Exome Chip Analysis of 14,026 Koreans Reveals Known and Newly Discovered Genetic Loci Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 0Division of Biomedical Informatics, Center for Genome Science, National Institute of Health, Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2514199
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0163
Abstract
Background Most loci associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) discovered to date are within noncoding regions of unknown functional significance. By contrast, exonic regions have advantages for biological interpretation.
Methods We analyzed the association of exome array data from 14,026 Koreans to identify susceptible exonic loci for T2DM. We used genotype information of 50,543 variants using the Illumina exome array platform.
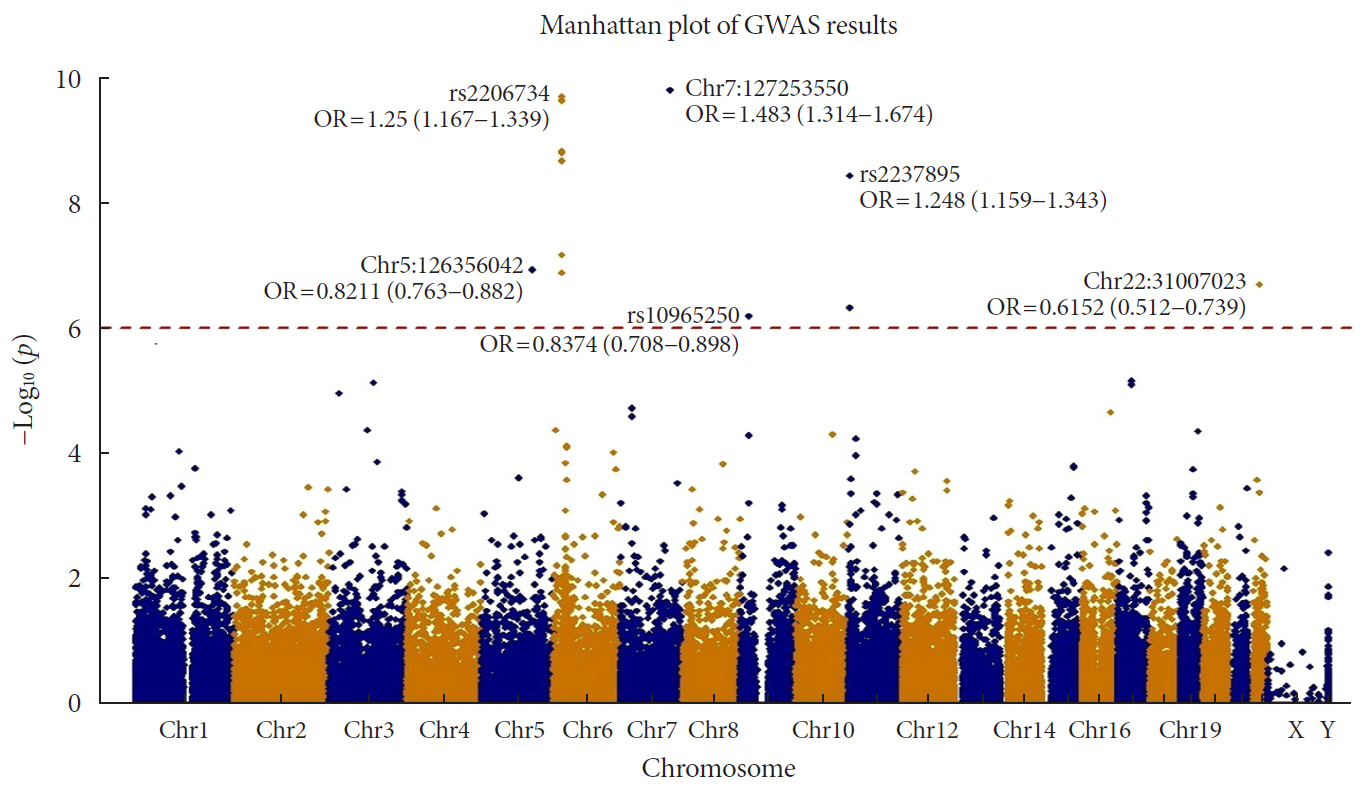
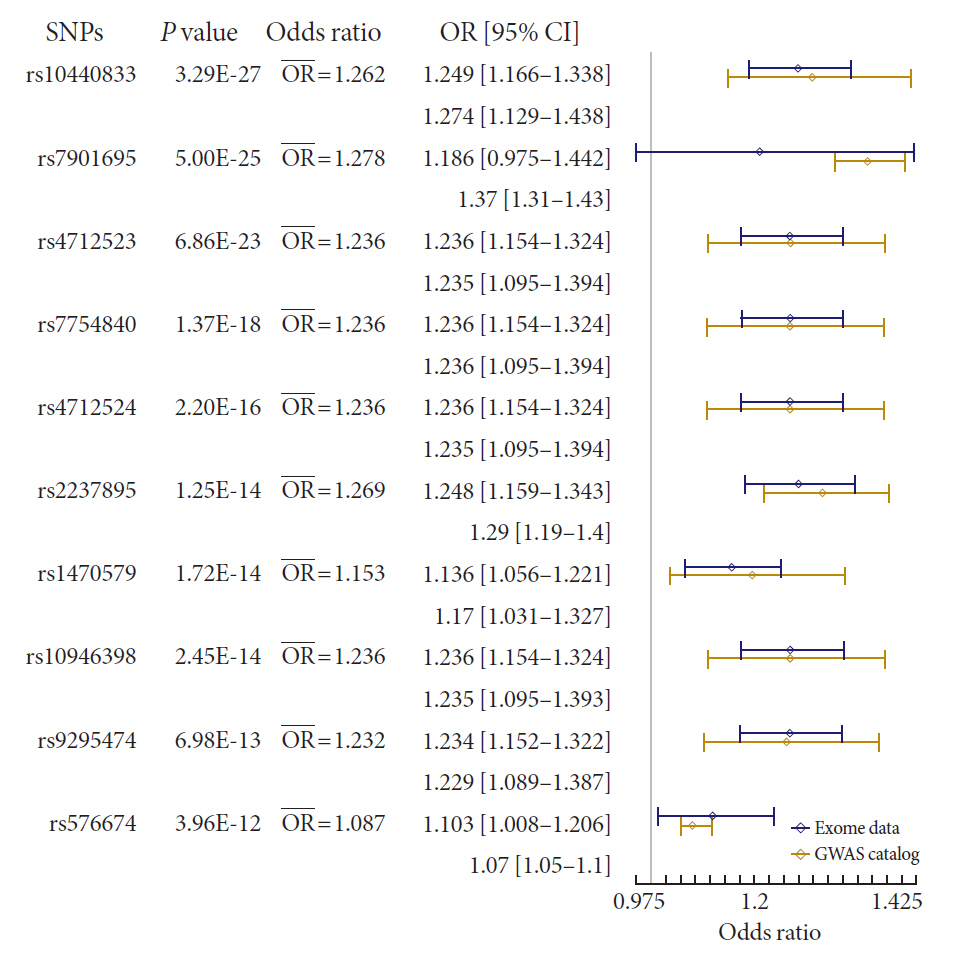
Results In total, 7 loci were significant with a Bonferroni adjusted
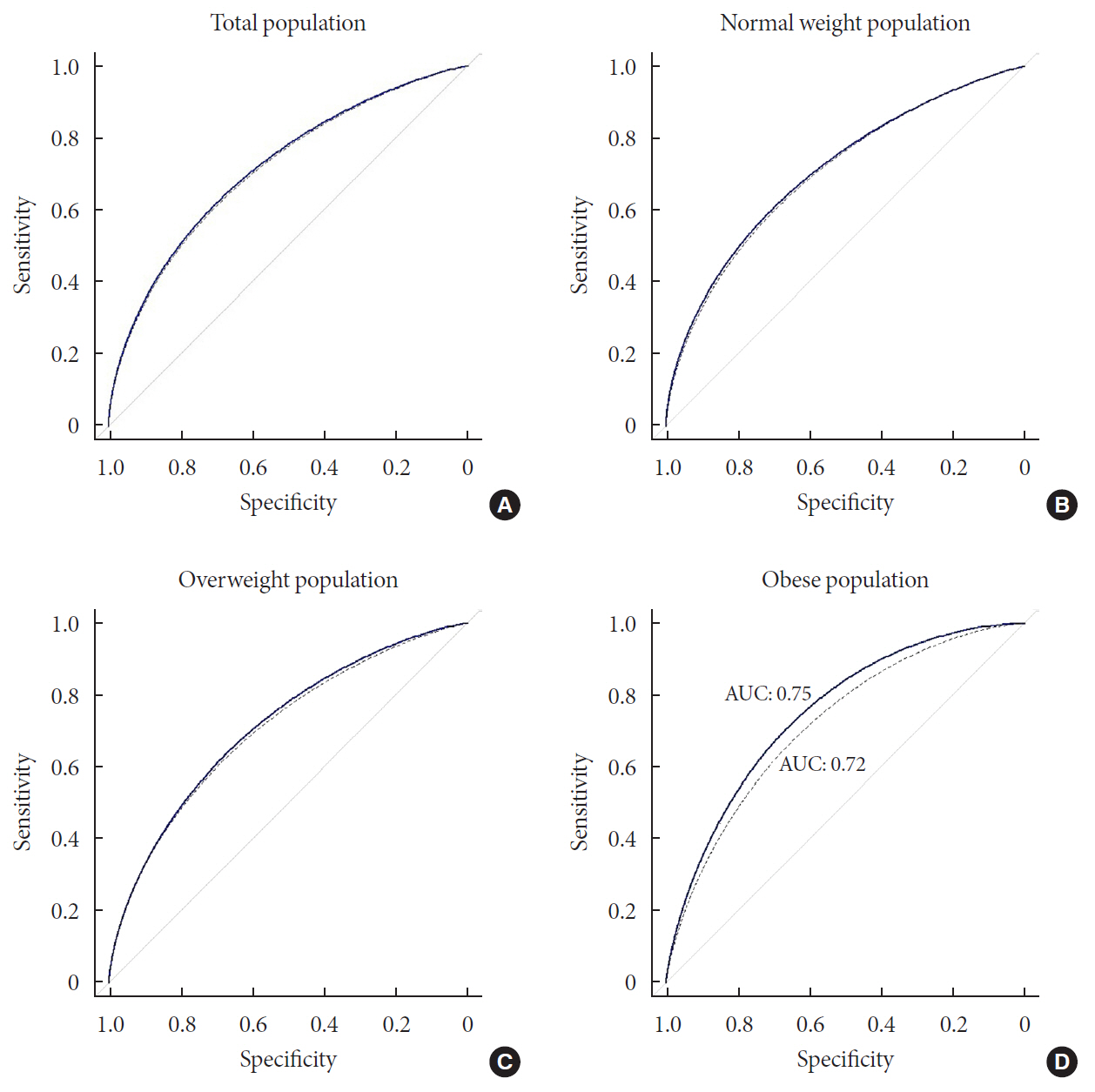
P =1.03×10−6. rs2233580 in paired box gene 4 (PAX4 ) showed the highest odds ratio of 1.48 (P =1.60×10−10). rs11960799 in membrane associated ring-CH-type finger 3 (MARCH3 ) and rs75680863 in transcobalamin 2 (TCN2 ) were newly identified loci. When we built a model to predict the incidence of diabetes with the 7 loci and clinical variables, area under the curve (AUC) of the model improved significantly (AUC=0.72,P <0.05), but marginally in its magnitude, compared with the model using clinical variables (AUC=0.71,P <0.05). When we divided the entire population into three groups—normal body mass index (BMI; <25 kg/m2), overweight (25≤ BMI <30 kg/m2), and obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) individuals—the predictive performance of the 7 loci was greatest in the group of obese individuals, where the net reclassification improvement was highly significant (0.51;P =8.00×10−5).Conclusion We found exonic loci having a susceptibility for T2DM. We found that such genetic information is advantageous for predicting T2DM in a subgroup of obese individuals.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Sex Differences in the Effects of
CDKAL1 Variants on Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Young Sun Hong
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):879-889. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0265.
