Kosin Med J.
2021 Jun;36(1):34-39. 10.7180/kmj.2021.36.1.34.
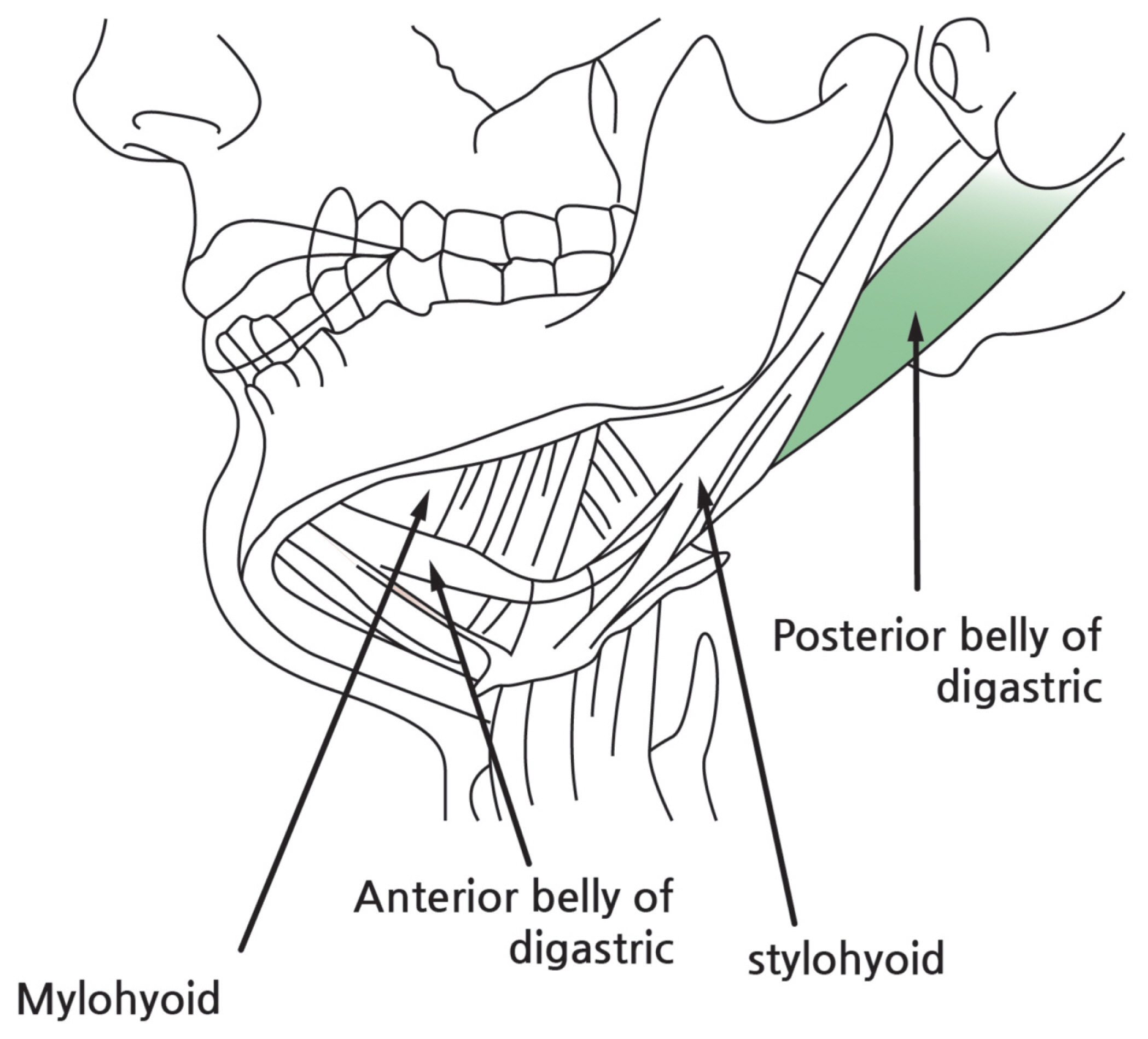
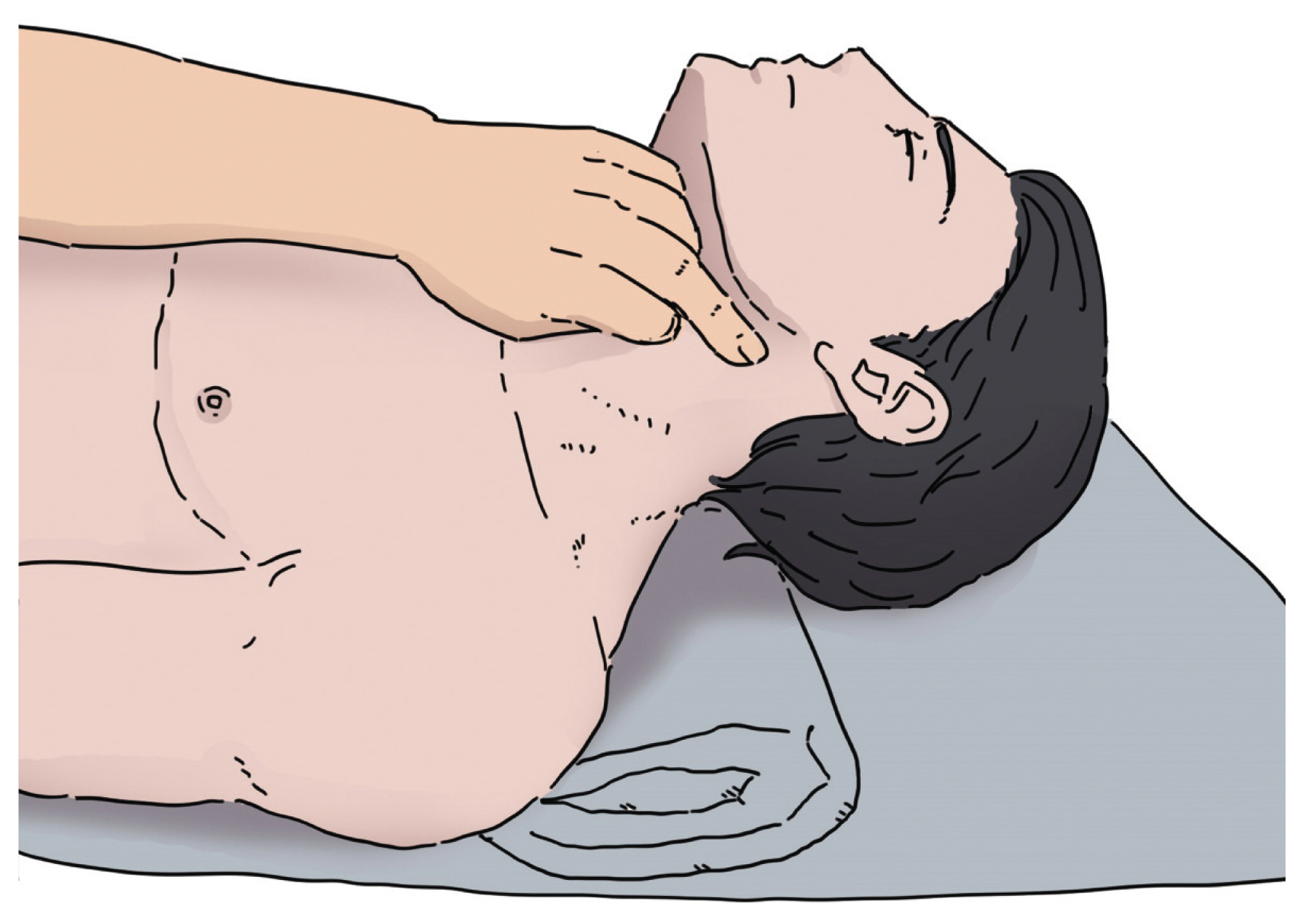
The Management of Foreign Body Sensation in the Throat after Stroke by Trigger Point Injection on Posterior Belly of Digastric Muscles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Graduate School, Dongguk University, Gyeongju-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Korea
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Korea
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Cheon Rehabilitation Medicine Clinic, Gwangju, Korea
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Kwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2517223
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2021.36.1.34
