Clin Endosc.
2021 May;54(3):428-431. 10.5946/ce.2020.244.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Endoscopic Outcomes in Patients with SARS-CoV-2
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Banner University Medical Center Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ, USA
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Phoenix VA Health Care System, Phoenix, AZ, USA
- KMID: 2516324
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.244
Abstract
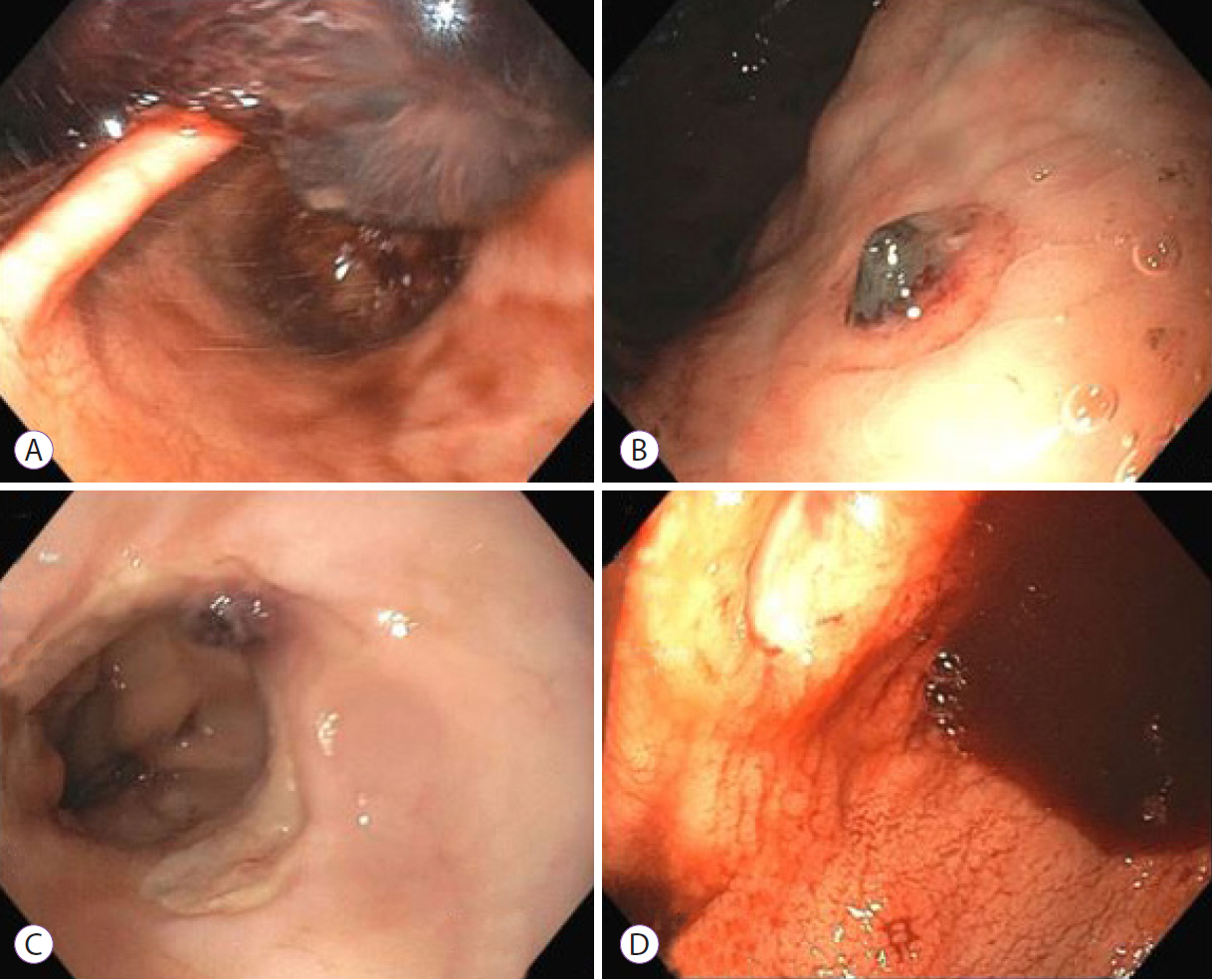
- Over the past year, the novel coronavirus has been a topic of significant research. Multiple gastroenterological symptoms have been associated with this infection, in addition to the well-established pulmonary presentations. Gastrointestinal bleeding can be a complication of infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, which can be exacerbated by the anticoagulants used to treat its thrombotic sequelae. We describe the clinical cases of four patients infected with the novel coronavirus, with significant upper gastrointestinal bleeding requiring endoscopic visualization, along with their clinical outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gadiparthi C, Perisetti A, Sayana H, Tharian B, Inamdar S, Korman A. Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020; 115:1283–1285.
Article2. Cavaliere K, Levine C, Wander P, Sejpal DV, Trindade AJ. Management of upper GI bleeding in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 92:454–455.
Article3. Lau JYW, Yu Y, Tang RSY, et al. Timing of endoscopy for acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:1299–1308.
Article4. Ranucci M, Ballotta A, Di Dedda U, et al. The procoagulant pattern of patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Thromb Haemost. 2020; 18:1747–1751.
Article5. Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020; 579:265–269.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastrointestinal AA Amyloidosis following Recurrent SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report
- Understandings and Prospects of Laboratory Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2
- Optical Analysis of Nasal Endoscopic Images From a Patient With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
- Challenges of Scaling Up SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Tests
- Outcomes and complications of embolization for gastrointestinal bleeding