Reference
-
1. Bellou V, Belbasis L, Tzoulaki I, Evangelou E. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus: an exposure-wide umbrella review of meta-analyses. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0194127.
Article2. Moore AF, Florez JC. Genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes and implications for antidiabetic therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2008; 59:95–111.
Article3. Billings LK, Florez JC. The genetics of type 2 diabetes: what have we learned from GWAS? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010; 1212:59–77.
Article4. Visscher PM, Wray NR, Zhang Q, Sklar P, McCarthy MI, Brown MA, et al. 10 Years of GWAS discovery: biology, function, and translation. Am J Hum Genet. 2017; 101:5–22.
Article5. Das S, Abecasis GR, Browning BL. Genotype imputation from large reference panels. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2018; 19:73–96.
Article6. McCarthy MI, Zeggini E. Genome-wide association studies in type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2009; 9:164–171.
Article7. Unoki H, Takahashi A, Kawaguchi T, Hara K, Horikoshi M, Andersen G, et al. SNPs in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations. Nat Genet. 2008; 40:1098–1102.
Article8. Voight BF, Scott LJ, Steinthorsdottir V, Morris AP, Dina C, Welch RP, et al. MAGIC investigators. GIANT Consortium. Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:579–589.9. Cook JP, Morris AP. Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study identifies novel locus for type 2 diabetes susceptibility. Version 2. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016; 24:1175–1180.10. Fuchsberger C, Flannick J, Teslovich TM, Mahajan A, Agarwala V, Gaulton KJ, et al. The genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2016; 536:41–47.11. Huyghe JR, Jackson AU, Fogarty MP, Buchkovich ML, Stancakova A, Stringham HM, et al. Exome array analysis identifies new loci and low-frequency variants influencing insulin processing and secretion. Nat Genet. 2013; 45:197–201.
Article12. Cheung CY, Tang CS, Xu A, Lee CH, Au KW, Xu L, et al. Exome-chip association analysis reveals an Asian-specific missense variant in PAX4 associated with type 2 diabetes in Chinese individuals. Diabetologia. 2017; 60:107–115.
Article13. Yasukochi Y, Sakuma J, Takeuchi I, Kato K, Oguri M, Fujimaki T, et al. Two novel susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes mellitus identified by longitudinal exome-wide association studies in a Japanese population. Genomics. 2019; 111:34–42.
Article14. Mahajan A, Wessel J, Willems SM, Zhao W, Robertson NR, Chu AY, et al. ExomeBP Consortium. MAGIC Consortium. GIANT Consortium. Refining the accuracy of validated target identification through coding variant fine-mapping in type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2018; 50:559–571.15. Kim Y, Han BG. KoGES group. Cohort profile: the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) consortium. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:e20.
Article16. American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes: 2018. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41 Suppl 1:S13–S27.17. Kim YK, Hwang MY, Kim YJ, Moon S, Han S, Kim BJ. Evaluation of pleiotropic effects among common genetic loci identified for cardio-metabolic traits in a Korean population. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016; 15:20.
Article18. Browning SR, Browning BL. Rapid and accurate haplotype phasing and missing-data inference for whole-genome association studies by use of localized haplotype clustering. Am J Hum Genet. 2007; 81:1084–1097.
Article19. Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007; 81:559–575.
Article20. Jung KS, Hong KW, Jo HY, Choi J, Ban HJ, Cho SB, et al. KRGDB: the large-scale variant database of 1722 Koreans based on whole genome sequencing. Database (Oxford). 2020; 2020:baz146.
Article21. R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing 2018. cited 2020 May 5. Available from: https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing.22. Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez JC, et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011; 12:77.
Article23. Kundu S, Aulchenko YS, van Duijn CM, Janssens AC. Predict-ABEL: an R package for the assessment of risk prediction models. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011; 26:261–264.
Article24. Kathiresan S, Willer CJ, Peloso GM, Demissie S, Musunuru K, Schadt EE, et al. Common variants at 30 loci contribute to polygenic dyslipidemia. Nat Genet. 2009; 41:56–65.