Abstract
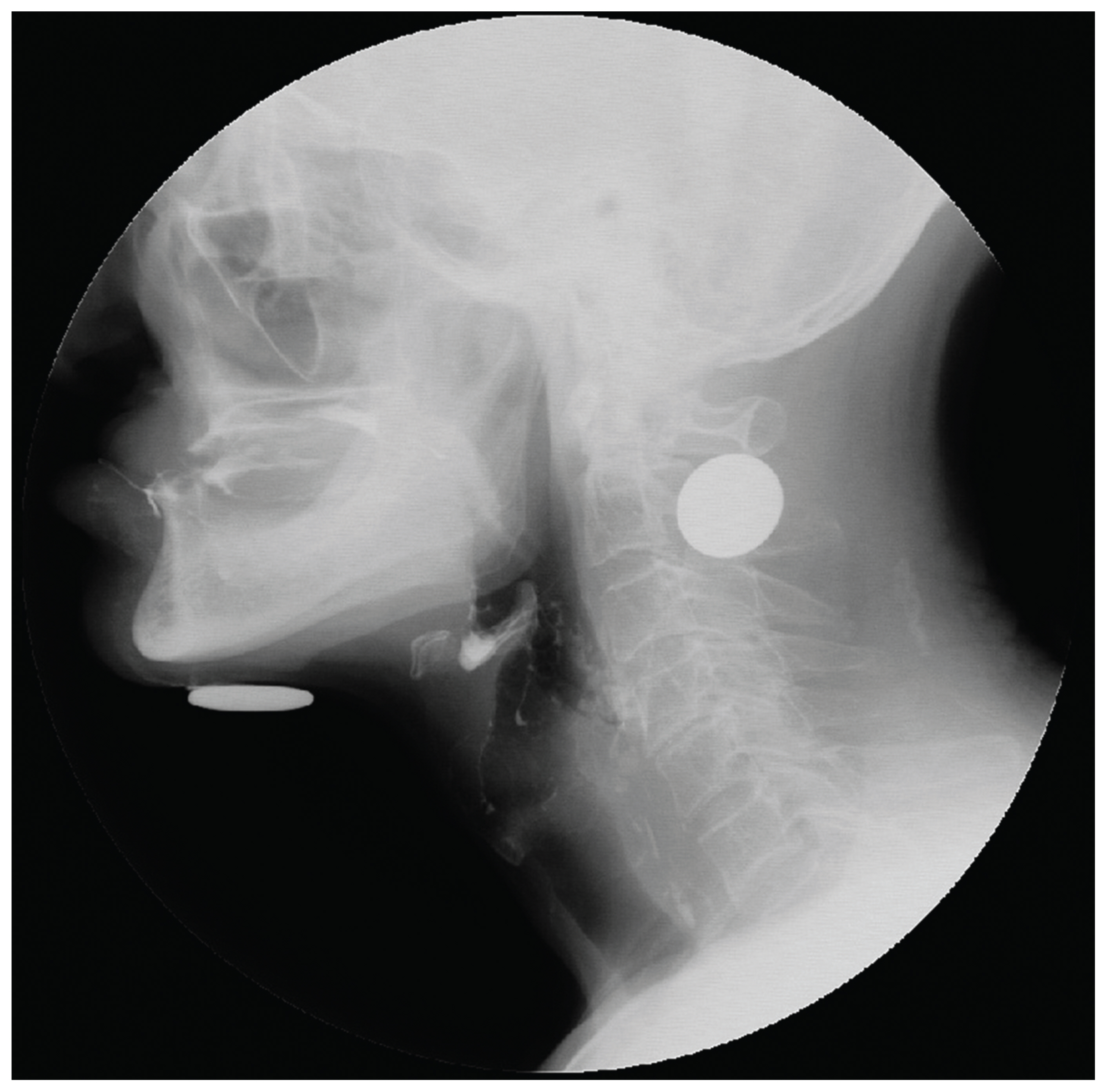
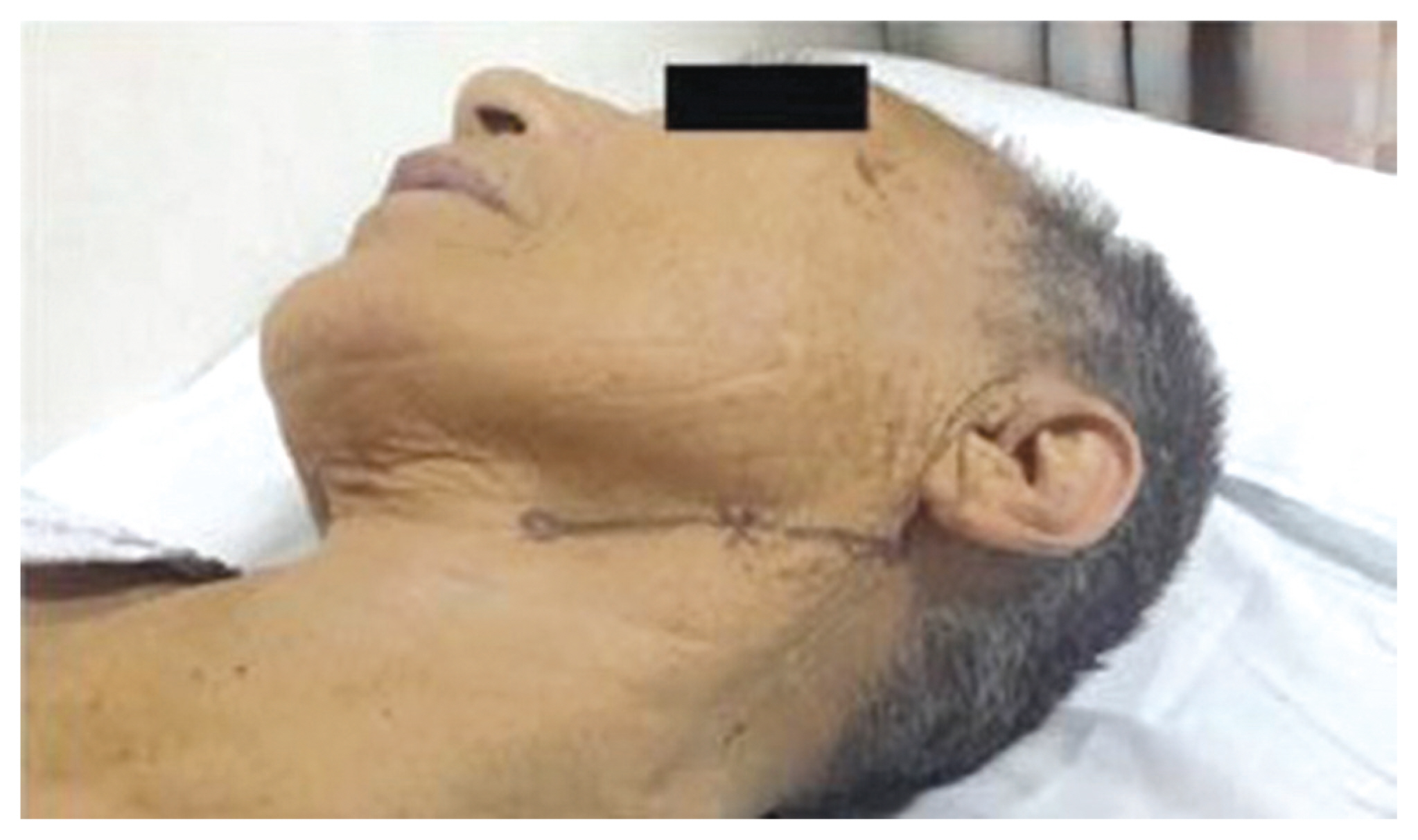
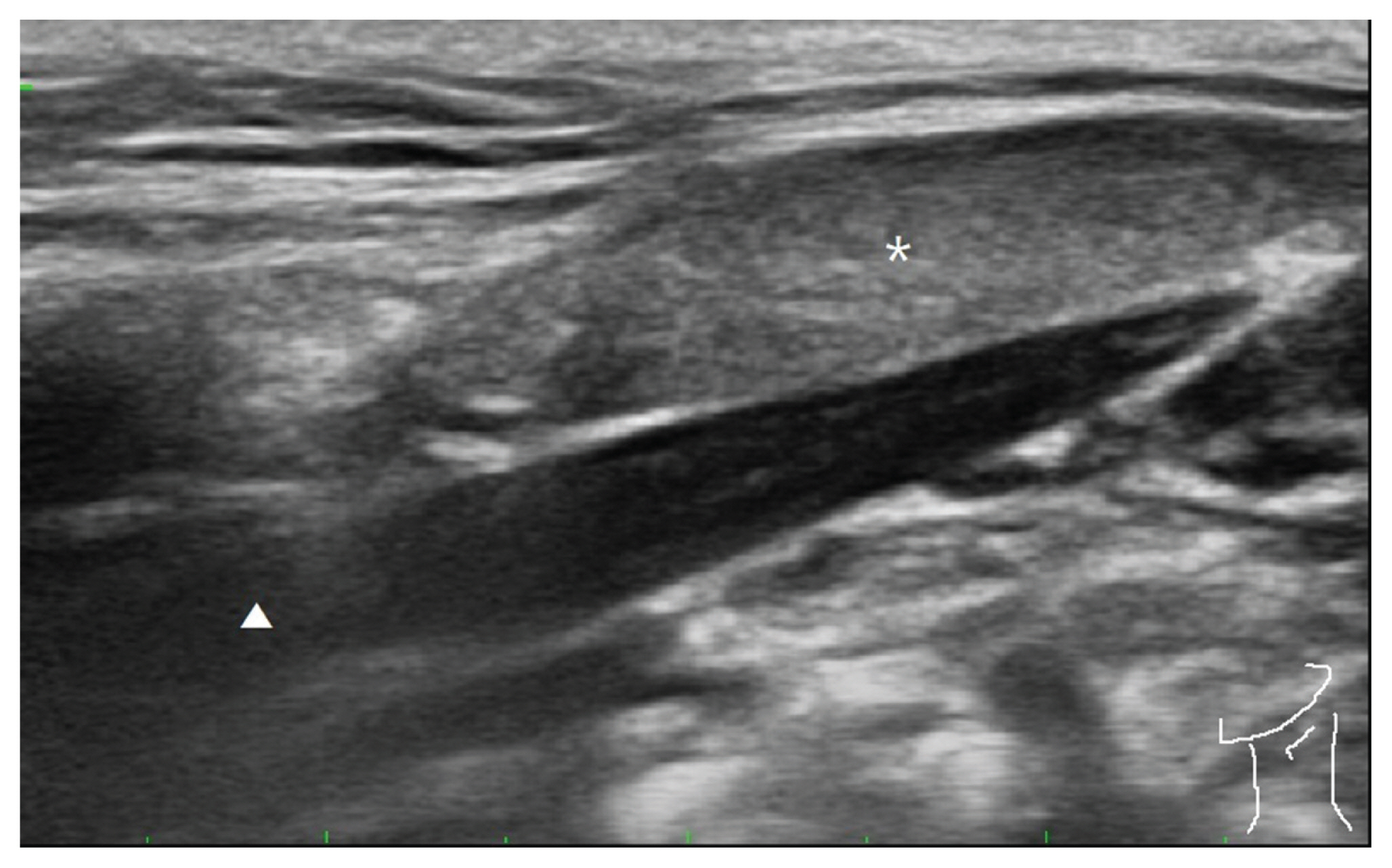
- Foreign body (FB) sensation in the throat is often a common symptom encountered in clinical practice. FB sensation in throat has numerous causes mainly caused by reflex diseases such as laryngopharyngeal reflux. Its treatment has been focused on organic problems or hysteria while musculoskeletal problem has been neglected. We hereby report a patient with dysphagia and complaint of FB sensation in the throat after nasogastric tube removal. It was relieved by trigger point injection on the posterior belly of digastric muscles.