM, Vissink A, den Hartog L, Meijer HJ. 2013; Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites: a prospective cohort study with 60 consecutive patients. Clin Oral Implants Res. 24:941–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02486.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02486.x. PMID: 22540833.
Article24. Vanlıoğlu BA, Kahramanoğlu E, Ozkan Y, Kulak-Özkan Y. 2014; Clinical and radiographic evaluation of early loaded maxillary anterior single-tooth bone-level implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 29:1369–73. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.3446 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.3446. PMID: 25397799.
Article25. Kang MH, Jung UW, Cho KS, Lee JS. 2018; Retrospective radiographic observational study of 1692 Straumann tissue-level dental implants over 10 years. II. Marginal bone stability. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 20:875–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12636 . DOI: 10.1111/cid.12636. PMID: 30048038.
Article26. Friedmann A, Gissel K, Soudan M, Kleber BM, Pitaru S, Dietrich T. 2011; Randomized controlled trial on lateral augmentation using two collagen membranes: morphometric results on mineralized tissue compound. J Clin Periodontol. 38:677–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2011.01738.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2011.01738.x,. PMID: 21557757.
Article27. Agustín-Panadero R, Martínez-Martínez N, Fernandez-Estevan L, Faus-López J, Solá-Ruíz MF. 2019; Influence of transmucosal area morphology on peri-implant bone loss in tissue-level implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 34:947–52. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.7329 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.7329. PMID: 30768662.
Article28. Makowiecki A, Botzenhart U, Seeliger J, Heinemann F, Biocev P, Dominiak M. 2017; A comparative study of the effectiveness of early and delayed loading of short tissue-level dental implants with hydrophilic surfaces placed in the posterior section of the mandible-a preliminary study. Ann Anat. 212:61–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2017.02.009 . DOI: 10.1016/j.aanat.2017.02.009. PMID: 28365383.
Article29. Kumar VV, Sagheb K, Kämmerer PW, Al-Nawas B, Wagner W. 2014; Retrospective clinical study of marginal bone level changes with two different screw-implant types: comparison between tissue level (TE) and bone level (BL) implant. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 13:259–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-013-0532-5 .
Article30. Lopez MA, Andreasi Bassi M, Confalone L, Gaudio RM, Lombardo L, Lauritano D. 2016; Retrospective study on bone-level and soft-tissue-level cylindrical implants. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 30(2 Suppl 1):43–8. PMID: 27469547.31. Hadzik J, Botzenhart U, Krawiec M, Gedrange T, Heinemann F, Vegh A, et al. 2017; Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of the implantation in the lateral part of the mandible between short tissue level (TE) and bone level (BL) implant systems. Ann Anat. 213:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2017.05.008 . DOI: 10.1016/j.aanat.2017.05.008. PMID: 28602825.
Article32. Ladwein C, Schmelzeisen R, Nelson K, Fluegge TV, Fretwurst T. 2015; Is the presence of keratinized mucosa associated with periimplant tissue health? A clinical cross-sectional analysis. Int J Implant Dent. 1:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-015-0009-z . DOI: 10.1186/s40729-015-0009-z. PMID: 27747633. PMCID: PMC5005560.
Article33. Wallner G, Rieder D, Wichmann MG, Heckmann SM. 2018; Peri-implant bone loss of tissue-level and bone-level implants in the esthetic zone with gingival biotype analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 33:1119–25. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.6641 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.6641. PMID: 30231100.
Article34. Canullo L, Menini M, Covani U, Pesce P. 2020; Clinical outcomes of using a prosthetic protocol to rehabilitate tissue-level implants with a convergent collar in the esthetic zone: a 3-year prospective study. J Prosthet Dent. 123:246–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.12.022 . DOI: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.12.022. PMID: 31227242.
Article35. Buser D, Janner SF, Wittneben JG, Brägger U, Ramseier CA, Salvi GE. 2012; 10-Year survival and success rates of 511 titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: a retrospective study in 303 partially edentulous patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 14:839–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2012.00456.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2012.00456.x. PMID: 22897683.
Article36. Lago L, da Silva L, Gude F, Rilo B. 2017; Bone and soft tissue response in bone-level implants restored with platform switching: a 5-year clinical prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 32:919–26. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.5859 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.5859. PMID: 28708924.
Article37. Lago L, da Silva L, Martinez-Silva I, Rilo B. 2019; Radiographic assessment of crestal bone loss in tissue-level implants restored by platform matching compared with bone-level implants restored by platform switching: a randomized, controlled, split-mouth trial with 3-year follow-up. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 34:179–86. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.6954 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.6954. PMID: 30282088.
Article38. Lago L, da Silva L, Martinez-Silva I, Rilo B. 2018; Crestal bone level around tissue-level implants restored with platform matching and bone-level implants restored with platform switching: a 5-year randomized controlled trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 33:448–56. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.6149 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.6149. PMID: 29534134.
