J Rheum Dis.
2021 Apr;28(2):85-93. 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.2.85.
Total Haemolytic Complement Activity at Diagnosis as an Indicator of the Baseline Activity of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Vasculitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea
- 2Institute for Immunology and Immunological Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2514119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2021.28.2.85
Abstract
Objective
The total haemolytic complement activity (CH50) assay evaluates the functioning of the complement system. Accumulating evidence indicates that the activation of the complement system plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV). Therefore, this study aimed to investigate whether CH50 levels at diagnosis could reflect the baseline activity of AAV.
Methods
This retrospective study included 101 immunosuppressive drug-naïve patients with AAV. At diagnosis, all patients underwent clinical assessments for disease activity, including measurement of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) and Five Factor Score (FFS), and laboratory evaluations, such as tests for CH50, C3, and C4 levels. The association between CH50 levels and disease activity was determined.
Results
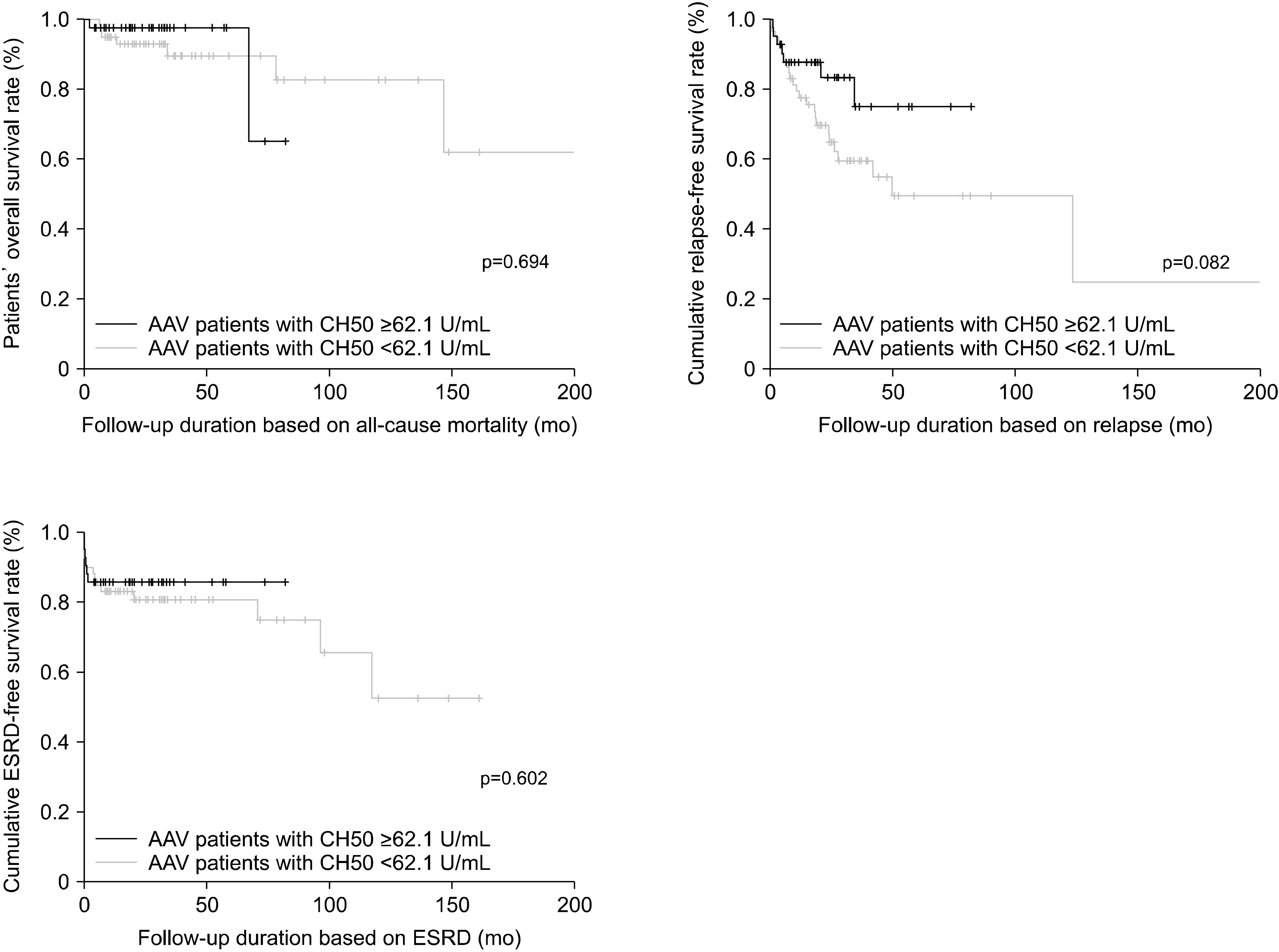
The median BVAS and FFS at diagnosis were 12.0 and 1.0, respectively, whereas the median CH50 level was 60.4 U/mL. There was a negative correlation between the CH50 level and BVAS (r=−0.241; p=0.015). A CH50 cut-off value of 62.1 U/mL was used to classify the patients into two groups: patients with CH50 levels <62.1 U/mL (low-CH50 group) and those with CH50 levels ≥ 62.1 U/mL (high-CH50 group). The low-CH50 group had a higher proportion of patients with high disease activity, based on the BVAS, than the high-CH50 group (52.5% vs. 23.8%, p=0.004). Additionally, the low-CH50 group exhibited a lower relapse-free survival rate than the high-CH50 group; however, this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.082).
