Kosin Med J.
2021 Jun;36(1):25-33. 10.7180/kmj.2021.36.1.25.
Immediate Changes of Glucose Metabolism After Gastretomy for Early Gastric Cancer in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2517222
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2021.36.1.25
Abstract
Objectives
It is well known that type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is dramatically improved after bariatric surgery, although the mechanisms have not been clearly identified. The skill required for gastric surgery for gastric cancer is very similar to that needed in bariatric surgery. In this study, we evaluated the immediate improvement of T2DM after gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Methods
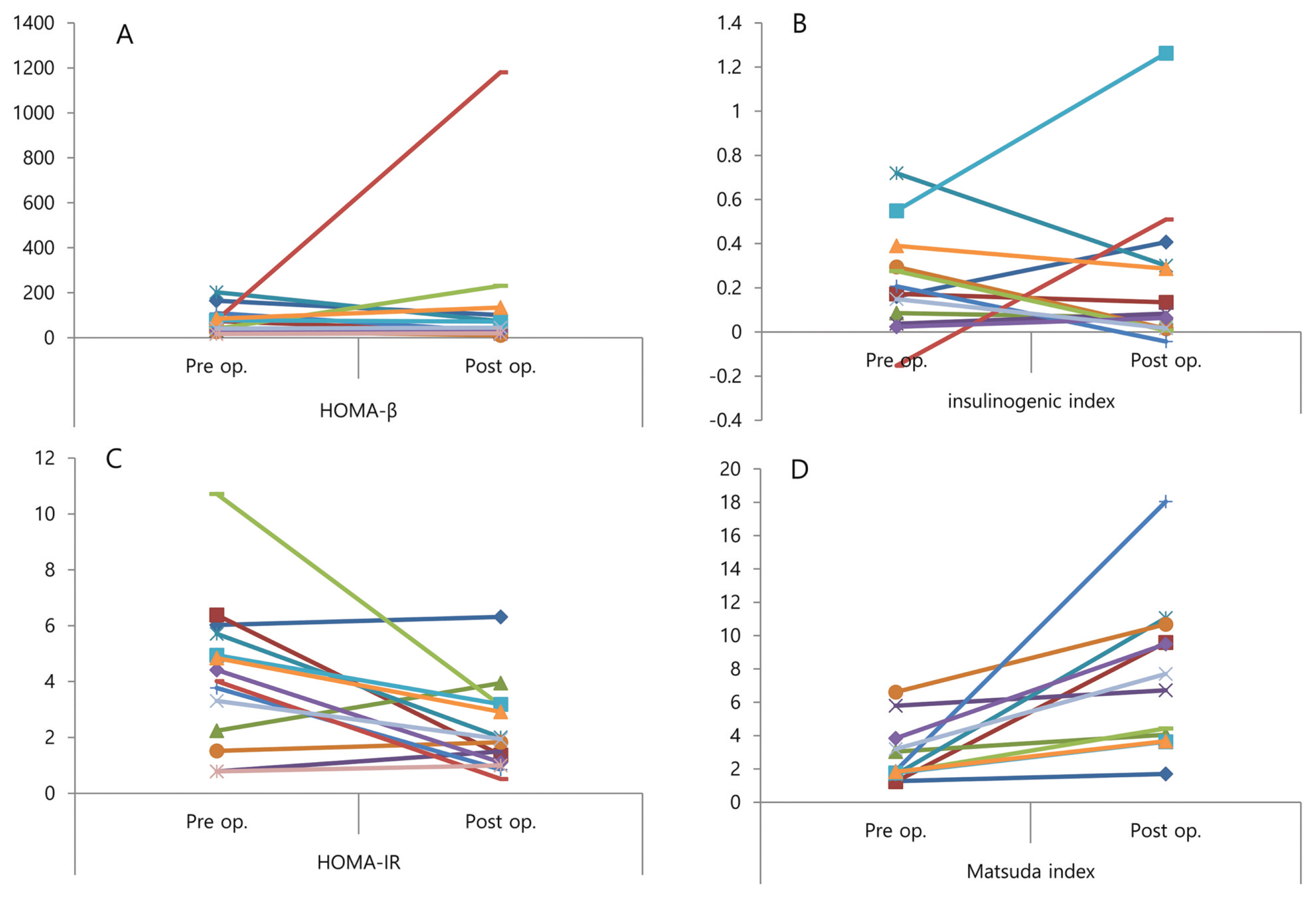
A total of nine patients who were diagnosed with early gastric cancer (EGC) and already had T2DM underwent a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) before surgery and within two weeks after gastrectomy. Glucose, insulin, and c-peptide were measured before, and 30 and 60 minutes after ingesting 75 g of glucose. From these trials, we calculated the HOMA-IR, insulinogenic index, Matsuda index, and area under the curve (AUC).