Article25. Yasuda K, Miyake K, Horikawa Y, Hara K, Osawa H, Furuta H, et al. Variants in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet. 2008; 40:1092–1097.26. Collins GS, Mallett S, Omar O, Yu LM. Developing risk prediction models for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of methodology and reporting. BMC Med. 2011; 9:103.
Article27. Kwak SH, Chae J, Lee S, Choi S, Koo BK, Yoon JW, et al. Nonsynonymous variants in PAX4 and GLP1R are associated with type 2 diabetes in an East Asian population. Diabetes. 2018; 67:1892–1902.28. Lorenzo PI, Juarez-Vicente F, Cobo-Vuilleumier N, Garcia-Dominguez M, Gauthier BR. The diabetes-linked transcription factor PAX4: from gene to functional consequences. Genes (Basel). 2017; 8:101.
Article29. Ma RC, Hu C, Tam CH, Zhang R, Kwan P, Leung TF, et al. DIAGRAM Consortium. MuTHER Consortium. Genome-wide association study in a Chinese population identifies a susceptibility locus for type 2 diabetes at 7q32 near PAX4. Diabetologia. 2013; 56:1291–1305.30. Sujjitjoon J, Kooptiwut S, Chongjaroen N, Semprasert N, Hanchang W, Chanprasert K, et al. PAX4 R192H and P321H polymorphisms in type 2 diabetes and their functional defects. J Hum Genet. 2016; 61:943–949.
Article31. Ottosson-Laakso E, Krus U, Storm P, Prasad RB, Oskolkov N, Ahlqvist E, et al. Glucose-induced changes in gene expression in human pancreatic islets: causes or consequences of chronic hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 2017; 66:3013–3028.
Article32. Pflipsen MC, Oh RC, Saguil A, Seehusen DA, Seaquist D, Topolski R. The prevalence of vitamin B(12) deficiency in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009; 22:528–534.
Article33. Vassy JL, Meigs JB. Is genetic testing useful to predict type 2 diabetes? Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 26:189–201.
Article34. Vassy JL, Hivert MF, Porneala B, Dauriz M, Florez JC, Dupuis J, et al. Polygenic type 2 diabetes prediction at the limit of common variant detection. Diabetes. 2014; 63:2172–2182.
Article35. Talmud PJ, Cooper JA, Morris RW, Dudbridge F, Shah T, Engmann J, et al. UCLEB Consortium. Sixty-five common genetic variants and prediction of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2015; 64:1830–1840.
Article36. Lall K, Magi R, Morris A, Metspalu A, Fischer K. Personalized risk prediction for type 2 diabetes: the potential of genetic risk scores. Genet Med. 2017; 19:322–329.
Article37. Gomez-Uriz AM, Milagro FI, Mansego ML, Cordero P, Abete I, De Arce A, et al. Obesity and ischemic stroke modulate the methylation levels of KCNQ1 in white blood cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2015; 24:1432–1440.38. Morris AP, Lindgren CM, Zeggini E, Timpson NJ, Frayling TM, Hattersley AT, et al. A powerful approach to sub-phenotype analysis in population-based genetic association studies. Genet Epidemiol. 2010; 34:335–343.
Article39. Perry JR, Voight BF, Yengo L, Amin N, Dupuis J, Ganser M, et al. MAGIC. DIAGRAM Consortium. GIANT Consortium. Stratifying type 2 diabetes cases by BMI identifies genetic risk variants in LAMA1 and enrichment for risk variants in lean compared to obese cases. PLoS Genet. 2012; 8:e1002741.
Article40. Timpson NJ, Lindgren CM, Weedon MN, Randall J, Ouwehand WH, Strachan DP, et al. Adiposity-related heterogeneity in patterns of type 2 diabetes susceptibility observed in genome-wide association data. Diabetes. 2009; 58:505–510.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sulwon Lecture 2009: The Search for Genetic Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Genetic Diseases Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
- Genetics in Diabetes Mellitus - Contribution to the Classification and Management
- Type 1 diabetes genetic susceptibility markers and their functional implications
- Study of the Allelic Frequency on Polymorphic Loci in the Short Arm of Chromosome 3 in Normal Koreans