Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2021 Jul;25(4):307-319. 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.4.307.
Wnt-C59 inhibits proinflammatory cytokine expression by reducing the interaction between β-catenin and NF-κB in LPS-stimulated epithelial and macrophage cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul 06974, Korea
- KMID: 2516870
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.4.307
Abstract
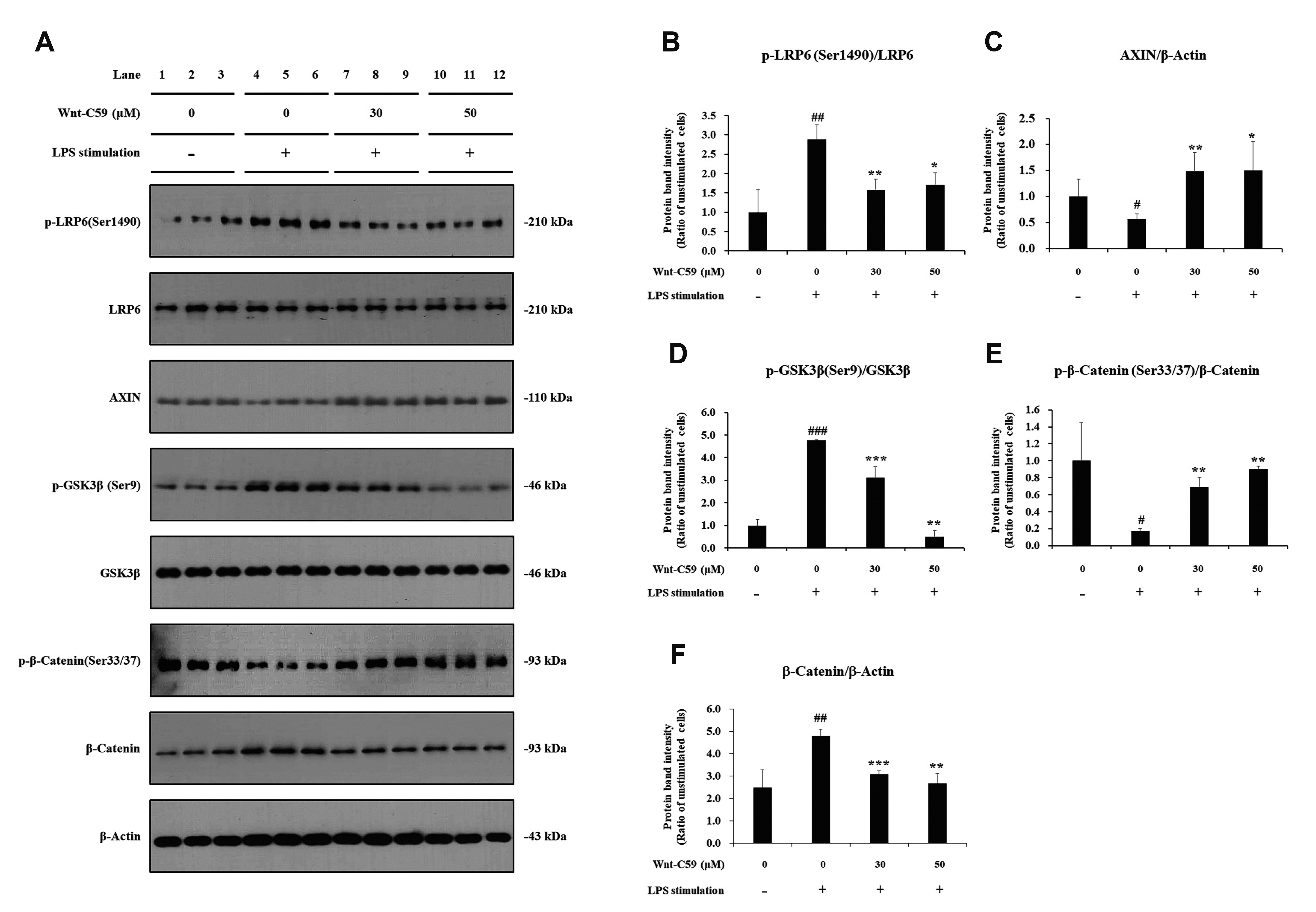
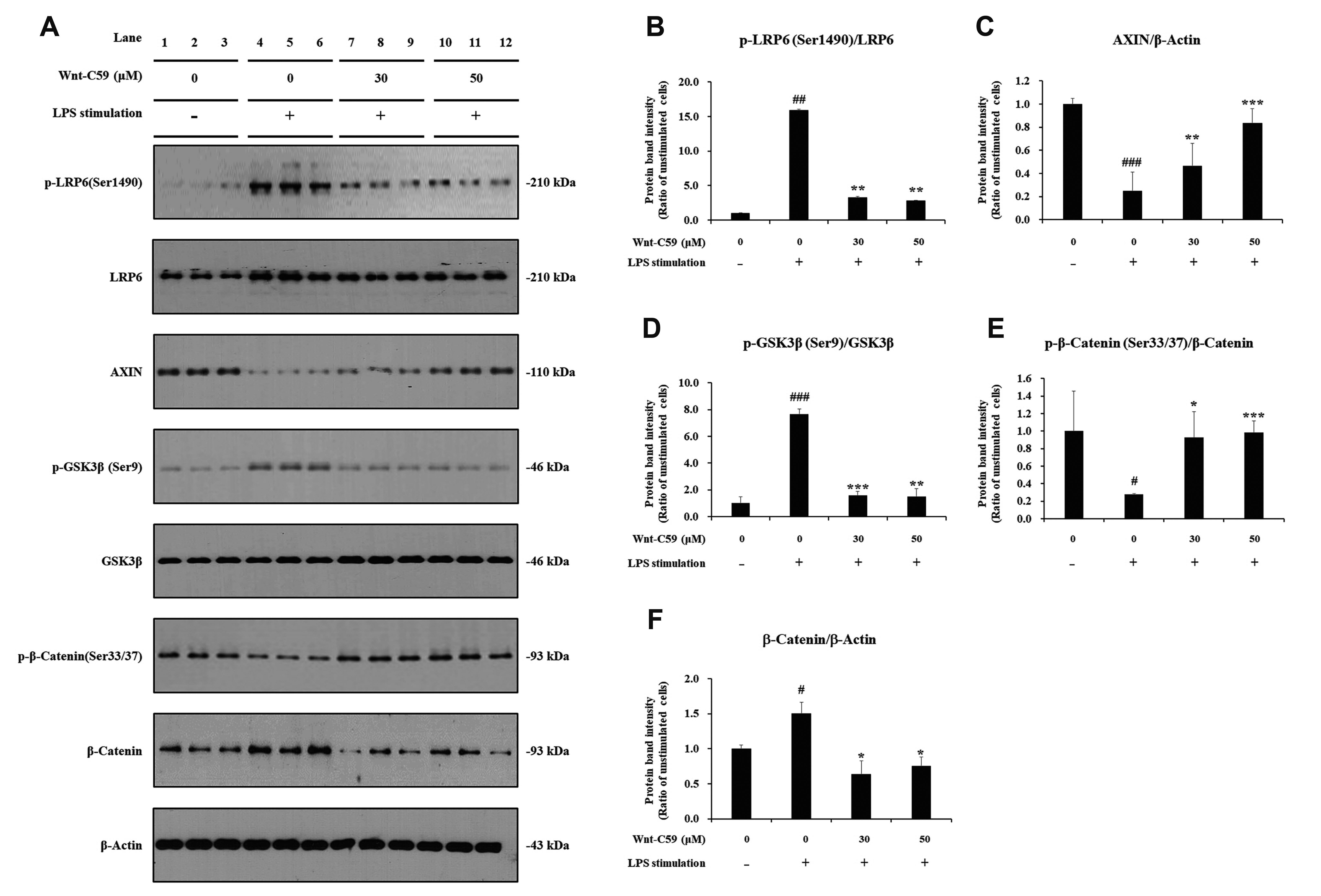
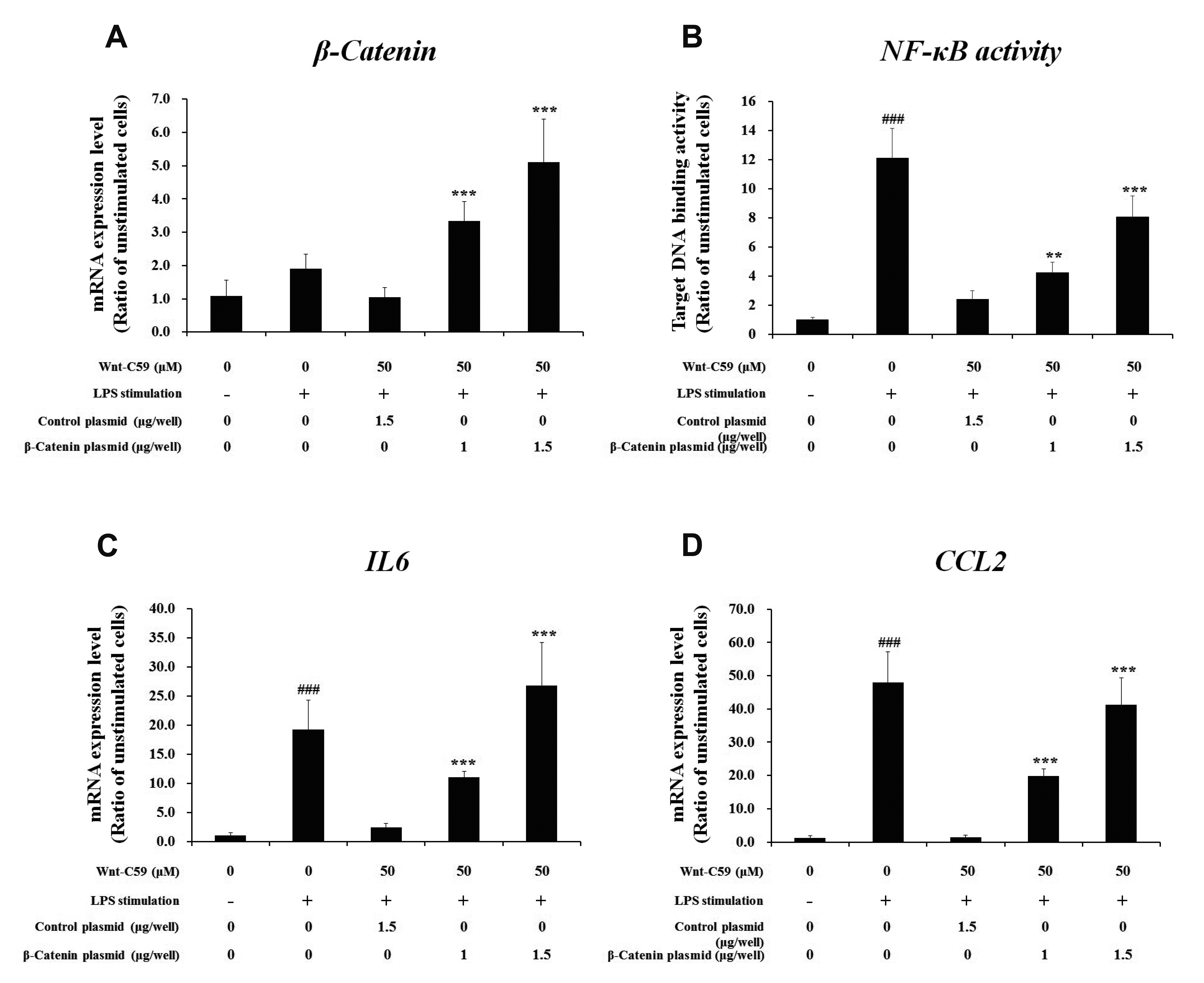
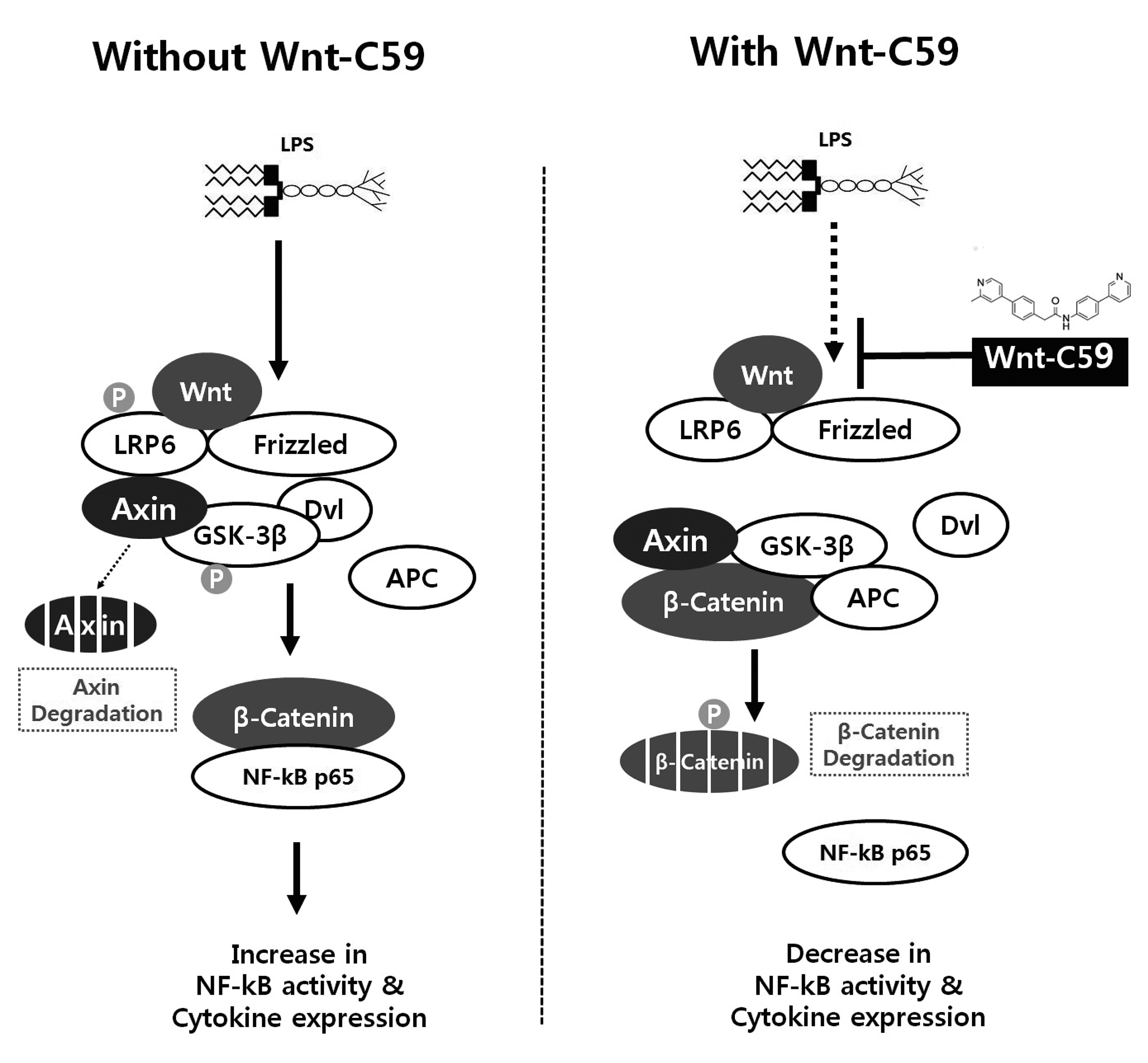
- Dysregulation of the Wnt pathway causes various diseases including cancer, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, osteoporosis, obesity and chronic kidney