Conclusion
Low CH50 levels at diagnosis may reflect high baseline activity of AAV.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, et al. 2013; 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 65:1–11. DOI: 10.1002/art.37715. PMID: 23045170.
Article2. Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, et al. 2007; Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 66:222–7. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.054593. PMID: 16901958. PMCID: PMC1798520.
Article3. Jennette JC, Falk RJ. 2014; Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-mediated disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:463–73. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.103. PMID: 25003769.
Article4. Lamprecht P, Kerstein A, Klapa S, Schinke S, Karsten CM, Yu X, et al. 2018; Pathogenetic and clinical aspects of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitides. Front Immunol. 9:680. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00680. PMID: 29686675. PMCID: PMC5900791.
Article5. Angioi A, Fervenza FC, Sethi S, Zhang Y, Smith RJ, Murray D, et al. 2016; Diagnosis of complement alternative pathway disorders. Kidney Int. 89:278–88. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2015.12.003. PMID: 26806831.
Article6. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Hu P, Xiao H. 2013; Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated small-vessel vasculitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 8:139–60. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011811-132453. PMID: 23347350. PMCID: PMC5507606.
Article7. Smith JG Jr. 1995; Vasculitis. J Dermatol. 22:812–22. DOI: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1995.tb03929.x. PMID: 8557852.
Article8. Kawakami T, Kimura S, Takeuchi S, Soma Y. 2013; Relationship among antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, blood urea nitrogen and complement in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome). J Dermatol. 40:511–5. DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.12163. PMID: 23594281.
Article9. Fukui S, Iwamoto N, Umeda M, Nishino A, Nakashima Y, Koga T, et al. 2016; Antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with hypocomplementemia has a higher incidence of serious organ damage and a poor prognosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e4871. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004871. PMID: 27631255. PMCID: PMC5402598.
Article10. Molad Y, Tovar A, Ofer-Shiber S. 2014; Association of low serum complement C3 with reduced patient and renal survival in antimyeloperoxidase-associated small-vessel vasculitis. Nephron Clin Pract. 126:67–74. DOI: 10.1159/000357154. PMID: 24577364.
Article11. Mukhtyar C, Lee R, Brown D, Carruthers D, Dasgupta B, Dubey S, et al. 2009; Modification and validation of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (version 3). Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1827–32. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2008.101279. PMID: 19054820.
Article12. Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Seror R, Mahr A, Mouthon L, Toumelin PL. French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG). 2011; The five-factor score revisited: assessment of prognoses of systemic necrotizing vasculitides based on the French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG) cohort. Medicine (Baltimore). 90:19–27. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0b013e318205a4c6. PMID: 21200183.13. McAdoo SP, Medjeral-Thomas N, Gopaluni S, Tanna A, Mansfield N, Galliford J, et al. 2019; Long-term follow-up of a combined rituximab and cyclophosphamide regimen in renal anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 34:63–73. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfx378. PMID: 29462348. PMCID: PMC6322443.
Article14. Yamamoto S, Kubotsu K, Kida M, Kondo K, Matsuura S, Uchiyama S, et al. 1995; Automated homogeneous liposome-based assay system for total complement activity. Clin Chem. 41:586–90. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/41.4.586. PMID: 7720251.
Article15. Ling M, Murali M. 2019; Analysis of the complement system in the clinical immunology laboratory. Clin Lab Med. 39:579–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.cll.2019.07.006. PMID: 31668271.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ANCA : The Marker Antibody of Vasculitis
- A Case of Propylthiouracil-induced Lupus Erythematosus Accompanied by Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-positive Vasculitis
- ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Presenting with Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis
- ANCA-Associated Vasculitic Neuropathy with Concurrent Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Serological Biomarkers and Indices for the Current Activity and Prognosis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Experience in a Single Centre in Korea