Neurointervention.
2021 Mar;16(1):59-63. 10.5469/neuroint.2020.00437.
Low-Dose 3D Rotational Angiography in Measuring the Size of Intracranial Aneurysm: In Vitro Feasibility Study Using Aneurysm Phantom
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2513345
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2020.00437
Abstract
- Purpose
Three-dimensional (3D) measurement of intracranial aneurysms is important in planning endovascular treatment, and 3D rotational angiography (RA) is effective in accurate measurement. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of low dose 3D RA (5 seconds 0.10 μGy/frame) in measuring an intracranial aneurysm using an in vitro phantom.
Materials and Methods
We investigated an in vitro 3D phantom of an intracranial aneurysm with 10 acquisitions of 3D RA with a conventional dose (5 seconds 0.36 μGy/frame) and 10 acquisitions with a low-dose (5 seconds 0.10 μGy/frame). 3D size and neck diameters of the aneurysm were measured and compared between the 2 groups (conventional and low-dose) using noninferiority statistics.
Results
The aneurysm measurements were well-correlated between the 2 readers, and noninferiority in the measurement of aneurysmal size of low-dose 3D RA was demonstrated, as the upper margin of the 1-sided 97.5% confidence interval did not cross the pre-defined noninferiority margin of 0.2 mm by the 2 readers.
Conclusion
Low-dose (5 seconds 0.10 μGy/frame) cerebral 3D RA is technically feasible and not inferior in in vitro 3D measurement of an intracranial aneurysm. Thus, low-dose 3D RA is promising and needs further evaluation for its clinical utility in the planning of endovascular treatment of an intracranial aneurysm.
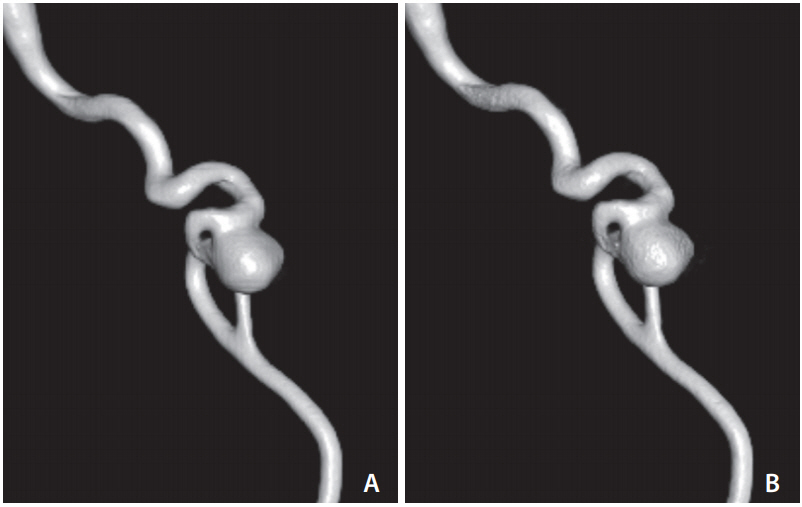
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gauvrit JY, Leclerc X, Vermandel M, Lubicz B, Despretz D, Lejeune JP, et al. 3D rotational angiography: use of propeller rotation for the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:163–165.2. Hochmuth A, Spetzger U, Schumacher M. Comparison of three-dimensional rotational angiography with digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1199–1205.3. Abe T, Hirohata M, Tanaka N, Uchiyama Y, Kojima K, Fujimoto K, et al. Clinical benefits of rotational 3D angiography in endovascular treatment of ruptured cerebral aneurysm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:686–688.4. Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Nakashima K, Hamatake S, Honda S, Takahashi M. Comparison of 2D and 3D digital subtraction angiography in evaluation of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1545–1552.5. van Rooij WJ, Sprengers ME, de Gast AN, Peluso JP, Sluzewski M. 3D rotational angiography: the new gold standard in the detection of additional intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:976–979.
Article6. Anxionnat R, Bracard S, Ducrocq X, Trousset Y, Launay L, Kerrien E, et al. Intracranial aneurysms: clinical value of 3D digital subtraction angiography in the therapeutic decision and endovascular treatment. Radiology. 2001; 218:799–808.
Article7. Pearl MS, Torok C, Katz Z, Messina SA, Blasco J, Tamargo RJ, et al. Diagnostic quality and accuracy of low dose 3D-DSA protocols in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015; 7:386–390.
Article8. Pearl MS, Torok CM, Messina SA, Radvany M, Rao SN, Ehtiati T, et al. Reducing radiation dose while maintaining diagnostic image quality of cerebral three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography: an in vivo study in swine. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014; 6:672–676.
Article9. Choi J, Kim B, Choi Y, Shin NY, Jang J, Choi HS, et al. Image quality of low-dose cerebral angiography and effectiveness of clinical implementation on diagnostic and neurointerventional procedures for intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019; 40:827–833.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Usefulness of 3 Dimensional CT Angiography in the Diagnosis of Intracranial Aneurysms: Comparative Study with Conventional Angiography
- Usefulness of Rotational Angiography in the Assessment of Cerebral Aneurysm and Arteriovenous Malformation
- A Pseudoaneurysm Associated with a Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Hypothesis on the Formation of the PA and Feasibility of Endovascular Treatment
- Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography with Volume Rendering Technique in the Evaluation of Intracranial Aneurysms: Comparison with Three-Dimensional Digital Subtraction Angiography
- Obtaining Informed Consent Using Patient Specific 3D Printing Cerebral Aneurysm Model