Clinical Application of the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag Test for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2514897
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e101
Abstract
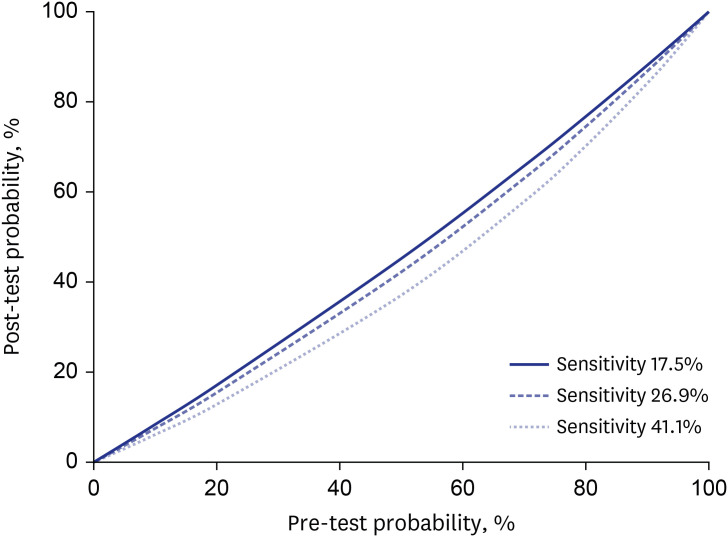
- We evaluated the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag test for the diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) compared to the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test. We applied both tests to patients who were about to be hospitalized, had visited an emergency room, or had been admitted due to COVID-19 confirmed by RT-PCR. Two nasopharyngeal swabs were obtained; one was tested by RT-PCR and the other by the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag test. A total of 118 pairs of tests from 98 patients were performed between January 5 and 11, 2021. The overall sensitivity and specificity for detecting severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) for the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag test compared to RT-PCR were 17.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.8–32.0%) and 100% (95% CI, 95.3–100.0%). Analysis of the results using RT-PCR cycle thresholds of ≤ 30 or ≤ 25 increased the sensitivity to 26.9% (95% CI, 13.7–46.1%), and 41.1% (95% CI, 21.6–64.0%), respectively.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
The Usefulness of the COVID-19 Rapid Diagnosis Kit
Chang-Seop Lee
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2021;26(2):134-136. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2021.26.2.134.Laboratory Diagnosis and Utilization for COVID-19
Mi-Na Kim, Hyun Soo Kim, Hye Gyung Bae, Hee Jae Huh, Heungsup Sung
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2021;26(2):47-56. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2021.26.2.47.Update of Guidelines for Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea
Ki Ho Hong, Gab Jung Kim, Kyoung Ho Roh, Heungsup Sung, Jaehyeon Lee, So Yeon Kim, Taek Soo Kim, Jae-Sun Park, Hee Jae Huh, Younhee Park, Jae-Seok Kim, Hyun Soo Kim, Moon-Woo Seong, Nam Hee Ryoo, Sang Hoon Song, Hyukmin Lee, Gye Cheol Kwon, Cheon Kwon Yoo
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(4):391-397. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.391.Comparison of Nasal Swabs, Nasopharyngeal Swabs, and Saliva Samples for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other Respiratory Virus Infections
Eun Ju Jung, Su Kyung Lee, Seon Hee Shin, Jin Soo Kim, Heungjeong Woo, Eun-Jung Cho, Jungwon Hyun, Jae-Seok Kim, Hyun Soo Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(5):434-442. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.434.
Reference
-
1. CDC's diagnostic test for COVID-19 only and supplies. Updated December 9, 2020. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/virus-requests.html.2. Pray IW, Ford L, Cole D, Lee C, Bigouette JP, Abedi GR, et al. Performance of an antigen-based test for asymptomatic and symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 testing at two university campuses - Wisconsin, September-October 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021; 69(5152):1642–1647. PMID: 33382679.3. Turcato G, Zaboli A, Pfeifer N, Ciccariello L, Sibilio S, Tezza G, et al. Clinical application of a rapid antigen test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients evaluated in the emergency department: a preliminary report. J Infect. 2021; 82(3):e14–6. PMID: 33347944.
Article4. Li D, Li J. Immunologic testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection from the antigen perspective. J Clin Microbiol. Forthcoming 2020. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02160-20.
Article5. Albert E, Torres I, Bueno F, Huntley D, Molla E, Fernández-Fuentes MÁ, et al. Field evaluation of a rapid antigen test (Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device) for COVID-19 diagnosis in primary healthcare centres. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021; 27(3):472.e7–472.e10.
Article6. Yamayoshi S, Sakai-Tagawa Y, Koga M, Akasaka O, Nakachi I, Koh H, et al. Comparison of rapid antigen tests for COVID-19. Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1420.
Article7. Mak GC, Lau SS, Wong KK, Chow NL, Lau CS, Lam ET, et al. Analytical sensitivity and clinical sensitivity of the three rapid antigen detection kits for detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus. J Clin Virol. 2020; 133:104684. PMID: 33176236.
Article8. Lindner AK, Nikolai O, Kausch F, Wintel M, Hommes F, Gertler M, et al. Head-to-head comparison of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid test with self-collected anterior nasal swab versus professional-collected nasopharyngeal swab. Eur Respir J. Forthcoming 2020. DOI: 10.1183/13993003.03961-2020.
Article9. Toptan T, Eckermann L, Pfeiffer AE, Hoehl S, Ciesek S, Drosten C, et al. Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test: potential to help reduce community spread? J Clin Virol. 2021; 135:104713. PMID: 33352470.
Article10. Krüger LJ, Gaeddert M, Köppel L, Brümmer LE, Gottschalk C, Miranda IB. Evaluation of the accuracy, ease of use and limit of detection of novel, rapid, antigen-detecting point-of-care diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv;Updated January 1, 2020. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.10.01.20203836v1.11. Candel FJ, Barreiro P, San Román J, Abanades JC, Barba R, Barberán J, et al. Recommendations for use of antigenic tests in the diagnosis of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection in the second pandemic wave: attitude in different clinical settings. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2020; 33(6):466–484. PMID: 33070578.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Challenges of Scaling Up SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Tests
- Verification of the Performance of the Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device for Implementation in the Clinical Laboratory
- COVID-19 and Breastfeeding
- Retrospective Validation of Xpert Xpress SARSCoV-2 and Rapid COVID-19 PCR Tests
- SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cell Responses in Patients with COVID-19 and Unexposed Individuals