diseases. The modulation of dysregulated Wnt pathway is absolutely necessary. In the present study, we evaluated the anti-inflammatory effect and the mechanism of action of Wnt-C59, a Wnt signaling inhibitor, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated epithelial cells and macrophage cells. Wnt-C59 showed a dose-dependent anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines including IL6, CCL2, IL1A, IL1B, and TNF in LPS-stimulated cells. The dysregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in LPS stimulated cells was suppressed by WntC59 treatment. The level of β-catenin, the executor protein of Wnt/β-catenin pathway, was elevated by LPS and suppressed by Wnt-C59. Overexpression of β-catenin rescued the suppressive effect of Wnt-C59 on proinflammatory cytokine expression and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activity. We found that the interaction between β-catenin and NF-κB, measured by co-immunoprecipitation assay, was elevated by LPS and suppressed by Wnt-C59 treatment. Both NF-κB activity for its target DNA binding and the reporter activity of NF-κB-responsive promoter showed identical patterns with the interaction between β-catenin and NF-κB. Altogether, our findings suggest that the anti-inflammatory effect of Wnt-C59 is mediated by the reduction of the cellular level of β-catenin and the interaction between β-catenin and NF-κB, which results in the suppressions of the NF-κB activity and proinflammatory cytokine expression.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Risk of Gastrointestinal Cancer on Daily Intake of Low-Dose BaP in C57BL/6 for 60 Days
Zhi Zheng, Jung Kuk Park, Oh Wook Kwon, Sung Hoon Ahn, Young Joo Kwon, Linjuan Jiang, Shaohui Zhu, Byoung Hee Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(30):e235. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e235.
Reference
-
1. Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K. 2012; The many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 31:2714–2736. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.150. PMID: 22617422. PMCID: PMC3380220.
Article2. Zimmerman ZF, Moon RT, Chien AJ. 2012; Targeting Wnt pathways in disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a008086. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008086. PMID: 23001988. PMCID: PMC3536347.
