Neonatal Med.
2021 Feb;28(1):41-47. 10.5385/nm.2021.28.1.41.
Transient Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Managed with Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) and Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2513358
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2021.28.1.41
Abstract
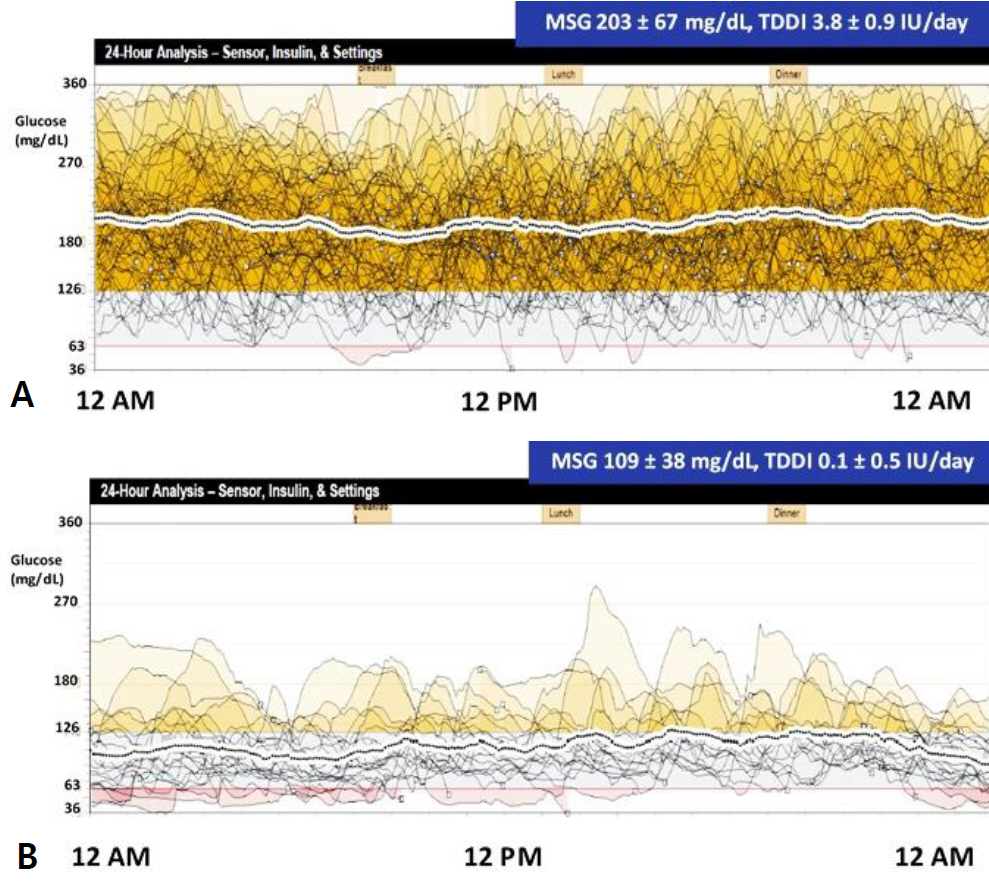
- Neonatal diabetes mellitus can be categorized as transient, permanent, or syndromic, and approximately half of the cases are transient. We present a case involving a term newborn who showed overt progression of transient neonatal diabetes mellitus, with complete remission within 6 months. On the second day of life, the patient presented with tachypnea, hyperglycemia, and decreased serum levels of C-peptide and insulin. Continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin and continuous glucose monitoring were well tolerated. The patient showed a normal growth pattern, with no hyperglycemic or hypoglycemic episodes at 6 months of age. As it is rare and often asymptomatic, hyperglycemia may be attributed to various factors, including intrauterine environment, perinatal stress, and diverse genetic background. Therefore, consistent blood glucose monitoring and prompt early insulin therapy are crucial for any term newborns with persistent hyperglycemia, to prevent further diabetic complications. Moreover, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and the utilization of continuous glucose monitoring devices are the most effective and practical management strategies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lemelman MB, Letourneau L, Greeley SAW. Neonatal diabetes mellitus: an update on diagnosis and management. Clin Perinatol. 2018; 45:41–59.2. Sahebi L, Niknafs N, Dalili H, Amini E, Esmaeilnia T, Amoli M, et al. Iranian neonatal diabetes mellitus due to mutation in PDX1 gene: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2019; 13:258.3. Touati A, Errea-Dorronsoro J, Nouri S, Halleb Y, Pereda A, Mahdhaoui N, et al. Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus and hypomethylation at additional imprinted loci: novel ZFP57 mutation and review on the literature. Acta Diabetol. 2019; 56:301–7.4. Huang K, Liang L, Fu JF, Dong GP. Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus in China. BMC Pediatr. 2014; 14:188.5. im JS, Lim SW, Ahn JH, Song BS, Shim KS, Hwang IT. New Korean reference for birth weight by gestational age and sex: data from the Korean Statistical Information Service (2008-2012). Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 19:146–53.6. Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015; 17:405–24.7. Simsek DG, Ecevit A, Hatipoglu N, Coban A, Arisoy AE, Bas F, et al. Neonatal hyperglycemia, which threshold value, diagnostic approach and treatment?: Turkish Neonatal and Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Societies consensus report. Turk Pediatri Ars. 2018; 53:S234–8.8. Hay WW Jr, Rozance PJ. Neonatal hyperglycemia-causes, treatments, and cautions. J Pediatr. 2018; 200:6–8.9. Suzuki S, Koga M, Niizeki N, Furuya A, Matsuo K, Tanahashi Y, et al. Evaluation of glycated hemoglobin and fetal hemoglobin-adjusted HbA1c measurements in infants. Pediatr Diabetes. 2013; 14:267–72.10. Kurnaz E, Aycan Z, Yildirim N, Cetinkaya S. Conventional insulin pump therapy in two neonatal diabetes patients harboring the homozygous PTF1A enhancer mutation: need for a novel approach for the management of neonatal diabetes. Turk J Pediatr. 