Article39. Fernández-Formoso N, Rilo B, Mora MJ, Martínez-Silva I, Díaz-Afonso AM. 2012; Radiographic evaluation of marginal bone maintenance around tissue level implant and bone level implant: a randomised controlled trial. A 1-year follow-up. J Oral Rehabil. 39:830–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2842.2012.02343.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2012.02343.x. PMID: 22889084.
Article40. Chiapasco M, Casentini P, Zaniboni M. 2014; Implants in reconstructed bone: a comparative study on the outcome of Straumann® tissue level and bone level implants placed in vertically deficient alveolar ridges treated by means of autogenous onlay bone grafts. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 16:32–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2012.00457.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2012.00457.x. PMID: 22494433.
Article41. Chiapasco M, Casentini P, Zaniboni M, Corsi E, Anello T. 2012; Titanium-zirconium alloy narrow-diameter implants (Straumann Roxolid(®)) for the rehabilitation of horizontally deficient edentulous ridges: prospective study on 18 consecutive patients. Clin Oral Implants Res. 23:1136–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02296.x . DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02296.x. PMID: 22092806.
Article42. Fretwurst T, Nack C, Al-Ghrairi M, Raguse JD, Stricker A, Schmelzeisen R, et al. 2015; Long-term retrospective evaluation of the peri-implant bone level in onlay grafted patients with iliac bone from the anterior superior iliac crest. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43:956–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2015.03.037 . DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.03.037. PMID: 25964006.
Article43. Buser D, Halbritter S, Hart C, Bornstein MM, Grütter L, Chappuis V, et al. 2009; Early implant placement with simultaneous guided bone regeneration following single-tooth extraction in the esthetic zone: 12-month results of a prospective study with 20 consecutive patients. J Periodontol. 80:152–62. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.080360 . DOI: 10.1902/jop.2009.080360. PMID: 19228101.
Article44. Le BT, Borzabadi-Farahani A. 2014; Simultaneous implant placement and bone grafting with particulate mineralized allograft in sites with buccal wall defects, a three-year follow-up and review of literature. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 42:552–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2013.07.026 . DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.07.026. PMID: 24529349.
Article45. Buser D, Chappuis V, Bornstein MM, Wittneben JG, Frei M, Belser UC. 2013; Long-term stability of contour augmentation with early implant placement following single tooth extraction in the esthetic zone: a prospective, cross-sectional study in 41 patients with a 5- to 9-year follow-up. J Periodontol. 84:1517–27. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2013.120635 . DOI: 10.1902/jop.2013.120635. PMID: 23347346.
Article46. Shin YK, Han CH, Heo SJ, Kim S, Chun HJ. 2006; Radiographic evaluation of marginal bone level around implants with different neck designs after 1 year. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 21:789–94. PMID: 17066642.47. Vianna TT, Taiete T, Casarin RCV, Giorgi MCC, Aguiar FHB, Silvério KG, et al. 2018; Evaluation of peri-implant marginal tissues around tissue-level and bone-level implants in patients with a history of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 45:1255–65. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12999 . DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12999. PMID: 30107048.
Article48. Sargolzaie N, Samizade S, Arab H, Ghanbari H, Khodadadifard L, Khajavi A. 2019; The evaluation of implant stability measured by resonance frequency analysis in different bone types. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 45:29–33. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.1.29 . DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.1.29. PMID: 30847294. PMCID: PMC6400699.
Article49. Schrott A, Riggi-Heiniger M, Maruo K, Gallucci GO. 2014; Implant loading protocols for partially edentulous patients with extended edentulous sites--a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 29 Suppl:239–55. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.2014suppl.g4.2 . DOI: 10.11607/jomi.2014suppl.g4.2. PMID: 24660201.
Article50. Lorenz J, Kubesch A, Korzinskas T, Barbeck M, Landes C, Sader RA, et al. 2015; TRAP-positive multinucleated giant cells are foreign body giant cells rather than osteoclasts: results from a split-mouth study in humans. J Oral Implantol. 41:e257–66. https://doi.org/10.1563/aaid-joi-D-14-00273 . DOI: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-14-00273. PMID: 25490579.
Article51. Degidi M, Piattelli A, Carinci F. 2008; Clinical outcome of narrow diameter implants: a retrospective study of 510 implants. J Periodontol. 79:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2008.070248 . DOI: 10.1902/jop.2008.070248. PMID: 18166092.
Article52. González-Martín O, Oteo C, Ortega R, Alandez J, Sanz M, Veltri M. 2016; Evaluation of peri-implant buccal bone by computed tomography: an experimental study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 27:950–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12663 . DOI: 10.1111/clr.12663. PMID: 26178780.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of crown-to-implant ratio on periimplant marginal bone loss in the posterior region: a five-year retrospective study
- The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
- Factors associated with the survival rate and the marginal bone loss of dental implant over 7-years loading
- RADIOGRAGHIC STUDY OF MARGINAL BONE LOSS AROUND OSSEOINTEGRATED IMPLANTS AFTER FUNCTIONAL LOADING
- A study on the effects of early loading on the surrounding bone tissue of the dental implants