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Malcomson KG. Globus hystericus vel pharyngis (a recommaissance of proximal vagal modalities). J Laryngol Otol. 1968; 82:219–30.2. Burch JG. Occlusion related to craniofacial pain. Philadelpia(PA): Lea & Febiger;1977.3. Hong CZ. Lidocaine injection versus dry needling to myofascial trigger point. The importance of the local twitch response. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1994; 73:256–63.4. Harvey PR, Theron BT, Trudgill NJ. Managing a patient with globus pharyngeus. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2018; 9:208–12.
Article5. Lee BE, Kim GH. Globus pharyngeus: a review of its etiology, diagnosis and treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:2462–71.
Article6. Jarvenpaa P, Arkkila P, Aaltonen LM. Globus pharyngeus: a review of etiology, diagnostics, and treatment. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018; 275:1945–53.
Article7. Penović S, Roje Ź, Brdar D, Graćan S, Bubić A, Vela J, et al. Globus Pharyngeus: A Symptom of Increased Thyroid or Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Acta Clin Croat. 2018; 57:110–5.
Article8. Bakheit AM. Management of neurogenic dysphagia. Postgrad Med J. 2001; 77:694–9.
Article9. Miles A, Allen JE. Management of oropharyngeal neurogenic dysphagia in adults. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 23:433–9.
Article10. Travell JG, Simons DG. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger PointManual: The Upper Extremities. 1. Baltimore(MD): Williams & Wilkins;1983.11. Lavelle ED, Lavelle W, Smith HS. Myofascial trigger points. Anesthesiol Clin. 2007; 25:841–51.
Article12. Dommerholt J, Hooks T, Chou LW, Finnegan M. A critical overview of the current myofascial pain literature - November 2018. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2019; 23:65–73.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A clinical perspective on the anatomical study of digastric muscle
- Anatomic Variation of the Anterior Belly of Digastric Muscle and Positional Relationship between the Posterior Belly of Digastric and Stylohyoid Muscle
- Correction of post-traumatic anterior open bite by injection of botulinum toxin type A into the anterior belly of the digastric muscle: case report
- Anatomy and variations of digastric muscle
- Bilateral variations of the head of the digastric muscle in Korean: a case report