2017; 59:458–62.11. Shah R, McKinlay CJD, Harding JE. Neonatal hypoglycemia: continuous glucose monitoring. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2018; 30:204–8.12. Cao B, Gong C, Wu D, Lu C, Liu F, Liu X, et al. Genetic analysis and follow-up of 25 neonatal diabetes mellitus patients in China. J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016:6314368.13. Naylor RN, Greeley SA, Bell GI, Philipson LH. Genetics and pathophysiology of neonatal diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2011; 2:158–69.14. Loomba-Albrecht LA, Glaser NS, Styne DM, Bremer AA. An oral sulfonylurea in the treatment of transient neonatal diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther. 2009; 31:816–20.15. Fu JL, Wang T, Xiao XH. Relapsed 6q24-related transient neonatal diabetes mellitus successfully treated with sulfonylurea. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019; 132:846–8.16. Barbetti F, D'Annunzio G. Genetic causes and treatment of neonatal diabetes and early childhood diabetes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 32:575–91.17. Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J. Neonatal diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev. 2008; 29:265–91.18. Rubio-Cabezas O, Ellard S. Diabetes mellitus in neonates and infants: genetic heterogeneity, clinical approach to diagnosis, and therapeutic options. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013; 80:137–46.19. Asl SN, Vakili R, Vakili S, Soheilipour F, Hashemipour M, Ghahramani S, et al. Wolcott-Rallison syndrome in Iran: a common cause of neonatal diabetes. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019; 32:607–13.20. Evliyaoglu O, Ercan O, Ataoglu E, Zubarioglu U, Ozcabi B, Dagdeviren A, et al. Neonatal diabetes: two cases with isolated pancreas agenesis due to homozygous PTF1A enhancer mutations and one with developmental delay, epilepsy, and neonatal diabetes syndrome due to KCNJ11 mutation. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2018; 10:168–74.21. Berg JS. Exploring the importance of case-level clinical information for variant interpretation. Genet Med. 2017; 19:3–5.22. Shah RP, Spruyt K, Kragie BC, Greeley SA, Msall ME. Visuomotor performance in KCNJ11-related neonatal diabetes is impaired in children with DEND-associated mutations and may be improved by early treatment with sulfonylureas. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:2086–8.23. Svalastoga P, Sulen A, Fehn JR, Aukland SM, Irgens H, Sirnes E, et al. Intellectual disability in KATP channel neonatal diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:526–33.24. Li X, Xu A, Sheng H, Ting TH, Mao X, Huang X, et al. Early transition from insulin to sulfonylureas in neonatal diabetes and follow-up: experience from China. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018; 19:251–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Understanding of type 1 diabetes mellitus: what we know and where we go
- Clinical Utilities of Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Pumps in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
- Recent Updates on Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Management for Clinicians
- Intensive Insulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes
- Glucose Management Using Continuous Glucose Monitors