Article3. Liu Y, Hao S, Yang B, Fan Y, Qin X, Chen Y, Hu J. 2017; Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays an essential role in α7 nicotinic receptor-mediated neuroprotection of dopaminergic neurons in a mouse Parkinson's disease model. Biochem Pharmacol. 140:115–123. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.05.017. PMID: 28551099.
Article4. Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y. 2016; Alzheimer disease: crosstalk between the canonical Wnt/Beta-catenin pathway and PPARs alpha and gamma. Front Neurosci. 10:459. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00459. PMID: 27807401. PMCID: PMC5069291.
Article5. Hoseth EZ, Krull F, Dieset I, Mørch RH, Hope S, Gardsjord ES, Steen NE, Melle I, Brattbakk HR, Steen VM, Aukrust P, Djurovic S, Andreassen OA, Ueland T. 2018; Exploring the Wnt signaling pathway in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 8:55. DOI: 10.1038/s41398-018-0102-1. PMID: 29507296. PMCID: PMC5838215.
Article6. Baron R, Gori F. 2018; Targeting WNT signaling in the treatment of osteoporosis. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 40:134–141. DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2018.04.011. PMID: 29753194.
Article7. Chen N, Wang J. 2018; Wnt/β-catenin signaling and obesity. Front Physiol. 9:792. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00792. PMID: 30065654. PMCID: PMC6056730.
Article8. Wang Y, Zhou CJ, Liu Y. 2018; Wnt signaling in kidney development and disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 153:181–207. DOI: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.11.019. PMID: 29389516. PMCID: PMC6008255.
Article9. Duchartre Y, Kim YM, Kahn M. 2016; The Wnt signaling pathway in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 99:141–149. DOI: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.12.005. PMID: 26775730. PMCID: PMC5853106.
Article10. Luu HH, Zhang R, Haydon RC, Rayburn E, Kang Q, Si W, Park JK, Wang H, Peng Y, Jiang W, He TC. 2004; Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway as a novel cancer drug target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 4:653–671. DOI: 10.2174/1568009043332709. PMID: 15578921.11. Cheng Y, Phoon YP, Jin X, Chong SY, Ip JC, Wong BW, Lung ML. 2015; Wnt-C59 arrests stemness and suppresses growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in mice by inhibiting the Wnt pathway in the tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget. 6:14428–14439. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3982. PMID: 25980501. PMCID: PMC4546477.
Article12. Proffitt KD, Madan B, Ke Z, Pendharkar V, Ding L, Lee MA, Hannoush RN, Virshup DM. 2013; Pharmacological inhibition of the Wnt acyltransferase PORCN prevents growth of WNT-driven mammary cancer. Cancer Res. 73:502–507. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2258. PMID: 23188502.
Article13. Zhang J, Cai H, Sun L, Zhan P, Chen M, Zhang F, Ran Y, Wan J. 2018; LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and predicts poor survival of glioma patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:225. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0864-6. PMID: 30208924. PMCID: PMC6136228.
Article14. Koo BK, van Es JH, van den Born M, Clevers H. 2015; Porcupine inhibitor suppresses paracrine Wnt-driven growth of Rnf43;Znrf3-mutant neoplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 112:7548–7550. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1508113112. PMID: 26023187. PMCID: PMC4475934.
Article15. Madan B, Patel MB, Zhang J, Bunte RM, Rudemiller NP, Griffiths R, Virshup DM, Crowley SD. 2016; Experimental inhibition of porcupine-mediated Wnt O-acylation attenuates kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 89:1062–1074. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.01.017. PMID: 27083283. PMCID: PMC4834146.
Article16. Dong Q, Jie Y, Ma J, Li C, Xin T, Yang D. 2021; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway promotes renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through inducing oxidative stress and inflammation response. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 41:15–18. DOI: 10.1080/10799893.2020.1783555. PMID: 32580617.