Results
The mean age of participants was 57.23 ± 11.08 years and eight of them were men. HOMA-IR (4.2 vs. 2.3, P = 0.012) levels were decreased after surgery. There were no significant differences of insulinogenic index, fasting blood sugar before and after surgery. The Matsuda index (3.3 vs. 8.3, P = 0.002) was significantly increased and AUC (512.9 vs. 388.7 mg-hr/dL, P > 0.001) upon 75 g OGTT was significantly decreased after surgery.
Conclusions
Insulin sensitivity was immediately improved after gastrectomy for early gastric cancer in patients with T2DM.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JW, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ, Choi SH, Noh SH. Outcome after gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:49–54.
Article2. Kang KC, Shin SH, Lee YJ, Heo YS. Influence of gastrectomy for stomach cancer on type 2 diabetes mellitus for patients with a body mass index less than 30 kg/m(2). J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 82:347–55.
Article3. Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, Long SB, Morris PG, Brown BM, et al. Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 1995; 222:339–50. discussion 350–2.
Article4. Fried M, Ribaric G, Buchwald JN, Svacina S, Dolezalova K, Scopinaro N. Metabolic surgery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with BMI <35 kg/m2: an integrative review of early studies. Obes Surg. 2010; 20:776–90.5. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–9.6. Seino Y, Ikeda M, Yawata M, Imura H. The insulinogenic index in secondary diabetes. Hormone and Metabolic Research. 1975; 7(1):07–15.
Article7. Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:1462–70.
Article8. Lee H-J, Kim H-H, Kim M-C, Ryu S-Y, Kim W, Song K-Y, et al. The impact of a high body mass index on laparoscopy assisted gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Surgical endoscopy. 2009; 23:2473–9.
Article9. Aoyama T, Yoshikawa T, Shirai J, Hayashi T, Yamada T, Tsuchida K, et al. Body weight loss after surgery is an independent risk factor for continuation of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:2000–6.
Article10. Salehi M, Prigeon RL, D’Alessio DA. Gastric Bypass Surgery Enhances Glucagon- Like Peptide 1–Stimulated Postprandial Insulin Secretion in Humans. Diabetes. 2011; 60:230 8–14.11. Anderwald C-H, Tura A, Promintzer-Schifferl M, Prager G, Stadler M, Ludvik B, et al. Alterations in gastrointestinal, endocrine, and metabolic processes after bariatric Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Diabetes care. 2012; 35:2580–7.
Article12. Jimenez A, Casamitjana R, Flores L, Delgado S, Lacy A, Vidal J. GLP-1 and the long-term outcome of type 2 diabetes mellitus after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese subjects. Ann Surg. 2013; 25(7):894–9.13. Huang C-K, Shabbir A, Lo C-H, Tai C-M, Chen Y-S, Houng J-Y. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus in Chinese patients with body mass index of 25–35. Obes surg. 2011; 21:1344–9.
Article14. Malapan K, Goel R, Tai C-M, Kao Y-H, Chang P-C, Huang C-K. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for nonobese type II diabetes mellitus in Asian patients. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014; 10:834–40.
Article15. Bojsen-Moller KN, Dirksen C, Jorgensen NB, Jacobsen SH, Serup AK, Albers PH, et al. Early enhancements of hepatic and later of peripheral insulin sensitivity combined with increased postprandial insulin secretion contribute to improved glycemic control after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetes. 2014; 63:1725–37.
Article16. Salinari S, Bertuzzi A, Asnaghi S, Guidone C, Manco M, Mingrone G. First-phase insulin secretion restoration and differential response to glucose load depending on the route of administration in type 2 diabetic subjects after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:375–80.
Article17. Bojsen-Moller KN, Dirksen C, Jorgensen NB, Jacobsen SH, Hansen DL, Worm D, et al. Increased hepatic insulin clearance after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:E1066–71.18. Lingvay I, Guth E, Islam A, Livingston E. Rapid improvement in diabetes after gastric bypass surgery : is it the diet or surgery? Diabetes care. 2013; 36:2741–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of the Kidney in Glucose Metabolism
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Patients with Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Letter: Early Assessment of the Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Can Fasting Parameters of Glucose Metabolism Contribute to Risk Prediction? (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:785–93)
- Response: Early Assessment of the Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Can Fasting Parameters of Glucose Metabolism Contribute to Risk Prediction? (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:785–93)
- Management of Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Current Status and Suggestions