J Neurocrit Care.
2021 Jun;14(1):36-45. 10.18700/jnc.210002.
Treatment of patients with severe traumatic brain injury: a 7-year single institution experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Jacobi Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
- 2Department of Surgery, NYU Langone Hospital–Long Island, NYU Long Island School of Medicine, Mineola, NY, USA
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Piedmont Atlanta Hospital, Piedmont Healthcare, Atlanta, GA, USA
- KMID: 2517131
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.210002
Abstract
- Background
This study was designed to compare the efficacy of multimodality monitoring and goal-directed therapy protocol (MM&GDTP), in patients with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores ≤8 with the conventional intracranial pressure (ICP)-cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) treatment.
Methods
The study was divided into two time periods, a 2-year historic period in which severe traumatic brain injury (sTBI) patients were treated with an ICP-CPP targeted strategy and a 5-year intervention period during which MM&GDTP was utilized. Patients with unsurvivable brain injuries were excluded. Variables of interest included mechanism of injury, age, sex, hemodynamics, GCS score, abbreviated injury score–head (AIS-H), Marshall Class, injury severity score, decompressive craniectomy, ventilator/intensive care unit days, length of stay, predicted mortality by corticosteroid randomization after significant head injury model, functional outcome, and mortality.
Results
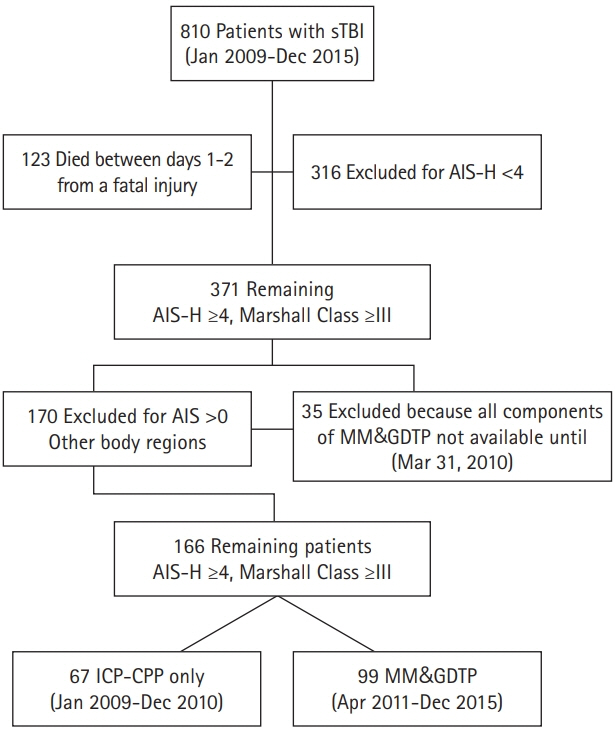
The study group comprised 810 sTBI patients, aged 14–93 years, admitted during a 7-year period; of these patients, 67 and 99 AIS-H≥4 and Marshall Class ≥III were included in control and intervention groups, respectively. The control group was treated with an ICP-CPP targeted approach, while the intervention group with an MM&GDTP. At presentation and after resuscitation, patients in the intervention group required a higher CPP to reach the endpoints of therapy. The MM&GDTP decreased mortality from 34.3% to 23.2%, yielding a 32.3% improvement in overall survival and improved functional outcome as measured by GOS >3 (MM&GDTP vs. ICP-CPP: 50/99 vs. 15/67, P=0.003).
Conclusion
Institution of MM&GDTP targeted to threshold-defined values improves functional outcomes and may reduce mortality among patients with sTBI compared to that of patients receiving an ICP-CPP–based treatment.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chesnut RM, Marshall LF, Klauber MR, Blunt BA, Baldwin N, Eisenberg HM, et al. The role of secondary brain injury in determining outcome from severe head injury. J Trauma. 1993; 34:216–22.
Article2. Spaite DW, Hu C, Bobrow BJ, Chikani V, Sherrill D, Barnhart B, et al. Mortality and prehospital blood pressure in patients with major traumatic brain injury: implications for the hypotension threshold. JAMA Surg. 2017; 152:360–8.3. Citerio G, Stocchetti N, Cormio M, Beretta L. Neuro-Link, a computer-assisted database for head injury in intensive care. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2000; 142:769–76.
Article4. Okonkwo DO, Shutter LA, Moore C, Temkin NR, Puccio AM, Madden CJ, et al. Brain oxygen optimization in severe traumatic brain injury phase-II: a phase II randomized trial. Crit Care Med. 2017; 45:1907–14.5. Barsan W. Brain oxygen optimization in severe TBI, phase 3 (BOOST 3). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03754114. Bethesda: U.S. National Library of Medicine;2021.6. MRC CRASH Trial Collaborators, Perel P, Arango M, Clayton T, Edwards P, Komolafe E, et al. Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: practical prognostic models based on large cohort of international patients. BMJ. 2008; 336:425–9.
Article7. Marini CP, Stoller C, Shah O, Policastro A, Lombardo G, Asensio JA, et al. The impact of early flow and brain oxygen crisis on the outcome of patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Am J Surg. 2014; 208:1071–7.
Article8. Chesnut RM, Temkin N, Carney N, Dikmen S, Rondina C, Videtta W, et al. A trial of intracranial-pressure monitoring in traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:2471–81.
Article9. Hutchinson PJ, Kolias AG, Timofeev IS, Corteen EA, Czosnyka M, Timothy J, et al. Trial of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic intracranial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1119–30.
Article10. Hawryluk GW, Rubiano AM, Totten AM, O'Reilly C, Ullman JS, Bratton SL, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury: 2020 update of the decompressive craniectomy recommendations. Neurosurgery. 2020; 87:427–34.
Article11. Stiefel MF, Spiotta A, Gracias VH, Garuffe AM, Guillamondegui O, Maloney-Wilensky E, et al. Reduced mortality rate in patients with severe traumatic brain injury treated with brain tissue oxygen monitoring. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103:805–11.
Article12. Stiefel MF, Udoetuk JD, Spiotta AM, Gracias VH, Goldberg A, Maloney-Wilensky E, et al. Conventional neurocritical care and cerebral oxygenation after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:568–75.
Article13. Spiotta AM, Stiefel MF, Gracias VH, Garuffe AM, Kofke WA, Maloney-Wilensky E, et al. Brain tissue oxygen-directed management and outcome in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:571–80.
Article14. Le Roux P, Menon DK, Citerio G, Vespa P, Bader MK, Brophy GM, et al. Consensus summary statement of the international multidisciplinary consensus conference on multimodality monitoring in neurocritical care: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Neurocrit Care. 2014; 21 Suppl 2:S1–26.15. Rosner MJ, Rosner SD, Johnson AH. Cerebral perfusion pressure: management protocol and clinical results. J Neurosurg. 1995; 83:949–62.
Article16. Hendrickson CM, Howard BM, Kornblith LZ, Conroy AS, Nelson MF, Zhuo H, et al. The acute respiratory distress syndrome following isolated severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016; 80:989–97.
Article17. Jaeger M, Dengl M, Meixensberger J, Schuhmann MU. Effects of cerebrovascular pressure reactivity-guided optimization of cerebral perfusion pressure on brain tissue oxygenation after traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med. 2010; 38:1343–7.
Article18. Dias C, Silva MJ, Pereira E, Monteiro E, Maia I, Barbosa S, et al. Optimal cerebral perfusion pressure management at bedside: a single-center pilot study. Neurocrit Care. 2015; 23:92–102.
Article