Article17. Deng J, Miller SA, Wang HY, Xia W, Wen Y, Zhou BP, Li Y, Lin SY, Hung MC. 2002; beta-catenin interacts with and inhibits NF-kappa B in human colon and breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2:323–334. DOI: 10.1016/S1535-6108(02)00154-X. PMID: 12398896.18. Kim JH, Kim B, Cai L, Choi HJ, Ohgi KA, Tran C, Chen C, Chung CH, Huber O, Rose DW, Sawyers CL, Rosenfeld MG, Baek SH. 2005; Transcriptional regulation of a metastasis suppressor gene by Tip60 and beta-catenin complexes. Nature. 434:921–926. DOI: 10.1038/nature03452. PMID: 15829968.19. Sun J, Hobert ME, Duan Y, Rao AS, He TC, Chang EB, Madara JL. 2005; Crosstalk between NF-kappaB and beta-catenin pathways in bacterial-colonized intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 289:G129–G137. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00515.2004. PMID: 15790758.20. Ma B, Hottiger MO. 2016; Crosstalk between Wnt/β-Catenin and NF-κB Signaling Pathway during Inflammation. Front Immunol. 7:378. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00378. PMID: 27713747. PMCID: PMC5031610.
Article21. Jang J, Jung Y, Kim Y, Jho EH, Yoon Y. 2017; LPS-induced inflammatory response is suppressed by Wnt inhibitors, Dickkopf-1 and LGK974. Sci Rep. 7:41612. DOI: 10.1038/srep41612. PMID: 28128299. PMCID: PMC5269682.
Article22. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. 2001; Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. DOI: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. PMID: 11846609.23. Li J, Zhang D, Ward KM, Prendergast GC, Ayene IS. 2012; Hydroxyethyl disulfide as an efficient metabolic assay for cell viability in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 26:603–612. DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2012.01.007. PMID: 22321380. PMCID: PMC3327773.
Article24. Seo E, Jho EH. 2007; Axin-independent phosphorylation of APC controls beta-catenin signaling via cytoplasmic retention of beta-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 357:81–86. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.03.117. PMID: 17418091.25. Cadigan KM, Liu YI. 2006; Wnt signaling: complexity at the surface. J Cell Sci. 119(Pt 3):395–402. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.02826. PMID: 16443747.
Article26. Zhan T, Rindtorff N, Boutros M. 2017; Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1461–1473. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.304. PMID: 27617575. PMCID: PMC5357762.
Article27. Ivanenkov YA, Balakin KV, Lavrovsky Y. 2011; Small molecule inhibitors of NF-kB and JAK/STAT signal transduction pathways as promising anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Mini Rev Med Chem. 11:55–78. DOI: 10.2174/138955711793564079. PMID: 21034406.28. Ma B, van Blitterswijk CA, Karperien M. 2012; A Wnt/β-catenin negative feedback loop inhibits interleukin-1-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression in human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 64:2589–2600. DOI: 10.1002/art.34425. PMID: 22328140.
Article29. Choi YS, Hur J, Jeong S. 2007; Beta-catenin binds to the downstream region and regulates the expression C-reactive protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:5511–5519. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm547. PMID: 17704137. PMCID: PMC2018623.30. Choi YS, Hur J, Lee HK, Jeong S. 2009; The RNA aptamer disrupts protein-protein interaction between beta-catenin and nuclear factor-kappaB p50 and regulates the expression of C-reactive protein. FEBS Lett. 583:1415–1421. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.04.002. PMID: 19358846.31. Koopmans T, Eilers R, Menzen M, Halayko A, Gosens R. 2017; β-catenin directs nuclear factor-κB p65 output via CREB-binding protein/p300 in human airway smooth muscle. Front Immunol. 8:1086. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01086. PMID: 28943877. PMCID: PMC5596077.
Article32. Jang J, Ha JH, Chung SI, Yoon Y. 2014; β-catenin regulates NF-κB activity and inflammatory cytokine expression in bronchial epithelial cells treated with lipopolysaccharide. Int J Mol Med. 34:632–638. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1807. PMID: 24938929.
Article33. Subhan MA, Torchilin VP. 2020; siRNA based drug design, quality, delivery and clinical translation. Nanomedicine. 29:102239. DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2020.102239. PMID: 32544449.
Article34. Munford RS. 2016; Endotoxemia-menace, marker, or mistake? J Leukoc Biol. 100:687–698. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.3RU0316-151R. PMID: 27418356. PMCID: PMC5014740.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Galangin Regulates Mucin 5AC Gene Expression via the Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor α/Nuclear Factor-κB p65 Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Anti-inflammatory effects of rutin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated canine macrophage cells
- Eriodictyol Inhibits the Production and Gene Expression of MUC5AC Mucin via the IκBα-NF-κB p65 Signaling Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells
- Docosahexaenoic Acid Inhibits Cytokine Expression by Reducing Reactive Oxygen Species in Pancreatic Stellate Cells
- Antineuroinflammatory Effects of 7,3’,4’-Trihydroxyisoflavone in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells through MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Suppression